
Chiora Hydropower Plant (HPP) - Technical Due Diligence, Georgia
Chiora Hydropower Plant (HPP) - Technical Due Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 30.05.2025

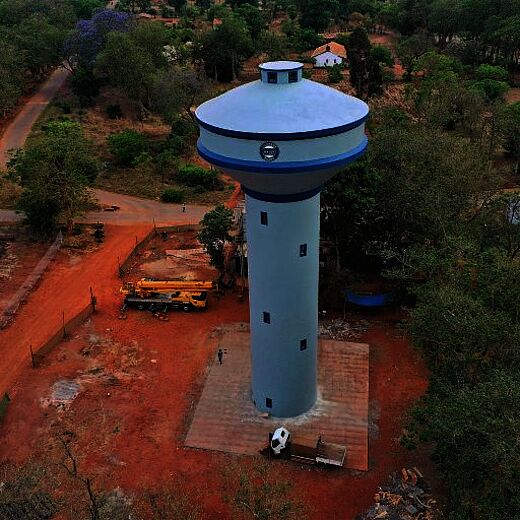
HPP Chiora is located between the villages Ghebi and Chiora. The headworks structures are located in the north-eastern valley, seen from the village Ghebi. The powerhouse itself is situated in Chiora on the opposite side of the mountain. The layout includes two intakes: the first intake is located on the Chveshura river and the second at the Khvargula river. Water abstracted at the first intake is diverted into the forebay of the second intake via a closed gravimetrical diversion channel. The forebay is directly attached to the sand trap of the second intake. From the forebay the water flows through a penstock to the powerhouse. The total length of the penstock amounts to 2.66 km. Thereof 880 meters are constructed within a tunnel.
The service involves the assessment of the technical design, project costs and agreement documentation as well as performing on-site risk assessments.
Assessment of technical documentation including:
- Project design: including technical solution and adequacy, track record of the equipment and contractors proposed, civil design, hydraulic and tunnel design, geotechnical stability, electrical design, grid connection and certification, the installed capacity and expected annual production
- Method statements and construction schedule, and potential natural hazards: including geological and flood risks, debris and sediment management and available energy potential, including upstream developments
- Construction management and execution: including Quality, Health, Safety, Security and Environment Management (QHSSE), manufacture and supply of equipment and transportation
- Environmental impact assessment report and social framework/context
- Proposed operations and maintenance execution
- Project schedule: including the feasibility of the proposed project milestones and the status of required licenses/permits.
Project costs and agreements, including assessment of:
- Investment budget and bill of quantities: including construction and other capital costs and spare parts management, EPC contracts and verification of owned funds invested
- Agreement and permits review: including PPA, grid connection, civil, mechanical and electrical agreements, operation and maintenance agreements
- Financial evaluation of the project: including key project dates, review of the total investment budget with breakdown as well as technical and other assumptions, revenues, annual operating costs, financial resources and loan repayment plan, financial model and results, and others as required
- Description of on-site visit results including risk assessment (completion and operation risks and environmental and social risk categorization and permits)

Consulting Services for the project: Management of Water Resources and Sanitation for Medium-Sized Cities, Zambia
Consulting Services for the project: Management of Water Resources and Sanitation for Medium-Sized Cities
Country: Zambia, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 20.06.2026

The project aims at the rehabilitation and extension of the water supply and sanitation infrastructure in the cities of Choma and Livingstone. It comprises the technical implementation consultancy, capacity building with Accompanying Measures as well as services to be provided by a nominated NGO in the field of container based sanitation and faecal sludge management.
The Implementation Measures comprise:
- Rehabilitation of existing and drilling of new groundwater wells
- Rehabilitation works at 2 existing dams
- Rehabilitation of 2 water treatment plants and 3 pump stations
- Expansion and modernization of water distribution networks
- A new water intake at the Zambezi river
- Container based on-site sanitation for low income areas, including a faecal sludge treatment plant and associated collection infrastructure
- Measures for aquifer recharge and in-situ ground water rehabilitation
- Introduction of renewable energy as well as energy efficiency components for reliable, cost-effective and climate resilient water supply
- Developing and establishing an integrated groundwater and surface water monitoring system to manage the raw water abstraction of boreholes as well as surface water sources in an integrated manner focusing on improved and climate resilient operation of water supply
The Accompanying Measures include:
- Capacity needs assessment
- Increase the capacity of SWSC to operate its water supply and sanitation infrastructure in Choma and in Livingstone
- Development and implementation of the maintenance management and operation processes
- Assist SWSC in setting up, operate and maintain district metered areas and pressure zones
- Increase the capacity of SWSC (Southern Water and Sewage Company) to plan, build and operate its plans in an energy-optimized manner
- Provide ESHS training
- Support in strengthening relevant aspects of the SWSC gender strategy
- Assist SWSC in optimization of the accounting and the associated receivables management based on improved water consumption metering. This includes, among other things, the expansion of software modules for accounting and the management information system
- Ensure the availability of operation and maintenance manuals for existing and new machinery and equipment
The investment volume is approx. EUR 25.3M and works shall be tendered using FIDIC Red/Pink book.
- Conceptual design
- Detailed design
- Hydraulic modelling
- Environmental and social impact screening and assessment
- Preparation of tender documents (FIDIC Red Book)
- Procurement assistance
- Construction supervision according FIDIC incl. services during DNP
- Capacity building and training

Support for Improved Water and Wastewater Services in Kazakhstan, Kazakhstan
Support for Improved Water and Wastewater Services in Kazakhstan
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 31.12.2025


Kazakhstan faces problems with water supply and sanitation services all over the country and there is significant need to upgrade related infrastructure. To support efforts of the Government of Kazakhstan (GoK), the World Bank Group is developing options for improving water and wastewater services to inform its dialogue with the GoK related to the National Project for the “Modernization of the Energy and Utility Sectors” 2025-2029.
P&P was hired to carry out assessment of the sector on national level, to assess the performance on utility level based on 5 selected towns and water utilities and to develop options based on international best practice for improved water and wastewater services in Kazakhstan.
The selected utilities include: State Communal Enterprise "Astana Su Arnasy" in Astana (pop 1.5M), LLP "Water Resources – Marketing" in Shymkent (pop 1.25M), LLP "Batys Su Arnasy" in Oral (pop 250K), State Communal Enterprise "Gorvodokanal" in Ekibastuz (pop 130K), and LLP "Shakhtinskvodokanal" in Shakhtinsk (58K). This selection ensures representation across different urban scales and operational environments, enabling a targeted approach to sectoral improvements.
The project focuses on assessing and enhancing the institutional, legal, and regulatory framework of Kazakhstan’s water and wastewater (W&WW) sector. This includes identifying barriers to private sector participation, strengthening institutional frameworks, assessing utilities' performance and investment needs, and proposing regulatory improvements. Additionally, the study emphasizes policy recommendations to support sustainable sector development.
- Conducted a comprehensive review of Kazakhstan’s legal, regulatory, and policy framework for the water and wastewater sector.
- Evaluated institutional structures and responsibilities at national and local levels.
- Assessed performance and investment needs of five selected utilities.
- Developed recommendations for institutional improvements and sectoral reforms.
- Analysed tariff structures and proposed pricing adjustments aligned with international best practices.
- Provided options for enhancing private sector participation.
- Elaboration of recommended improvement measures on local and national level

Reconstruction and expansion of the sewerage systems in Nukus, Taqiyatas and Xodjeyli cities of the Republic of Karakalpakstan, Uzbekistan
Reconstruction and expansion of the sewerage systems in Nukus, Taqiyatas and Xodjeyli cities of the Republic of Karakalpakstan
Project end: 06.05.2027
Karakalpakstan, located in the Turan Depression, is bordered by the Karakum and Kyzylkum Deserts and the Aral Sea’s drying bed. The region experiences a sharply continental climate with cold winters, hot summers, and annual precipitation below 100 mm. The drying of the Aral Sea has exacerbated the harsh climate and environmental conditions.
Currently, sewerage coverage in the project cities is very low, i.e. in Nukus the capital of the region with a population of some 320,000 only 29%, in Taqiyatas (53,000 pop.) 12% and in Xodjeyli (78,600 pop.) some 4% are served by centralized sewerage systems. There are some wastewater treatment facilities existing however they only provide minimal treatment, if any. This lack of adequate infrastructure leads to environmental degradation and increased health risks. The project aims to reconstruct and expand the sewerage systems in these cities, including the development of sewage networks, pumping stations, and wastewater treatment plants to address these critical issues.
The scope of the project covers review of the feasibility study (TEO), preliminary design, detailed design, preparation of bidding documents and author / design supervision services during the actual construction works.
The measures included are construction of:
- Gravity sewer network: 246 km
- Sewer pumping Stations: 24 no with capacties up to 800 l/s
- Pressure sewer mains: 40km
- Wastewater Treatment Plants: Nukus _ 450,000 PE (73,800 m³/d) and Takhiatash + Xodjeyli - 176,000 PE (30,512 m³/d)
Fields of Specialisation:
- Sanitation engineering
- Design of sewer system
- Wastewater pumping stations
- Wastewater treatment
- Environmental management plan
- Topographical and Geotechnical survey
- Coordination with authorities and management of construction permits
- Develop design documents including sewerage networks, pumping stations and waste water treatment plant
- Preparation of environmental and social safe guard documents in accordance with Uzbekistan and International states
- Procurement Assistance
- Author / design supervision
- Reporting

Improving water supply of the Sirdaryo, Gulistan, Sayxunobod districts and Yangiyer city of the Sirdaryo region, Uzbekistan
Improving water supply of the Sirdaryo, Gulistan, Sayxunobod districts and Yangiyer city of the Sirdaryo region
Project end: 06.05.2028
The project aims to finance the construction and rehabilitation of water supply systems in Gulistan, Sayxunobod, Sirdaryo districts, and Yangiyer city in Sirdaryo Region, Uzbekistan. This region experiences a dry, continental climate with minimal rainfall.
Planned works include:
- Gulistan district: 34 wells, 32 water towers, 121.6 km of pipelines
- Sayxunobod district: 27 wells, 29 water towers, 107.3 km of pipelines
- Sirdaryo district: 45 wells, 50 water towers, 173.4 km of pipelines
- Yangiyer city: 11 wells, 10 water towers, 39.3 km of pipelines, and 33 km of main pipeline
Several works identified in a preceding Feasibility Study (TEO) had been implemented already upon start of the assignment and during the Inception Phase new villages and areas of works had to be identified and agreed upon with the Client.
Fields of Specialisation:
The purpose of this assignment is to obtain the following services:
- Review and assessment of the Project Feasibility Study to identify possible gaps and shortcomings
- Preparation of the Detailed Engineering Design and Bidding documents
- Procurement assistance
- Provision of design and construction supervision services
- Services during the commissioning of the works
- Services during defect liability period for construction works
- Feasibility Study Review
- Hydraulic Modelling and GIS
- Detailed Engineering Design
- Bidding Documents and procurement assistance
- Author / design Supervision
- Construction Supervision
- Reporting

Integrated Solid Waste Management Programme Serbia - Consulting Services for the Implementation of the Programme and Accompanying Measures, Serbia
Integrated Solid Waste Management Programme Serbia - Consulting Services for the Implementation of the Programme and Accompanying Measures
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 01.02.2029
The project aims to implement regional sustainable municipal solid waste management systems in the two Serbian regions, i.e. Kruševac and Vranje, to align with EU standards. Each regional system includes four to five satellite municipalities.
It includes optimized waste collection (covering both residual waste and recyclables), transfer systems for remote areas, a Material Recovery Facility (MRF) for sorting recyclables, composting units for biodegradable waste, and biological stabilization (BS) of residual waste.
A central sanitary landfill (SLF) with leachate treatment and potential landfill gas use will be established. The project also involves closing old dumpsites and building Regional Waste Management Centers (RWMC) with facilities for waste processing, composting, and recycling. Smaller satellite PUCs will retain independence, managing recyclables, composting, and residual waste transfer. Total Investment value of EUR 49.2M.
This investment project is supported by Accompanying Measures, which implementation is supported by this assignment. It includes assessment of the status quo, improvement of commercial procedures, development of tariff model and new tariff system, introduction of performance criteria, legal and institutional support, institutional setup of the solid water utilities, workshops and training of staff, marketing of recyclables and integrating the informal sector, visibility and public awareness campaigns.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Financial assessment of utilities
- Development of a tariff system for regional utilities
- Support utilities and municipalities in introducing new tariff systems
- Analysis of current tariff system
- development of new regional tariff systems with integration of all municipalities
- supporting the utilities and municipalities in introducing the new tariff systems

Consulting Services for Accompanying Measures for the Capacity Building and Institutional Strengthening of the DWSRU and Support to AKUM/PUC in Implementing the Program, Albania
Consulting Services for Accompanying Measures for the Capacity Building and Institutional Strengthening of the DWSRU and Support to AKUM/PUC in Implementing the Program
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 07.11.2027




The water supply system of Durrës and surrounding settlements is operated by Durrës Water and Sewerage Regional Utility (DWSRU). The surrounding settlements which are included in the service area comprise a total of 5 municipalities and 10 communes. This is the result of the recent clustering of utilities, whereby the former Durrës Water and Sewerage Utility was merged with the following utilities:
- Krujë Water and Sewerage Utility,
- Fushë-Krujë Water and Sewerage Utility,
- Rrogozhinë Water and Sewerage Utility.
The current supply is intermittent, the average duration of service is only 12 hours/day. The DWSRU utility´s main challenge is to provide adequate, continuous supply services within its service area of approx. 1,000 km2. Currently DWSRU has 1,163 employees and the total number of population served by water supply by DWSRU is roughly 480,000.
The production wells are located in Fushë Kuqe, Fushë-Krujë and Fushë Milot. Durrës city and the suburban areas are served by 8 reservoirs. The villages and municipalities are served by 22 reservoirs situated along Fushë Kuqe and Fushë-Krujë transmission mains.
The total length of the water distribution network is approximately 1,000 km.
The shortcomings regarding the performance of DWSRU can be summarized as follows:
- Inefficient infrastructure and management: there is a need to rehabilitate water infrastructure, to improve its operation and maintenance and ensure continuous service. The O&M costs are 1.5% of total expenses, which indicates a very poor approach and shall be improved;
- Unserved areas: distribution networks shall be extended to cover villages and municipalities located along the transmission main pipes coming from Fushe Kuqe and Fushe Kruje wellfields
- Very high NRW figure: systematic actions are urgently needed for NRW reduction
- Very high energy costs, due to long pumping distances and low efficiency of equipment, and also due to poor operation and monitoring procedures
- Inadequate asset management
- Lack of adequate work processes and performance-driven approach.
In line with the national strategy for water and sanitation and with the government reform objectives, there is a need to increase capacities of AKUM and DWSRU and enable them to build and operate water and sanitation facilities in a socially, environmentally and financially sustainable way, to be able to serve water to its customers continuously and in good quality and also to provide adequate sanitation services to an increasing customer base.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Capacity building
- Accompanying measures to support water utilities
- NRW, GIS, O&M
- Project management support
Task 1: PIU support in project management
Task 2: Assessment & diagnostic
Task 3: PIP & CMP
|
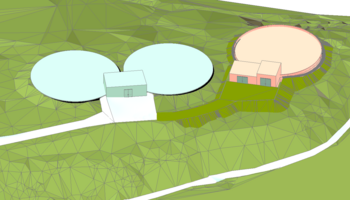
Rehabilitation of communal Infrastructure of New Batumi Consulting Services for Project Implementation, Georgia
Rehabilitation of communal Infrastructure of New Batumi Consulting Services for Project Implementation
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 07.03.2029
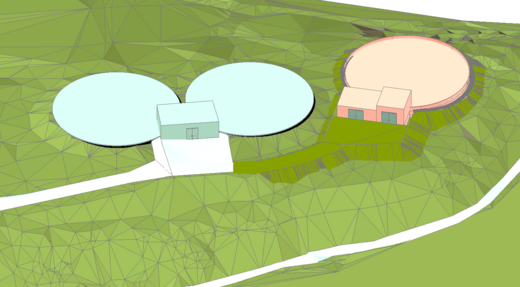
The KfW Investment Program "Rehabilitation of Communal Infrastructure of New Batumi" aims to extend the water supply and wastewater infrastructure to areas incorporated into Batumi Municipality during the 2016 amalgamation of Municipalities. The administrative units (AU) affected by this amalgamation include AU Greencape, AU Industrial, AU Airport, adm. unit Kakhaberi, and AU Gonio, all transferred from other Municipalities to Batumi Municipality. Previous KfW investment programs (Phases I to IV) since 2007 focused on rehabilitating sewer systems, WWTP Adlia, and water infrastructure within the pre-2016 city borders.
The goal of the new program is to extend central water supply and wastewater disposal services to areas that have not previously benefited from investments, relying on private wells or micro networks with inadequate disinfection and unorganized wastewater disposal. The program aims to ensure continuous and demand-oriented water supply, ecologically sound wastewater disposal and treatment, and resilience against heavy rain and flooding. Additionally, it seeks to improve bathing water quality, fish migration on Chakvistskali river, and drinking water quality for consumers, while bringing the WWTP Adlia in compliance with Georgian and EU effluent standards.
The total investment required for these goals amounts to EUR 120M. The investment scope is divided into three phases, with Phase I being primarily funded by KfW financing. The Phase I investments include extending the central water supply and sanitation services, addressing specific sewer concerns in remote rural areas, and making necessary structural adjustments to the city's wastewater pumping system. Investments in subsequent phases will be contingent on bid prices and local financing availability.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Water supply
- Sanitation
- Wastewater treatment
- Stormwater collection and pumping stations
- Design review
- Feasibility study
- Detailed design
- Tender documents
- Procurement support
- Construction supervision
- Overall project management
- Design review, detailed design and preparation of tender documents
- Review and update of feasibility study for water supply and sanitation
- Procurement assistance
- Construction supervision according FIDIC including services during the DNP
- Ensure full ESHS compliance of all works
- Works contract management

Local Communities Programme (LOCOMO) - Improved Public Infrastructure and Public Utilities Performance in Selected Local Communities - Site Supervision and Capacity Development, Moldova
Local Communities Programme (LOCOMO) - Improved Public Infrastructure and Public Utilities Performance in Selected Local Communities - Site Supervision and Capacity Development
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 16.08.2027


The Republic of Moldova is one of the priority countries of the Austrian Development Cooperation (ADC) in South-Eastern/Eastern Europe. Among others, ADC focuses on water and wastewater management including capacity development for local public authorities and service utilities, thus contributing to the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
The Project comprises the following:
Edinet Waste Water Treatment Plant (WTP) (FIDIC Yellow Book)
New surface water intake with Pumping Station-01 (PS), ≈1 km pumping main to connect to the existing main, a new pre-fabricated WTP of 60 l/s, plus the rehabilitation of PS-02A, PS-03, PS-04 and a 6000m³ reservoirs.
Cupcini (FIDIC Red Book)
Approx. 1 km new water main towards Cupcini village, plus 5.8 km distribution system including house connections in the area of most public institutions.
Leova Region (FIDIC Red Book)
- Hănăsenii Noi Village: Rehabilitation and construction of 14 sanitary blocks (toilets and associated facilities in public institutions), of 434 m sewer network connecting the mayor’s office, library and medical point, gymnasium and kindergarten, including 17 m house connections, 2 grease separators and 1 small scale WWTP
- Sîrma Village: Rehabilitation and construction of 21 sanitary blocks, 8 m outdoor water network, 536 m sewer network connecting the mayor’s office, gymnasium, kindergarten, shop, café/bar, and a 2-level apartment block, 137 m house connections, 2 grease separators and 1 small scale WWTP
- Leova Town, Vocational Education and Training Centre: Rehabilitation and construction of 11 sanitary blocks and 5 washing basins, 156 m of water supply network, 94 m of sewer network, 62 m house connections, 1 grease separator.
- Iargara Town: Setting up a local landfill and procurement of 2 solid waste trucks and 1 bulldozer and 50 large and 2000 small waste bins will be procured by ADA. No supervision is needed for this task
Strășeni Region (FIDIC Red Book)
- Scoreni Village: Rehabilitation and construction of 450 m sewer network connecting the kindergarten, and the FPC/medical point, 205 m house connections, 1 grease separator, 1 small scale WWTP
- Gălești Villages: Rehabilitation and construction of 3.7 km sewer network connecting the Lyceum, kindergarten, FPC/medical point, mayor’s office, 200 m house connections, 2 grease separators and 1 small scale WWTP
- Căpriana Village: Rehabilitation and construction of 2.29 km sewer network connecting the Lyceum, kindergarten, FPC/medical point, mayor’s office, community
Fields of Specialisation:
- Construction supervision according FIDIC (Red & Yellow)
- Works contract management
- Water supply and sanitation engineering
- Claim management
- Capacity development
- Water utility training
Description of Actual Services Provided:
- Review and approval of water treatment plant and intake design
- Construction supervision
- Works contract management of FIDIC Red and Yellow Book Contracts
- Start-up and commission

TA Support for completion of the Mykolayiv Water Project TACONT, Ukraine
TA Support for completion of the Mykolayiv Water Project TACONT
Country: Ukraine, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 18.10.2026

Mykolaiv is one of the largest cities in Ukraine with a (pre-war) population of approx. 510,000. The Water Utility Mykolayiv Vodokanal (MVK) had been supported before to identify priority investment needs which were defined and agreed on in a Short Term Investment Programme (STIP). Posch & Partner had been selected in Nov. 2014 as the Technical Assistance Consultant (TAC) to support MVK in the implementation of the STIP with an investment volume of 31.8 Mill. EUR. The TAC contract ended in December 2021, but the investments had not been completed yet. The launch of the tender for the new TAC assignment had to be postponed by the European Investment Bank (EIB) due to the Russian aggression to Ukraine starting on 24 February 2022. The contract could only be awarded in June 2023.
The new TAC assignment includes the following tasks:
- Project Management Support to the PIU
- Capacity Building to MVK
- Construction Supervision Support
- Procurement supervision and monitoring of grant and loan expenditures on behalf of the Bank
- Preparation of a Sludge Strategy for MVK.
The investments measures could only be partially completed before the outbreak of the war and the available funding of approx. 15 Mill. EUR is earmarked for the following investment measures:
- Establishment of pilot district metering areas of the distribution system for reduction of NRW
- Rehabilitation and upgrading of PS2
- Rehabilitation of the wastewater treatment plant
The implementation of the tasks is strongly affected by the Russian aggression to Ukraine and the effects caused by it.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Project management
- Preparation of yellow book tender
- Tender evaluation
- Capacity building
- Training needs assessment and trainings
- Construction supervision
- Preparation of sustainable sludge strategy
- Project Management support to PIU
- Training of Vodokanal staff
- Procurement of works contract following EIB procurement guidelines
- Construction supervision support
- Monitoring of grand and loan expenditures on behalf of the Bank
- Preparation of Sludge Strategy

Nabeghlavi Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence, Georgia
Nabeghlavi Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.01.2023

Hydropower Plant (HPP) Nabeghlavi is located in the South-Western part of Georgia in the municipality of Chokhatauri in Guria Region:
HPP Nabeghlavi is a typical diversion scheme, consisting of a concrete weir with lateral intake, headrace tunnel, forebay, penstock and powerhouse.
The key salient features of HPP Nabeghlavi are as follows:
- Water source: Gubazeuli, 224 km² at intake
- Built in 2014
- Penstock: Steel, diameter 1300, length 2x 42 m
- Design flow: 2x 4 m³/s
- Installed capacity: 1.99 MW
- Turbines: 2x horizontal Francis from 2014
- Net head: 28.5 m
- Generator: 1,176.5 kVA nominal output
Technical Due-Diligence comprising following aspects:
- Detailed check of the project design in terms of international industry standards and practises
- Review the adequacy and quality of the structures, main equipment and electricity connection facilities
- Review on current performance and operation practices of the plant including grid system and transmission line
- Assessment of hydrological data, measurements and calculations regarding their reliability
- Provision of an independent assessment of the energy yield and long-term projections for the main probability scenarios
- Risk and cost assessment for short-, mid- and long-term operation of the project

Natsheshari Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due Diligence, Georgia
Natsheshari Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 28.02.2023

Hydropower Plant (HPP) Natseshari is located on the river with the same name. The powerhouse is located close to village Idliani, at an elevation of 510 m.a.s.l., while the intake is located at elevation 710 m.a.s.l.
The general project idea follows the common and proven concept of a run-of-the-river HPP, with a river diversion stretch, consisting of a small dam with a Tyrolean Weir intake at the dam crest, a diversion channel, sand trap, outflow chamber, penstock, powerhouse with electro-mechanical equipment and a transmission line.
This report aims at assessing the documents submitted to the bank regarding the realization of the HPP Natseshari and provides an independent evaluation from a technical, economic, environmental and social point of view.
Fields of Specialisation:
Preparation of a echnical Due-Diligence-report.
The following assessments have been conducted to achieve this task:
- Submitted documents and information available on the project have been checked for completeness and quality
- The hydrological, topographical, geological studies have been assessed regarding their method used and conclusions made
- The technical design has been assessed for appropriateness and state of the art
- The investment budget has been checked for plausibility and completeness

Joghornashumi Hydropower Plant (HPP) - Technical Due Diligence, Georgia
Joghornashumi Hydropower Plant (HPP) - Technical Due Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 28.02.2023

Hydropower Plant (HPP) Joghornashumi is located on the river with the same name. The powerhouse is located near the village of Khaishi, at an elevation of 525 m.a.s.l., while the intake is located at an elevation of 888 m.a.s.l.
The general project idea follows the common and proven concept of a run-of-the-river HPP, incorporating a river diversion stretch, which consists of a small dam with a Tyrolean Weir intake at the dam crest, a diversion channel, sand trap, outflow chamber, penstock, powerhouse with electro-mechanical equipment and a transmission line.
This report aims to assess the documents submitted to the bank regarding the realization of the HPP Joghornashumi and provides an independent evaluation from a technical, economic, environmental and social perspective.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Preparation of a Technical Due-Diligence-report.
The following assessments have been conducted to achieve this task:
- Submitted documents and information available on the project have been checked for completeness and quality
- The hydrological, topographica and geological studies have been assessed regarding the methods used and the conclusions reached
- The technical design has been assessed for appropriateness and state of the art
- The investment budget has been checked for plausibility and completeness
- Technical documentation, including:
- Project design
- Method Statements and Construction schedule
- Potential natural hazards
- Debris and sediment Management
- Assessment of available energy potential
- Construction management and execution
- Environment (QHSSE) management,
- Environmental impact assessment report and social framework / context
- Operations and maintenance execution
- Project schedule
- Project costs and agreements, including:
- Investment budget and bill of quantities
- Operating and maintenance expenses
- EPC contracts and risk distribution between contractors and developer
- Verification of owned funds invested into the project based on the check of documentation including contracts and invoices and bank accounts
- Agreement and permits review
- Financial evaluation of the project
- On-site visit results
- Risk assessment

Feasibility Study for Wastewater Collection and Treatment Project for the Municipality of Veliko Gradište, Serbia
Feasibility Study for Wastewater Collection and Treatment Project for the Municipality of Veliko Gradište
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 16.08.2023
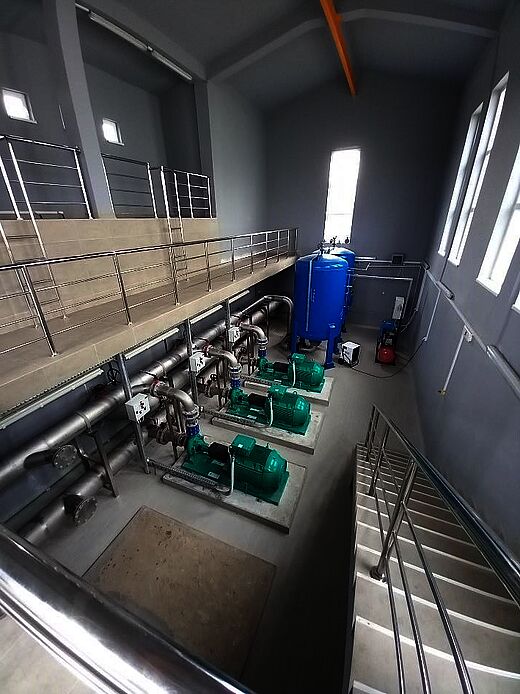

Veliko Gradište is located in the northeast of central Serbia. The public utility company (PUC) "Dunav"- Veliko Gradište provides drinking water to the 17,600 inhabitants of the urban area of Veliko Gradište and the surrounding areas. The water distribution system is based on groundwater and was recentlyupgraded with of new wells, a waste water treatment plant (WWTP), a transmission main and a water tower, with P&P acting as engineers in accordance with FIDIC.
The same PUC is also responsible for the sewage network, which in practice operates as a combined system despite being designed as a separated system. The total length is of approximately 41 km. The diameters of the collectors range from DN200 -DN800. Around 90% of the population in the urban area are connected. Currently, there is no treatment of the collected wastewater.
The objective of this assignment is to develop a Feasibility Study for the Wastewater Collection and Treatment Project for the Municipality of Veliko Gradište, ensuring compliance with the requirements for financing from international and national funding sources.
The Study shall enable the Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) and Public Investment Management Office (PIMO) to make informed decisions regarding the viability of the priority project for financing and provide a very solid foundation for future project preparation steps, leading to the construction of the sewage system and WWTP.
- Preparation of a bankable Feasibility Study
- Technical assessment of existing water supply and wastewater collection services in the Municipality
- Develop the Long-Term investment Programme for wastewater collection and treatment in the Municipality
- Develop the priority Investment Project for wastewater collection and treatment for the urban agglomerations
- Develop the Sludge Management and Disposal Concept
- Conduct an Organisational and Institutional Review
- Undertake Financial Analysis
- Development of the Cost Benefit Analysis for the Priority Investment Project
- Conduct Environmental and Social Due Diligence Study
- Develop a procurement and Implementation Strategy

Bakhvi I & II Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence, Georgia
Bakhvi I & II Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 30.09.2022

Bakhvi 1&2 HPP’s are typical diversion schemes, each consisting of water intake, sand trap, penstock, and powerhouse. Water is diverted and used for energy generation according to natural availability without using a regulated water storage facility.
Bakhvi 1, 2, and lower, already in operation, Bakvhi 3 HPP, form a cascade system with Bakvhi 1 as first stage, Bakhvi 2a as second, Bakhvi 2b as third and Bakhvi 3 as fourth HPP in the cascade.
The general project idea follows the common and proven concept of a run-of-the-river HPP with a dam with diversion structure, penstock, powerhouse with E&M equipment and transmission line.
The main key salient features are as follows:
| Description | Bakhvi 1 | Bakhvi 2a | Bakvhi 2b |
| Catchment Area at Intake [km²] | 52.1 | 60.1 | 68.6 |
| Design Flow [m³/s] | 4.00 | 4.60 | 5.30 |
| Gross Head [m] | 342.40 | 311.50 | 550.85 |
| Hydraulic Losses at Design Flow [m] | 19.15 | 13.16 | 20.28 |
| Net Head at Design Flow [m] | 323.25 | 298.34 | 530,57 |
Environmental Flow (10% of MAF) [m³/s] | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.39 |
| Installed Capacity [MW] | 10.95 | 11.62 | 23.85 |
| Mean Annual Generation [GWh] | 45.06 | 47.68 | 96.76 |
| GRP (upper section) [DN/length] | 1.300 / 3.217m | 1.400 / 3105.1m | 1.500 / 2464.5m |
| Steel Penstock [DN/length] | 1.100 / 533m | 1.200 / 158.3m | 1.300 / 1301.42m |
Technical Due-Diligence consisting of:
- Review of provided Feasibility Study
- Assessment of available hydrological, topographical, and geological studies
- Check provided hydrological data for reliability, completeness, accuracy, and consistency; explain implications of missing and incomplete measurement data; compare the methodologies
- Risk assessment on flood and natural hazards
- Calculation of theoretical energy production figures from an independent point of view; review the estimated monthly electricity output; provide a hydrological duration curve picturing the long-term behaviour of the river
- Detailed check of proposed method statements & construction schedule; review cost estimations and construction contracts
- Review cost estimations, construction contracts,
- Construction management & execution including QHSSE management, manufacture & supply of equipment, transportation

Tskhenistsqali Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence, Georgia
Tskhenistsqali Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 30.09.2022

HPP Tskhenistsqali is located on same named river, close to village Mele, following the road Kutaisi-Tskaltubo-Tsageri-Lentehki-Lasdili northwards. The powerhouse is located close to the confluence of river Tskhenistsqali with river Zeskho.
The general project idea follows the common and proven concept of a run-of-the-river HPP, with river diversion stretch, consisting of a small dam with lateral diversion structure, penstock, powerhouse with E&M equipment and transmission line.
The main key salient features of HPP Tskhenistsqali are as follows:
- Catchment area: 93.4 km²
- Design flow: 2.1 – 2.3 m³/s per unit, in total 8.8 m³/s
- Installed capacity: 22.7 MW
- Upstream WL: 1,729.75 m.a.s.l.
- Turbine axis: 1,405.32 m.a.s.l.
- Gross head: 324.40 m
- Net head at design flow: 305.20 m (max. hydraulic losses up to 19.20 m)
- Penstock length total: 7,684 m
- Section 1 DN 2000: 1,329 m
- Section 2 DN 2200: 6,217 m
- Section 3 DN 2400: 1,38 m
Technical Due-Diligence consisting of:
- TA of project design including technical solution & adequacy & track record of equipment and contractors proposed, civil design, hydraulic & tunnel design, geotechnical stability, electrical design, grid connection & certification, assessment of the installed capacity & expected annual production.
- Detailed check of proposed method statements & construction schedule
- Assessment of hydrological & power studies; construction management & execution including QHSSE management, manufacture & supply of equipment, transportation; EIA report & social framework/context; project schedule - incl. feasibility of the proposed project milestones & status of all required licenses/permits.
- Financial evaluation of the project and risk assessment

Consulting Services for Preparation of Preliminary design, Tender Documents and Construction Supervision of Eastern Wastewater Treatment Plant (44 MGD) of Faisalabad City (Phase I), Pakistan
Consulting Services for Preparation of Preliminary design, Tender Documents and Construction Supervision of Eastern Wastewater Treatment Plant (44 MGD) of Faisalabad City (Phase I)
Country: Pakistan, Asia
Project end: 14.06.2025

The project will contribute to improving the sanitary conditions and the livelihoods of the 2,600,000 registered water and sewrage consumers living in the Faisalabad District, while also protecting water resources through an adequate treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater.
The capacity of the wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), located at the Madhuana site, will have a capacity of 200,000 m3/day by the year 2038 to comply with the National Environmental Quality Standards (NEQS) as well as the EU discharge standards, and WHO guidelines for disinfection.
The WWTP process will consist of a trickling filter, constructed in two modules with a capacity of 100,000 m3/day each (equivalent to 22 MGD per module) with biogas production due to the high industrial wastewater discharge. The effluent pumping station capacity is designed to handle a peak flow of 240,000 m3/d.
- Review preliminary design
- Assist WASA-F in the process of carrying out pre-qualification of contractors.
- Prepare tender documents
- Assistance to WASA-F in the tendering process
- Enter evaluation report and contract negations
- Review detailed designs prepared by the DBO contractor
- Training including needs assessment
- Construction supervision: commissioning and start-up

Nakhiduri Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence, Georgia
Nakhiduri Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due-Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 15.04.2022

HPP Nakhiduri is located on the Khrami river in the municipality of Bolnisi, Kvemo Kartli Region downstream of Khrami I and II cascade and Tsalka water reservoir.
The general project idea follows the common and proven concept of a run-of-the-river HPP with a reservoir, a dam with diversion structure, penstock, powerhouse with E&M equipment and transmission line.
The main key salient features of HPP Nakhiduri are as follows:
- Design flow: 11m³/s per unit, in total 22m³/s
- Installed capacity: 7.2 MW, two equal sized units each with a max. output of 3.6 MW.
- Upstream WL: 460.00 m.a.s.l. (daily regulated reservoir)
- Downstream WL: 416.50 m.a.s.l.
- Gross head: 43.50m
- Net head: min. 37.56 m (at design flow/max. hydraulic losses) up to 40.92 m
- GRP penstock (PN6 / SN 5.000), DN 3,000, executed in three sections each with different diameter according provided drawings.
- Chainage 0.000 – 0.825: 3.200 mm
- Chainage 0.825 – 1.740: 3.000 mm
- Chainage 1.740 – 2,675.95: 2.800 mm
- Total length 2,675.95m
- Two river crossings (pipe bridges)
Technical Due-Diligence consisting of:
- TA of project design including technical solution & adequacy & track record of equipment and contractors proposed, civil design, hydraulic & tunnel design, geotechnical stability, electrical design, grid connection & certification, assessment of the installed capacity & expected annual production.
- Detailed check of proposed method statements & construction schedule
- Assessment of hydrological & power studies; construction management & execution including QHSSE management, manufacture & supply of equipment, transportation; EIA report & social framework/context; project schedule - incl. feasibility of the proposed project milestones & status of all required licenses/permits.
- Financial evaluation of the project and risk assessment

Tendering and Construction Supervision of Lunyangwa Dam Raising, Malawi
Tendering and Construction Supervision of Lunyangwa Dam Raising
Country: Malawi, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 15.09.2023
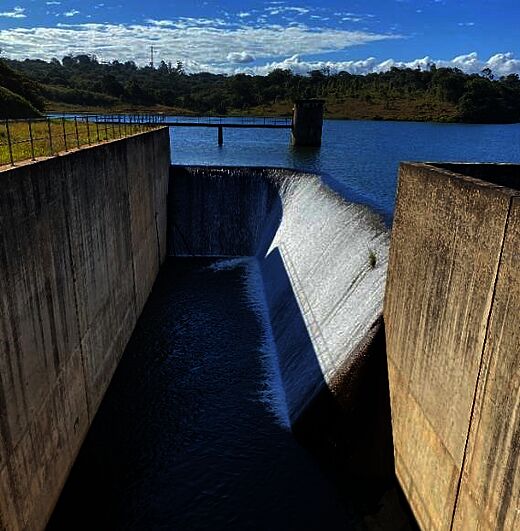

The Lunyangwa dam is a zoned earth dam, 540 m long and max. 18 m high, built in the 1990s. It forms a reservoir with a storage capacity of approximately 4.36 Mm³, providing water supply for the town of Mzuzu. The dam is equipped with a fixed L-shaped spillway with a chute and an intake tower connected to gravity mains supplying the water treatment plant.
The project aims at raising the design water level in the Lunyangwa reservoir by 1.5 m and thereby increasing the storage volume by approximately 1.18 Mm³, or 27%. An option analysis revealed that raising the fixed spillway and adjacent training walls by 1.5 m, combined with the constructing of a parapet wall along the dam crest, is the most cost-effective solution while also ensuring dam safety.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Water supply engineering
- Dam and geotechnical engineering
- Hydrology and hydraulic engineering
- Preparation of tender documents
- Procurement support
- Construction supervision
- Project management
- Hydrological Study to determine design flood levels
- Topographic survey and geotechnical site investigations
- Detailed design including structural design
- Preparation of drawings and maps
- Preparation of Tender Documents according FIDIC Red Book
- Construction Supervision
- Study tour to Austria on dam monitoring and reservoir management

Ipari, Khelra and Nakra Hydropower Plants (HPPs) – Technical Due-Diligence, Georgia
Ipari, Khelra and Nakra Hydropower Plants (HPPs) – Technical Due-Diligence
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.10.2021

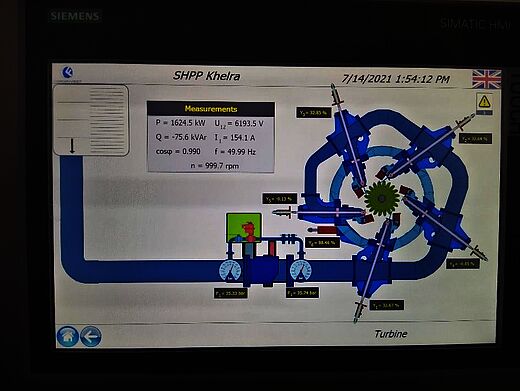

All three plants are located in the municipality of Mestia, situated on tributaries of the Enguri river. The sites are characterised by very steep and narrow gorges and valleys shaped by the river.
The HPPs follow a typical diversion scheme, consisting of an intake, sand trap, penstock, powerhouse, and tailrace. The overall design approach is identical for all three plants. Aside from variations in sizing due to hydrological and hydraulic factors - such as the weir, intake, fish pass, sand trap length, penstock diameter - and specific local requirements like the penstock length, the general design scheme of the plants is identical.
Based on the available information, the key features of the Ipari, Khelra and Nakra HPPs are as follows:
| Project Name | HPP Ipari | HPP Khelra | HPP Nakra |
| River | Ipari | Khelra | Nakra |
| Installed Capacity [MW] | 3.450 | 3.867 | 10 |
| PPA (US$ Cents) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Capacity Factor (P75%) | 53% | 51% | 57% |
| Design Flow [m³/s] | 1.5 | 1.2 | 6.4 |
| Gross Head [m] | 271.4 | 386.7 | 194.12 |
| Length of Penstock [m] | 3,107 | 3,526 | 2,865 |
| Type of Turbine | Pelton | Pelton | Pelton |
| Number of Turbines | 1 | 1 | 2 |
Technical Due-Diligence consisting of:
- Technical analysis of project design including technical solution and adequacy and track record of equipment and contractors proposed, civil design, hydraulic and tunnel design, geotechnical stability, electrical design, grid connection and certification, assessment of the installed capacity and expected annual production
- Detailed check of proposed method statements & construction schedule
- Assessment of hydrological & power studies; construction management and execution including QHSSE management, manufacture and supply of equipment, transportation; EIA report and social framework/context
- Project schedule - incl. feasibility of the proposed project milestones and status of all required licenses/permits.

Market Study for Individual Appropriate Sanitation Solutions, Moldova
Market Study for Individual Appropriate Sanitation Solutions
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 31.10.2021
The objective of this study is to conduct a market study to gather data on the implementation and operation of so-called Individual Appropriate Sanitation (IAS) systems in Moldova, specifically in settlements below 2,000 population equivalents (pe). The findings will inform an upcoming pilot project for on-site sanitation, aprovide an overview of technologies currently available and in use, and provide some guidance for developing sanitation projects in rural areas where IAS systems can serve as a cost-effective alternative to centralized sanitation networks.
The study includes the following tasks:
- Task A: Definition of suitable technologies for and actual conditions of IAS systems in Moldova
- Task B: Review of existing legal and regulatory framework to IAS systems in Moldova and financial incentives
- Task C: Assessment of the scale of IAS requirements in Moldova
- Task D: Standardized selection procedure and standardized designs of IAS
- Task E: Cost assessments
Fields of Specialisation:
- On-site sanitation
- Development of rural areas
- Sanitation engineering
- Legal and regulatory review and assessment
- Primary and secondary data collection
- Market research on available IAS technologies
- Define suitable technologies for Moldova
- Cost assessment for different connection sizes up to 2,000 p.e.
- Develop a decision guide for IAS application

Lukhuni Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Lenders Engineer, Georgia
Lukhuni Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Lenders Engineer
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.05.2021

The Client, the International Energy Corporation, plans to construct a hydropower plant on the Lukhuni River near the village of Uravi. The project follows a typical diversion scheme and includes the construction of a headrace tunnel. Work on the tunnel originally commenced in 2011 but was halted in March 2013. On behalf of TBC Bank, Georgia, Posch & Partner (P&P) has been engaged as the Lender’s Engineer to oversee the detailed design and the rehabilitation and construction works for the tunnel.
General Key data:
- Design flow: 8 m³/s
- Gross Head: 259 m
- Installed Capacity: 17 MW
- Average annual generation: 86 GWh
Tunnel Key data/Salient Features:
- Total tunnel length: 4,622 m
- Total excavated tunnel length: 2,195 m
- From the intake: 216 m
- Access tunnel (to the headrace tunnel): 90 m
- From the end of the access tunnel towards upstream: 488 m
- From the end of the access tunnel towards downstream: 183 m
- From the downstream portal: 1,308 m
- Total remaining length of the tunnel to be excavated: 2,427 m
- Overburden min. / max. ~ 30 m / ~ 316 m
- Elevation of intake/downstream portal: 1,145.50 m a.s.l./1,124.30 m a.s.l.
Fields of Specialisation:
- Hydropower
- Geology
- Tunnel Construction
- Review of Terms of Reference: Tunnel Design Works
- Review of Detailed Design of Tunnel Rehabilitation: Construction Works
- Detailed Design Review Report
- Quarterly construction supervision
- Progress monitoring on behalf of the Client
- Review and Recommendation Reports

Kasleti 1 Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due Diligence and Construction Monitoring, Georgia
Kasleti 1 Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Technical Due Diligence and Construction Monitoring
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.05.2025

The Client, Kasleti 1 LLC, intends to construct a hydropower plant at the Kasleti river in Mestia region in Northern Georgia. The hydropower scheme follows a typical diversion scheme design, consisting of a lateral intake, a small concrete crest weir, a sand trap, a penstock, and a powerhouse. Due to specific side conditions, extensive geological safety and protection measures are required. On behalf of BoG Bank, Georgia, P&P was engaged as the Lender’s Engineer to perform a Technical Due-Diligence of the proposed detail design.
This was followed by on-site monitoring of construction activities to verify that the renewable energy project was implemented in accordance with the approved design including disbursement clearance, within the prescribed timeframe following the corresponding site visit for the approval of the Bank.
Salient Features:
- Design flow: 3.5 m³/s
- Gross Head: 300 m
- Installed Capacity: 8.2 MW
- Average annual generation: 42 GWh
- Penstock: DN 1,200; 2,085 km
- Two Pelton turbines with vertical axis
Technical Due-Diligence consisting of:
- TA of project design including technical solution and adequacy and track record of equipment and contractors proposed, civil design, hydraulic and tunnel design, geotechnical stability, electrical design, grid connection and certification, assessment of the installed capacity and expected annual production
- Detailed check of proposed method Statements and construction schedule
- Assessment of hydrological and power studies; construction management and execution including QHSSE management, manufacture and supply of equipment, transportation; EIA report and social framework/context
- Project schedule - incl. feasibility of the proposed project milestones and status of all required licenses/permits

Water Supply and Wastewater Programme VI in Medium-Sized Municipalities in Serbia, Phase I, Serbia
Water Supply and Wastewater Programme VI in Medium-Sized Municipalities in Serbia, Phase I
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 31.12.2021


This programme aims at securing environmentally and hygienically safe disposal and treatment of wastewater in line with the EU Acquis Communautaire for the population at socially acceptable costs and to protect the surface and groundwater as well as water bodies downstream in 8 medium sized towns in Serbia. The project comprises the preparation of 8 no. full scale bankable feasibility studies for the extension and improvement of the sanitation system followed by the preparation of respective tender documents in line with KfW guidelines and standard bidding documents (FIDIC Pink and Yellow Book).
Investments comprise the construction of new and the rehabilitation of wastewater collection systems, the rehabilitation of 2 no. WWTPs and the construction of 5 no. new WWTPs with a total investment volume of EUR 93.6 Million.
The project also features a capacity development component to improve institutional and administrative management capacities as well as the operation and financial performance of the Municipalities and its’ Utilities in order to increase sustainability of the services they provide to citizens.
- Overall project management
- Hydraulic modelling
- Process design
- Sludge management concept
- Preliminary and detailed design of wastewater collection and treatment systems
- Preparation of tender documents according FIDIC Pink and Yellow Book
- Financial analysis of water utilities
- Tariff modelling
- Institutional support

Nabeghlavi Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Plausibility Check, Georgia
Nabeghlavi Hydropower Plant (HPP) – Plausibility Check
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 30.11.2019


The Client, a special purpose vehicle established solely for the purpose to acquire Nabeghlavi hydropower plant, is a subsidiary of a Georgian company, which itself is a wholly owned subsidiary of an Italian parent company – an investment company primarily focused on renewable energy projects in Central Europe and Central Eastern Europe.
The Client has requested a loan from the Bank of Georgia (BoG) to refinance the acquisition. which was initially financed by the local Georgian company with its own funds.
For this purpose, the BoG has requested that the Client to engage an independent international consultant to perform a Due Diligence Report.
Technical Key Data and salient features:
- Construction date: 2014
- Design flow: 8 m³/s
- Lateral intake, small reservoir, max. storage height 5.5 m, total length: 40.00 m.
- Headrace tunnel: length: 1,195m, 2.3 x 2.6 arch-shaped.
- Forebay: rectangular concrete basin: 34.10 x 5.3 m.
- Penstock: 2 x 42 m, diameter: 1,300 mm.
- Turbine: 2 horizontal Francis
- Installed capacity: 2.0 MW
Fields of Specialisation:
- Hydropower
- Hydrology
- E&M equipment
- Environment
- Health and Safety
- Overview of current technical condition and description of key equipment: salient features (turbines, etc.) and associated risk factors.
- Estimation of the to be expected maintenance capital expenditures for a proper function during next 15 years.
- Evaluation of operational expenditures based on comparisons and historical records
- Analysis of possible energy production based on different hydrological flow regimes; e.g. 90 %, 75% and 50% percent possibility.
- Evaluation of plant performance, comparison of theoretical possible energy production and in fact produced energy, incl. description of possible improvement measures, if any.

Establishing Safe Wastewater Disposal in the Town of Cantemir - Site Supervision for Construction Works and Capacity Development for ApaCanal, Moldova
Establishing Safe Wastewater Disposal in the Town of Cantemir - Site Supervision for Construction Works and Capacity Development for ApaCanal
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 19.11.2022


The purpose of the assignment is to supervise the implementation of water supply and sanitation works in Cantemir and to implement a capacity development programme for the water utility and the future operator of the new infrastructure.
The works to be supervised are tendered under a single FIDIC Yellow Book contract and comprise the following components:
- Construction of an completely new, fully functional wastewater treatment plant for 5,420 PE60, utilizing a treatment process based on low-load trickling filters following primary sedimentation in Imhoff tanks and than followed by secondary sedimentation. This includes, but is not limited to: Inlet and outlet
- Rehabilitation of the raw water pumping station
- Construction of a new sewer system, including three new sewage pumping stations and the replacement of parts of the existing sewer system:
- 16.3 km gravity sewer (PP, DN200 – DN315)
- 1.7 km pressure sewer (PE, OD63-OD90)
The duties include the full tasks and responsibilities of the Engineer as defined under FIDIC, up to issuance of the performance certificate.
The activities under the capacity development include:
- Tariffs, billing and budgeting
- Organizational structure
- Consumer awareness and water governance
- Gender, social, environmental and sustainability standards
- Technical training in operation and maintenance (O&M)
- Review and approval of wastewater treatment plant design
- Review and approval of the raw water pumping station
- Construction supervision of WWTP, RWPS and sewer system
- Works contract management of FIDIC Yellow Book Contract

Technical Option Analyses for Vushtrri Wastewater Treatment, Kosovo
Technical Option Analyses for Vushtrri Wastewater Treatment
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 15.10.2019


Previous studies have identified the need for new wastewater treatment facilities and sewerage improvements in the area of Mitrovica.
The objective of this assignment is to identify and prepare any additional materials necessary to complete a technically, environmentally and socially compliant study for the Mitrovica project area, extending the scope to include the wider Vushtrri catchment to the project area. The Municipality of Vushtrri, located upstream, has a population of approximately 60,000.
The study analyses the technical and economic feasibility of two options: treatment of the wastewater from Vushtrri at a single WWTP in Mitrovica or treating it in a separate, dedicated WWTP.
- Identification of feasible wastewater treatment processes
- Comparison of alternatives for wastewater collection and treatment
- Analysis of options for the treatment and disposal of wastewater sludge
- Identification of energy efficiency measures, optimisation opportunities and raw materials reduction
- Preparation of quantity and cost estimates, including investment and operational costs
- Identification of key project risks, milestones and the overall project timetable
- Preparation of financial model, affordability analysis and estimation of tariff increases
- Evaluation of climate change impacts
- Update of the Environmental and Social Assessment (“ESA”)

Introduction Integrated Solid Waste Management, Serbia
Introduction Integrated Solid Waste Management
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 30.09.2019
The Serbian National Waste Management Strategy for 2010-2019 calls for a “planned network of regional waste management centers.” KfW is supporting the Government of Serbia – specifically the Ministry of Construction, Transport, and Infrastructure – in its efforts to develop integrated solid waste management systems (ISWM) for two proposed waste catchment areas (WCA), namely Kruševac and Vranje, each comprising six “satellite” municipalities.
The development of the solid waste collection, separation, transport and deposting at regional landfills to be constructed is ongoing. P&P has been engaged by the Government of Serbia to provide financial analysis services within the framework of the Main Program. The scope of work includes financial and institutional services, with a primary focus on the development of comprehensive tariff models for the two regional systems (covering 14 public utility companies (PUCs)) and support in establishing an institutional arrangement (inter-municipal agreements) acceptable to the participating cities and municipalities.
- Assessment of the financial situation of the participating public utility enterprises (PUC)
- Preparation of tariff models for the two regional systems, permitting flexibility regarding cost-sharing between the partner entities
- Determination of socially affordable tariff thresholds
- Development of the institutional set-up
- Development of inter-municipal agreements
- Development of key performance indicators
- Development of eligibility criteria for municipalities and PUCs to participate in the project and subsequent project phases

Khobi 2 Hydropower Plant - Lender’s Engineering, Georgia
Khobi 2 Hydropower Plant - Lender’s Engineering
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.12.2022

Khobi II is a typical run-of-river hydropower scheme and comprises a lateral intake with a concrete weir structure in the river with 8m height, a sand trap, a 6.6km long headrace tunnel, a steel penstock of 660m and a powerhouse equipped with two Pelton units with installed capacity of some 45MW. The gross head is 278m with a design flow of some 20m³/s.
P&P was contracted to carry out the services of the Lender’s Engineer and a full-scale Design and Planning Review upon commencement of the EPC contract. This review comprises:
- Geology and Topography
- Review of method statement and relevant survey works for tunnelling
- Review of Dam design and construction, geotechnical stability
- Review of debris and sediment management
- Review of E&M equipment design, installation, testing and commissioning
- Review of EPC contract
- Evaluation of construction schedule and its compliance with MoU and quality management set-up (evaluation of proposed site management and supervision)
- Risk assessment of tunnel, penstock construction and network connection
- Review of environmental impact assessment report
- Review of equipment suppliers and equipment specifications and their compliance with adequate standards
- Review of operational expenses
- Review of maintenance expense including spare parts management / capex and its adequacy
- Report about deviations from international standards for all above listed works, goods and services
- Evaluate if all required permits, licenses are on place which is required for construction, commissioning, electricity generation and grid connection of the HPP
A comprehensive report shall be prepared for the developer and the banks financing the investment.
- Overall project management and liaison with the Client, EPC contractor and the banks
- Design and planning review of the EPC contractors design
Kikinda Water Treatment Plant - Yellow Book Tender Review, Serbia
Kikinda Water Treatment Plant - Yellow Book Tender Review
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 31.05.2019
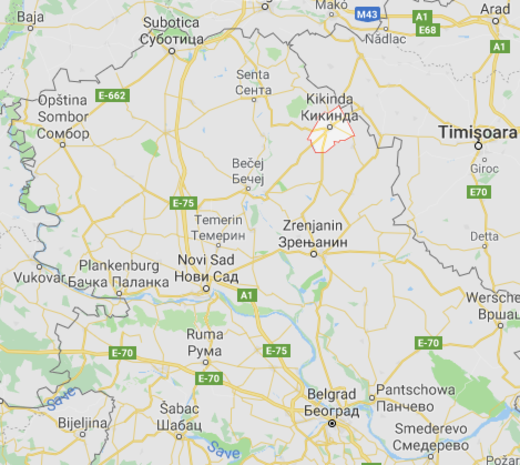
A water treatment plant shall be constructed for PUC Kikinda, the local utility aiming to treat the water origin from a well field currently pumped directly into the water supply network of the town. The plant shall comply with EU and Serbian drinking water legislation, latter requiring a very stringent Bor and Sodium removal. The investment is financed by KfW and the Republic of Serbia.
P&P was contracted to revise and update tender documents based on FIDIC Yellow Book duly considering the latest decisions made on the treatment target and facilities to be constructed and incorporating comments received by the Ministry of Construction, Transport and Infrastructure as PEA of the KfW Programme and by PUC and its consultants. The treatment process is based on findings from a pilot plant performed by DVGW-Technologiezentrum Wasser (TZW).
The revision to be carried out on the tender documents aims to ensure consistency within the tender dossiers and provide an unambiguous basis for carrying out the works and especially the testing of the plant. Functional guarantees will be defined accordingly.
- Design review
- Revision of employer’s requirements
- Revision of the general parts of the tender dossiers including Instruction to Bidders, Post-qualification requirements, Evaluation procedures, schedule of prices, etc.
- Discussion of the final tender with all stakeholders

Midterm-Final Evaluation of the IPA 2013 Programme to Albania in the field of Environment and Climate Change, Albania
Midterm-Final Evaluation of the IPA 2013 Programme to Albania in the field of Environment and Climate Change
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 31.07.2019


The project has been awarded within the EU FWC SIEA 2018 - LOT 1: Sustainable management of natural resources and resilience and aims at a Midterm-Final Evaluation of the IPA 2013 Programme to Albania in the field of Environment and Climate Change. Two service and two grant contracts with a total budget ot EUR 17.8M are subject to the evaluation, namely:
- IBECA Project - "Technical Assistance for Institution Building of the Ministry of Environment in Enforcing Environmental and Climate Acquis"
- NaturAL Project - "Natura 2000 and Protected Areas"
- PRO NEWS Albania - "Programme for Improving National Early Warning System and flood prevention in Albania"
- Technical Assistance for Integrated Solid Waste Management Systems for selected cities/region (Kukes, Gjirokaster}
A comprehensive Evaluation of the effectiveness, efficiency, sustainability and EU Added value & Coherence of the Action following the DCED Guidelines is being carried out. The services comprise an inception phase, desk phase, field phase synthesis and disseminations phase.
- Intervention logic
- Prepare questionnaires
- Review of all programme documentation
- Field visits
- Reporting

Gjilan & Mitrovica Wastewater Infrastructure - Technical Addendum to the Feasibility Study including Environmental and Social Due Diligence, Kosovo
Gjilan & Mitrovica Wastewater Infrastructure - Technical Addendum to the Feasibility Study including Environmental and Social Due Diligence
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 17.12.2018


Feasibility Studies (FS) for sewerage network expansion, interceptors and new wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) were performed for the towns of Gjilan (Regional Water Company Hidromorawa) in 2013 and for Mitrovica (Mitrovica Regional Water Company) in 2015, with WWTP capacities of 92,000 and 66,000 PE. The financing banks require updating of the FSs and performing the environmental and social due-diligence. The assignment includes updating baseline data, validation of the technical solutions, preparation of tariff model, financial and economic analysis, environmental and social impact assessment (ESIA) including preparation of screening report, environmental and social audit of the regional water companies, environmental & social action plan, land acquisition and livelihood restoration framework, stakeholder engagement plan and the non-technical summary; furthermore, preparation of the Green Economy Transition (GET) Report, refresh the Procurement and Implementation Strategy taking into consideration EBRD’s Procurement Policies and Rules and EIB’s Guide to Procurement.
- Review Baseline Data
- Validation of Technical Solution for Sewer Networks and WWTPs
- Preparation of Financial Analysis and develop a Tariff Model
- Environmental and Social Assessment

Biodiversity and Water Protection Lake Palić and Lake Ludaš, Serbia
Biodiversity and Water Protection Lake Palić and Lake Ludaš
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2021
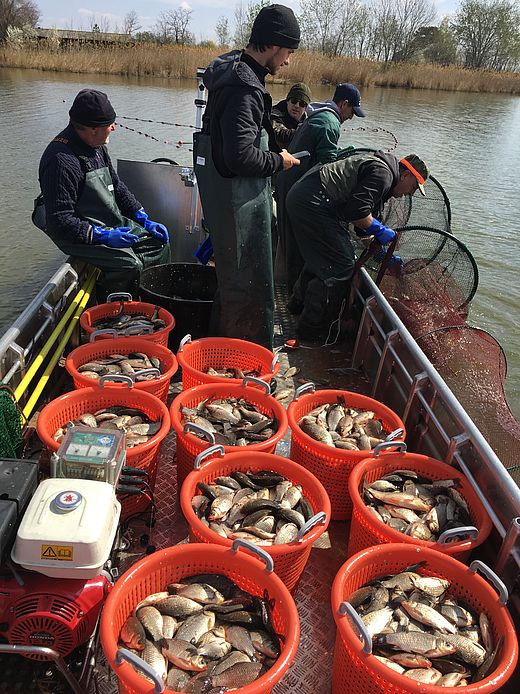
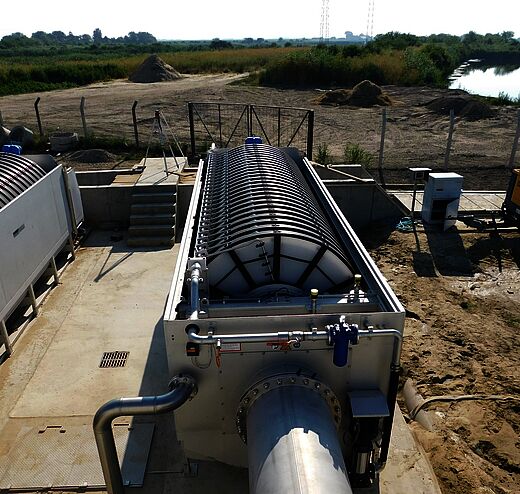



Lake Ludas was classified as a RAMSAR site in 1977 and Lake Palic is a Nature Park and part of the Kamaras Landscape Protection Area. Both are shallow Pannonian lakes and home of a large number of bird species. Lake Palic was also a recreational centre in former times till the environmental and biodiversity degradation took place. Both lakes are hypertrophic resulting in blue algae blossoming, frequent fish kill and bad odours. Reducing the phosphorus discharge to the lakes was identified as one priority issue for improving the water quality, since the effluent of the Subotica wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) constitutes the main lake inflow. Another issue is that wastewater from village Palic is discharged untreated. Establishing a buffer zone of bushes and trees between agricultural land and the lakes shall reduce diffuse nitrogen and phosphorus release to the lake and reduce wind erosion. Overpopulation of the crucian carp contributes to water pollution and requires biomanipulation interventions. For addressing the above, the Biodiversity Programme was developed including five investment components i) improvement of the WWTP effluent, ii) expansion of Palic sewerage network and iii) pumping the collected wastewater to the Subotica WWTP, iv) establishment of a buffer zone with bicycle track, visitor view points and procurement of buffer zone maintenance equipment for the Public Enterprise (PE) Palic-Ludas and v) biomanipulation for Lake Palic which includes reduction of the Prussian carp population and introduction of predator fish. The investment programme is supported by three Accompanying Measures i) technical assistance (TA) to the PUC Subotica Waterworks, ii) TA to PE Palic-Ludas and iii) TA to the City of Subotica.
Click here for to see a short promotion video for the programme.
- Overall project management and reporting
- Assessment of WWTP operation and identification of measures for enhanced P-removal; design, procurement and supervision of the works
- Design, procurement and supervision of sewerage network, sewage pumping station and long-distance pumping main
- Design of buffer zone with indigenous trees and bushes, roads, bicycle lanes, footpaths, bird watch towers; procurement and supervision of works; procurement of maintenance equipment
- Specification and procurement of tailormade fishery boat, trap nets and fishery equipment
- Procurement of international and national professional fishing companies for selective fishing campaigns, supervision of services
- Tariff modelling, public relation activities, indirect sewerage discharge data base, legal advice

Consultancy Services for Detailed Design and Construction Supervision for Water Distribution Network Rehabilitation and Expansion in Lilongwe City , Malawi
Consultancy Services for Detailed Design and Construction Supervision for Water Distribution Network Rehabilitation and Expansion in Lilongwe City
Country: Malawi, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 31.12.2024



The aim of this project is to upgrade, rehabilitate and expand the water distribution network in Lilongwe, the capital of Malawi. The length of the Lilongwe Water Board’s (LWB) water distribution network is approx. 1,758 km serving a total of 67,518 connections and about 70% of the fast-growing population are currently served.
The network is generally characterised by low operating pressures and frequent interruption of supply due to a combination of minimum elevation difference between the reservoir and the customers, insufficient hydraulic capacity of some key pipes and leakage.
With financial support from the World Bank LWB is now implementing 3 investment packages, namely:
- Priority distribution network investments comprising:
- Replacement of 124km of pipelines (DN50 – DN800)
- Permanent pressure and leakage control system
- 3 no. PV plants with capacities up to 132 KWp and BESS up to 192 KWh at pumping station sites
- Priority transmission network investments comprising:
- Construction of 27km new transmission mains (DN300 – DN800)
- Construction of 4 no. new reservoirs with 650m³ each and of 8 no. new pumping stations
- Network Expansion comprising in total:
- Construction of 186km new pipelines
- 14,700 new house connections and 60 no. new communal water points
- Construction of 3 no new service reservoirs and of 3 no. new pumping stations
- Overall project management
- Hydraulic modelling of current and future network
- Detailed design of all new constructions and rehabilitation works
- Preparation of tender documents according FIDIC MDB and World Bank SBDs
- Construction Supervision – perform the duties of the Engineer according FIDIC

Belarus Water Sector Framework, 2nd phase - Regionalisation, Belarus
Belarus Water Sector Framework, 2nd phase - Regionalisation
Country: Belarus, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 30.06.2019


The Belarusian water sector is currently fragmented having a large number of small municipal water utility companies in most cases owned by the Regions which are unable to utilize economies of scale. The capacity of these companies to properly manage the operation of the facilities at quality level and to undertake the much-needed large reconstruction projects is relatively weak. Their organisational structure and management practices are often suboptimal.
The Ministry of Housing and Communal Services, who is the main regulatory body in the sector, would like to assess the possibilities of regionalising the water operations via merging the individual utility companies on an Oblast level or in another similar way. The Ministry has selected Vitebsk Region as a pilot region for the purposes of this study.
The aim of this study is to help assess the regionalisation opportunities for water utilities in Vitebsk Region and allow the Ministry to assess the possibilities of regionalising at the state level.
In a first step the Viability of Regionalisation versus the “Status-quo” will be assessed on several levels and especially in terms of potential economic benefit. If this approach is deemed viable, then a suitable set up of a regional water company shall be elaborated.
- Overall project management
- Technical and institutional analysis of the status-quo
- Elaboration of regionalization concepts and their technical, legal and institutional analysis
- Quality Control & Quality Assurance
- Reporting

Rehabilitation of Municipal Infrastructure in Batumi Phase III and IV, Georgia
Rehabilitation of Municipal Infrastructure in Batumi Phase III and IV
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.08.2022


This project is the continuation of the Batumi Phase III and IV projects concerning the rehabilitation and extension of the water supply network and the rehabilitation of the sewer system in Batumi.
The related Implementation Consultancy service for Phase III and Phase IV have been started in 2012 and 2016 respectively, but have been terminated by the Employer by end of 2017. This project aims now at completion of the started works and services, i.e.
- Component A – Review and completion of design and tender documents, tendering
- Component B – Construction supervision (new construction contracts)
- Component C – Construction supervision (continuation of on going contracts)
- Component D – Assistance during defects notification period (ongoing contracts)
- Component E – Review and update of a Feasibility Study for a city district west of Adlia WWTP and the airport
The measures include stormwater system with large pumping stations, water supply and sewerage networks and a small WWTP in a nearby village. The total value of all works contracts for Components A-D is EUR 97.4M whereof approx. EUR 25M have been disbursed already and the rest has to be implemented now. The estimated investment volume for the Feasibility Study is EUR 85.6M.
Click here for a short video about construction of a pumping station and here for a collector. (By clicking on the link(s) you acknowledge that you will be directed to a third party site).
- Overall project management
- Design review, detailed design and preparation of tender documents
- Review and update of feasibility study for water supply and sanitation
- Procurement assistance
- Construction supervision according FIDIC
- Works contract management

Malawi NRWB Water Efficiency Project, Malawi
Malawi NRWB Water Efficiency Project
Country: Malawi, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 30.11.2021


The water supplies in Mzuzu and Ekwendeni predominantly rely on the Lynyangwa River. Due to rising urban water demand and climate variation the reliability of these services are at stress. Northern Region Water Board (NRWB), as the regional water utility, has identified the need to invest in additional production and transport/distribution capacity and the need to capacitate its organization and employees, to promote business wise sound operations leading to financial sustainable provision of water services to its people. EIB is financing those investments with some EUR 20M and launched this Technical Assistance contract to ensure the proper and sustainable implementation of the needed measures and build capacity within NRWB.
The project comprises survey and geotechnical investigations, detailed design, design review, preparation of tender documents, procurement support, feasibility study for sanitation as well as operational support to NWRB by developing a GIS and hydraulic model, introduce a SCADA and MIS and implement a NRW reduction programme.
P&P held responsible for the following out of the 12 tasks of this TA:
- Task 1 Design Review
- Task 2 Design and Supervision of the Groundwater Drilling Programme
- Task 8 Procurement Supervision
- Task 9 Project Management and Monitoring
- Task 10 Assessment of Potential Sanitation Investments
- Task 11 Lunyangwa Dam Raising
- Task 12 Design of Two River Intakes

SHPP Jochberg – Detailed Design, Austria
SHPP Jochberg – Detailed Design
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 31.08.2018


The small hydropower plant Jochberg with an installed capacity of 445kW, an annual production of 2.19GWh/a, is located in the same named municipality at the river Saukaserbach in the Eastern part of Tyrol. The plant is a typical diversion scheme consisting of a Tyrolean intake, a sand trap, a 940m long GRP penstock with an internal diameter of 900mm and a powerhouse equipped with a Ossberger free jet turbine.
Special features of the project:
- Parallel implementation of a flood projection dam together with the public authorities.
- The penstock passes below the flood protection dam and is partly located in the retention basin of beforementioned flood protection dam.
- Combined project management with the authority to manage and handle project overlaps and to avoid negative project interferences.
- Overall project management
- Detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents
- Procurement
- Construction supervision
- Commissioning

Mtkvari Hydropower Plant – Due Diligence Review, Georgia
Mtkvari Hydropower Plant – Due Diligence Review
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 04.06.2019


HPP Mtkvari is located on the river Mtkvari close to the Turkish border. With an installed capacity of 53MW the plant is currently the largest Renewable Energy Project in Georgia. Total cost of the project amounts to USD 130 mln, while the loan amount makes USD 65 mln. P&P acts as Lender’s engineer performing design review, advice on technical aspects, construction and implementation monitoring. Special focus is paid on the implementation of the 10km long tunnel stretch conveying water from the intake to the power house.
- Design Review and risk classification
- Revision of critical design issues
- Construction and implementation monitoring and preparation of corresponding Quarterly Monitoring Reports

Semey Water Project: Project Implementation Support, Engineering Design Services and Contract Supervision, Kazakhstan
Semey Water Project: Project Implementation Support, Engineering Design Services and Contract Supervision
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.02.2020


Semey, until 2007 known as Semipalatinsk, is a city in East Kazakhstan Region on the Irtysh River near the border with Russia, around 620km east of Astana and a population of 340,000.
The project aims at setting up and strengthening the capacity and at implementing a previously identified Priority Investment Programme in the water and sanitation system of some EUR 8 million.
The service comprises preparing the missing detailed designs, preparing 11 no. packages of tender documents, procurement assistance and subsequent construction supervision and works and supply contract administration.
In parallel project implementation has been closed monitored in close cooperation with PIU to be established and strengthened in all aspects of large scale project implementation and management.
- Overall project management
- Design review and detailed design of water and sanitation infrastructure
- Preparation of tender documents
- Construction supervision according FIDIC MDB
- Operational performance improvement of the utility
- Monitoring of the Project Implementation Plan

Urban Services Improvement Investment Program, Tranche 5, Georgia
Urban Services Improvement Investment Program, Tranche 5
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.06.2020


The program financed through the Asian Development Bank and implemented by UWSCG aims rehabilitating, improving and expanding sanitation facilities in the 2 secondary towns Zugdidi and Mestia.
The scope of the Consultancy is to perform the duties of the Engineer according to FIDIC for the following works contracts:
- Sewerage Network – FIDIC Pink Book (MDB Harmonized Construction Contract) Construction of approximately 178km sewer lines and 23 sewage pumping stations
- Sewage Treatment Plant – FIDIC Gold Book (Design-Build-Operate) WWTP with capacity of 11,122 m³/d in Zugdidi
- Sewage Treatment Plant – FIDIC Gold Book (Design-Build-Operate) WWTP with capacity of 1,478 m³/d in Mestia
The total investment volume to be supervised under this contract amounts to USD 76 million.
Click here for a short video on construction on Zugdidi sewage system and here on construction of wastewater treatment plant Zugdidi.
- Supervision of all construction works
- Design review of the WWTPs being implemented under FIDIC Design & Build & Operate contracts
- Providing on-the-job training to the seconded counterpart UWSCG engineers
- Providing assistance for commissioning and handing over of works to UWSCG
- Works Contract Administration

Study on the Brine Disposal Pipeline of the Red Sea – Dead Sea Phase I , Jordan
Study on the Brine Disposal Pipeline of the Red Sea – Dead Sea Phase I
Country: Jordan, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.08.2017


This study is part of the greater Red Sea Dead Sea Project which aims at providing fresh water supply to Jordan, Israel and Palestine and the same time “saving” the dead sea by slowing or even stopping the further water level drop which is currently 40m below the water level in the 1930s. Water shall be extracted from the Red Sea at Aqaba, where part of it is desalinated and used for drinking water. The brine together with additional Red Sea water is pumped over some 225 km to the Dead Sea. Due to the elevation of the Dead Sea a gross head of some 430m can be used for hydropower generation.
This study contributes to the overall project by preparing two pre-feasibility studies, one regarding the possible application of the pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) technology and using beside the hydropower potential also the osmotic gradient between the brine and the Dead Sea and the second for establishing a monitoring research centre on the Dead Sea. It also includes preparing ToR for an aquifer monitoring program with respect to potential leakage from the brine conveyor system and preparing the stakeholder engagement plan.
The first Phase of the Red Sea Dead Sea project is estimated to cost some USD 1.1 billion and shall be implemented by an BOT arrangement. The tendering started in 2016 already.
- Overall project management and liaison with the numerous stakeholders
- Preparation of pre-feasibility study of Osmosis Power Generation
- Preparation of pre-feasibility study for the Development of Research Centre
- Prepare terms of references for an Aquifer Monitoring Programme
- Stakeholder Engagement Plan

Technical Implementation Consultant for Nairobi Satellite Towns Water and Sanitation Development Programme. Phase 1: Ruiru-Juja and Kiserian-Ongata Rongai Water Supply Projects, Kenya
Technical Implementation Consultant for Nairobi Satellite Towns Water and Sanitation Development Programme. Phase 1: Ruiru-Juja and Kiserian-Ongata Rongai Water Supply Projects
Country: Kenya, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 30.04.2026



The objective of the project is to provide sustainable access to potable water supply services in urban and peri-urban areas in the fast growing satellite towns around Nairobi. The existing water supply systems are often old and degraded and major new living areas are not connected. Following approximately 31 Mio EUR investments in extension and rehabilitation approx. 365,500 people will benefit from new connections or improved services. The main components are as follows:
1. Ruiru – Juja Water Supply Project: Augment the existing pump station at the water intake, enhance the capacity of the existing water treatment plant by 13,000 m³/d by constructing an additional treatment line, construct a new transfer main DN800-1000, 13.5km long, and construct / extend the distribution network (around 135 km), install necessary consumer connections, construct 10 additional boreholes.
2. Kiserian – Ongata Rongai Water Supply Project: construct new storage tanks (2,300m3) and booster pumping stations, rehabilitate two water treatment plants, construct new and extend the existing water supply system (around 135 km), install necessary household connections with water metering, construct and equip 17 new boreholes, out of which 10 were equipped with solar power (island and hybrid) and solarize (hybrid) 6 existing boreholes.
For both projects, a total of around 16,700 consumer meters plus fittings as well as operations & maintenance equipment will be procured. For all those investments, project management, detailed design, preparation of tender documents, procurement and construction supervision services are provided.
- Detailed design
- Design review of existing designs
- Prepare tender documents and specifications according to FIDIC Red Book
- Undertake Environmental and Social Impact Assessment studies and monitor the implementation during the course of the construction
- Undertake a Resettlement Action Plan for the proposed infrastructure
- Procure the Works Contractors and Supply Contractors
- Supervise the construction and handover of the water supply infrastructure
- Assistance to PIU
Enhancing Readiness of ADB Developing Member Countries for Scaled Up Climate Finance, Myanmar
Enhancing Readiness of ADB Developing Member Countries for Scaled Up Climate Finance
Country: Myanmar, Pacific
Project end: 01.04.2017
The TA is assisting ADB DMCs to enhance their capacity to identify priority investment projects that mitigate climate change and/or support climate change adaptation while creating sustainable development co-benefits.
ADB, with co-financing by NEDA and TICA, and possibly the Green Climate Fund, prepared a loan for the water supply and solid waste infrastructure of three main towns in Myanmar’s Greater Mekong Subregion (total loan amount 117 M USD). The main objective of the individual assignment was to identify eligible project components for financing by the GCF and prepare the corresponding funding proposal in accordance to the established criteria.
- Prepare concept paper submitted to the GCF, and subsequently prepare, alongside the assigned ADB staff, a full application for project financial support, using the outline and approach required from the GCF;
- Work with the partner agencies and with the PPTA consulting team recruited to obtain necessary information and analysis;
- Interact with the GCF Secretariat, GCF Board Members, and members of the Independent Technical Advisory Panel, as needed and directed by the supervising ADB staff;
- Evaluate the feasibility of re-locating the water intake in Mawlamyine to prevent salinity intrusion due to sea level rise;
- Assess the technical and financial capacity of the agencies responsible for planning and management of water supply services in Kayin State Government and Mon State Government to develop climate resilient capacity development programs for them.

Services of Risk Assessment of Voda Donbassa Water Supply Services in Donetsk Oblast of Ukraine, Ukraine
Services of Risk Assessment of Voda Donbassa Water Supply Services in Donetsk Oblast of Ukraine
Country: Ukraine, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.03.2017



The armed conflict lasting since mid of 2014 in the Donbass of Ukraine continues to affect the supply of essential services such as water and electricity in the region. The bulk water supply system operated by PU “Company Voda Donbassa” dates back to the 1930s and provides water to about 3.9 Mio consumers in Donetsk Oblast. Its infrastructure runs from Sloviansk all the way to Mariupol – and is therefore situated close to, and in fact crosses several time, the contact line, whilst serving people in areas controlled by the Ukrainian government, as well as the self-proclaimed “Donetsk People’s Republic”.
UNICEF has contracted Posch and Partners with the implementation of a risk assessment in the Donbass area. The objective of the assessment is to identify and cost priority investment opportunities to increase the resiliency of water services to people supplied by Voda Donbassa’s main water system, based on system and management vulnerabilities in the presence of conflict-related risks.
The assessment focusses on risks threatening the safe and reliable supply of bulk water by Voda Donbassa. It considers relevant governance, institutional, financial and technical issues directly and indirectly connected to the current context.
- Data collection review of all technical and financial documentation available
- Extensive field inspection of the water supply systems on both sides of the contact line
- Technical assessments of all water treatment and distribution facilities
- Financial and managerial assessments of the regional offices of Vodo Donbassa
- Analysis of O&M practice
- Institutional and legal assessment
- Environmental risk screening

Technical Assistance to the Water Resources Development Fund for the “Urban Water Supply Programme”, Ethiopia
Technical Assistance to the Water Resources Development Fund for the “Urban Water Supply Programme”
Country: Ethiopia, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 05.07.2024


The Urban Water Supply Programme is a water supply and sanitation rehabilitation and expansion programme for small and medium towns across Ethiopia. This shall be financed from Water Basket Funds of EUR 94M provided by IDC, AfD and EIB and to be managed by Water Resources Development Fund under the Ministry through a revolving fund mechanism. This shall be done on 2 levels, i.e.:
The aim of this TA is to contribute to improving the management and operation of the WRDF.
- Activity 1: Support to the WRDF in its core activities of all aspects of program projects appraisal, review of study and design documents, procurement procedures and processes, monitoring and evaluation of program projects, Contract administration, and financing of TWUs projects,
and
- Activity 2: Financial Management and Monitoring of the IDC-AFD-EIB funded Programme in collaboration with WRDF.
A feasibility study has been performed upfront developing a clear Project Implementation Manual addressing all aspects for improvement on Programme and also on Project level which now shall be implemented and adapted under the guidance of a project team comprising international and national engineers, financial, social, environmental and monitoring experts.
- Design review of water supply projects and review of tender documents
- Project Appraisal including financial, environmental and social assessment
- Procurement Assistance
- Programme Financing and Fund Management
- Programme and Project Monitoring and Evaluation
- Capacity Building

Municipal Infrastructure III – Berat, Kucova and Librazhd, Albania
Municipal Infrastructure III – Berat, Kucova and Librazhd
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2020


The Programme “Municipal Infrastructure III” encompasses 2 project locations, i.e. the service areas of water utilities UK Berat-Kucova (~ 120,000 population) and of UK Librazhd (~24,000 population), both with low connection rates to the sewer system and deficient wastewater treatment and disposal systems.
The service contract comprises 2 components:
Component A: Consulting Services for the preparation of investment measures
- Review Investment Projects together with the respective Municipality and the respective water utility company
- Conduct or update feasibility studies for the preparation of the investments for Component B.
- Review status of current drinking water resources protection
Component B Consulting Services for the implementation of investment measures
- Preparation of the detailed design and tender documents
- Tender evaluation and contract negotiations for works and supply
- Construction supervision and final acceptance of the works
Water supply and sewerage networks shall be rehabilitated, upgraded and extended and in total 4 no. new WWTPs shall be constructed with Berat: 60,000 PE, Kucova: 30,000 PE, Librazhd: 8,000 PE, and Përrenjas: 8,000 PE.
- Overall project management
- Coordination of the team of national and international experts for feasibility study, design and preparation of tender documents
- Conceptual design of water supply and sanitation infrastructure
- WWTP process design
- Detailed design and preparation of tender documents
- Procurement assistance
- Support in acquiring permits

Machakhela HEPP, Georgia
Machakhela HEPP
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.01.2017


HEPP Machakhela LLC intends to construct a 25 MW hydropower plant near Batumi, close to the Turkish border in the south west of Georgia. The HPP shall be constructed through an Engineering, Procurement and Construction Contract and a Turkish Designer has been assigned with carrying out the required conceptual design services and to prepare the tender documents. HEPP Machakhela LLC has engaged P&P as its Owners Engineer to assist in all technical and economic implementation matters and to supervise the conceptual design engineer.
The HP scheme consists of a 15m high concrete dam, a lateral intake structure connected to a 6.5km long pressure tunnel and a powerhouse with a tailrace channel. The annual energy generation is estimated to be 138GWh based on a design flow of 20m³/s and a gross head of 135m.
- Assistance and support during preparation phase
- Review of detailed option analysis
- Conceptual design review
- Identification and evaluation of technological alternatives
- Identification of project risks incl. advice on mitigation measure
- Review and advice of EPC bidding documents
- Representing of the Clients/Owners’ interest towards Conceptual Designer

Water Supply and Sanitation in Southern Moldova, Moldova
Water Supply and Sanitation in Southern Moldova
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.01.2017


The overall objectives of this programme are to provide safe and reliable potable water supply and to establish sustainable wastewater management schemes for the urban and rural population of Rayon Cahul. For this purpose a comprehensive bankable feasibility study for the water supply and sanitation system of the city and the region was to be prepared.
The water supply system and facilities for wastewater collection and treatment in Cahul city as well as in the rural areas of the rayon were in rather poor conditions. The necessary investments and also institutional measures were to be identified and developed to improve the general service level and sanitation situation.
- Overall project management and reporting
- Assessment and appraisal of existing infrastructure
- Preliminary design of a new water treatment plant (WTP) including raw water source in Cahul, and the connection of nearby communities in the Rayon for which this approach is technically feasible and cost-effective
- Preliminary design of a new wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) in Cahul, and connection of nearby communities in the Rayon for which this approach is technically feasible and cost-effective
- Determine improvement measures in the water distribution network and sewer system in Cahul and connected communities
- Elaborate water supply and sanitation concepts for non-connected communities on Master Plan level
- Preparation of an Environmental and Social Impact Analysis and Climate Change Risk Analysis for the programme

Renewable Energy in Montenegro, Montenegro
Renewable Energy in Montenegro
Country: Montenegro, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2016

The Development Bank of Austria (OeEB-Österreichische Entwicklungsbank AG) has set itself the objective to support renewable energy projects in selected countries. This study has been prepared for that purpose and supports project developers, investors and banks in the assessment of renewable energy projects by providing detailed information of the energy and electricity sector in Montenegro with a special focus on renewable energies.
Besides a general overview the study provides detailed information about institutional framework conditions, barriers and risks, market potential for the development of renewable energy projects, ongoing and planned project activities as well as key players.
- Assessment of the market potential for the development of renewable energies
- Assessment of the institutional framework
- Identification of implementation barriers and risks
- Identification of ongoing and planned project activities and key players in the sector

Development of Detailed Project Report for Sierra Leone, Sierra Leone
Development of Detailed Project Report for Sierra Leone
Country: Sierra Leone, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.11.2017


This project is aimed at taking a programmatic approach to promote renewable energy and energy efficiency projects at both the national and regional level in West Africa.
Under this project a Detailed Project Report is conducted for the Moyamba SHPP project, addressing properly the technical, economic and financial issues as well as the environmental and socio-economic conditions.
The expected tentative technical key data for the Moyamba SHPP project are: design discharge130m³/s, gross head 9m, installed capacity 10MW, annual production 34GWh.
- Project management, site visits and desktop studies
- Design and layout of the SHPP scheme, hydro structures, as well as electro and mechanical hydropower equipment, integration into electrical grid
- Hydrology assessment and calculations of power production capacity
- Contracting and supervision of the works of topographical survey, geological investigations, hydrological studies and analyses, environmental and social investigations
- Cost estimation
- Financial and economic analysis

Project Preparation and Feasibility Studies for Construction / Reconstruction of Water Supply Systems in Rural Areas, Albania
Project Preparation and Feasibility Studies for Construction / Reconstruction of Water Supply Systems in Rural Areas
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.03.2017



The overall objective of this Rural Water Supply Program III programme is to improve the living conditions of the inhabitants in rural areas and support the economic development of these areas. This objective shall be attained through small and medium scale investments in the water supply systems for provision of reliable and hygienically safe water supply at O&M cost recovering tariffs. The programme is financed through KfW and implemented by the Albanian Development Fund.
In a first application phase municipalities and utilities all over the country are encouraged to apply for funding in their water supply systems and the Consultant will select and rank the possible sub-projects based on transparent and agreed criteria.
In the second phase social and technical feasibility studies will be performed for an overall investment amount of more than EUR 30 million.
- Support to the PEA in the overall management of the implementation
- Elaboration of detailed villages selection procedure with minimum exclusion, evaluation, and ranking criteria
- Implementation of the application phase including development of a strategy for a country-wide information and promotion campaign
- Establishment of a data base of sub-projects, evaluation of the application and preparation of an Initial Long-list subject to approval by the PEA and KfW
- Preparation of Social Feasibility Studies (SFS)
- Preparation of Technical Feasibility Studies (TFS) for socially feasible projects
- Ranking of sub-projects (villages) according previously defined criteria and parameters elaborated in the SFS and TFS

Independent Assessor for Performance Based Water Operator Partnership Contract, Malawi
Independent Assessor for Performance Based Water Operator Partnership Contract
Country: Malawi, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.09.2019
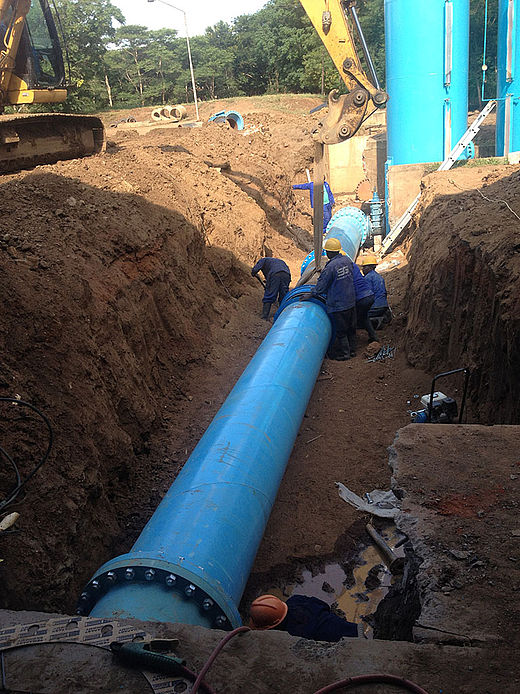


The aim of this assignment is to monitor and assess the services provided by Vitens-Evides International (VEI) to Lilongwe Water Board (LWB), the utility of the capital of Malawi serving almost a population of 1 million, through a Performance Based Water Operations Partnership (PBWOP) agreement.
The objective of this agreement is to improve the operational and financial efficiency of Lilongwe’s water service provider, to extend its service area and to reduce non-revenue water. To secure the future water supply situation LWB is planning to implement investments for more than USD 100 million over the next years and in the light of these challenges ahead was seeking the support of an international advisory firm.
The role of P&P as the Independent Assessor is to check yearly the performance of VEI, monitor the overall progress within the various tasks and ultimately to calculate the performance based compensation which VEI is entitled to according to their agreement with LWB.
- At the start of the assignment, assist LWB and VEI with regard to the methodology for annual performance assessment;
- Once every year for four years, following the end of each Agreement Year (AY), assess the performance within the PBWOP;
- Based on the Annual Performance Assessment, determine the PBC payable to VEI;
- After the second AY review of Performance Targets for the remaining years, if so initiated and proposed by one of the PBWOP parties;
- Resolve any disputes between VEI and LWB on the calculation of the PBC.

Establishing Safe Wastewater Disposal in the Town of Cantemir – Moldova, Moldova
Establishing Safe Wastewater Disposal in the Town of Cantemir – Moldova
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.04.2016


The water and wastewater services in the town of Cantemir are provided by the Municipality owned utility “Apa Canal”.
Nowadays, after the implementation of a comprehensive water supply project, Cantemir has a 24h/7day water supply system and the Municipality has extended the service area to neighboring villages. However, the wastewater system is in dire state and needs significant upgrade to improve sanitation in Cantemir. The sanitation services have been on quite low levels for many years and the WWTP has not been operative since the early 1990s. As a result, none of the existing WWTP infrastructure is in a condition that their rehabilitation would be economically feasible.
The overall objective of the project was to implement a new wastewater disposal system for the rayon capital of Cantemir. The identified works comprised the rehabilitation and extension of the existing sewer system as well as the construction of a new WWTP (trickling filter; final stage 16,500 PE). A secondary goal was the identification of optimisation measures for the existing water supply system.
The scope of the assignment included the review and update of the previously developed feasibility study for the wastewater system and the preparation of the conceptual and detailed design of all works. In addition, all required permits for design and construction had to be obtained and the tender documents were prepared (4 components, based on WB PDSI SBD). Further, a socio-economic analysis of the town as well as an institutional analysis of Apa Canal were carried out. Finally, suitable funding instruments for the capital investments were identified and the corresponding applications supported (at national level to the Regional Development Fund and the Environmental Fund, at international level to the EU AAP 2016).
- Project management and reporting
- Preparation of conceptual and detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents
- Carry out socio-economic analysis and institutional analysis
- Identification of funding instruments and support of preparation of relevant applications

Promotion of Direct Investments in Priority Climate Technology Projects, Fiji
Promotion of Direct Investments in Priority Climate Technology Projects
Country: Fiji, Pacific
Project end: 01.09.2015


ADB, with possible co-financing by EIB, Green Climate Fund (GCF) and Government of Fiji, was preparing a loan which foresaw major investments in the water and wastewater infrastructure of Greater Suva Area (total loan amount 230 M USD).
The main objectives of the individual assignment was to inform the technology selection of the project proponents towards increased resilience in light of climate change and greenhouse gas emission mitigation as well as to prepare a study on the feasibility of different packages of water and wastewater technologies for deployment in the investment project. In addition the identification of climate change adaptation and mitigation measures to be included in the proposed investment programme and the estimation of related additional or incremental costs was an important aspect of the assignment. Further, the technical part of a funding proposal to the GCF for financing identified adaptation and mitigation measures was prepared.
Secondary objective of the assignment was the preparation of Terms of Reference for additional consulting services on the optimisation of the sewer system of Greater Suva Area aiming at a reduction of the number of existing sewage pumping stations and therefore a reduction of O&M costs for Water Authority Fiji.
- Provision of support and information regarding the technology selection of project components towards increased resilience in light of climate change.
- Preparation of a feasibility study of different suitable packages for water and wastewater technologies.
- Identification of climate change adaptation and mitigation measures to be included in the proposed investment programme and estimation of related additional or incremental costs.
- Preparation of technical part of funding proposal submitted to Green Climate Fund for financing identified adaptation and mitigation measures.
- Preparation of Terms of Reference for additional consulting services on the optimisation of the sewer system.
- Completion of the assignment through engineering, financial and situational analyses based on site visits and interviews with project stakeholders, including desktop research and studies on water and wastewater technology best practice.

Feasibility Study for Modernisation of the Wastewater Management System of the City of Polotsk, Belarus
Feasibility Study for Modernisation of the Wastewater Management System of the City of Polotsk
Country: Belarus, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.08.2015


The City of Polotsk would like to construct its own wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) that would serve its population of 85,000 people and commercial customers in Polotsk. The WWTP would include aeration tanks, sedimentation tanks, sludge pumps, air blowers, etc. The work on a WWTP was started in 2008 however, the works stopped in 2011 due to lack of financing. It is estimated that approximately 20 per cent of the works had been completed up to that point.
On this basis, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) engaged a consultant to prepare a feasibility study, which shall include:
- identification and a detailed assessment of the PIP that will cover the financing period of 13 years and evaluate its benefits including assessing its environmental and social feasibility
- detailed financial analysis of the Unitary Enterprise Polotskvodokanal
- preparation of overall procurement and project implementation plans
The main objective of this assignment is to prepare a feasibility study that will determine the priority investment for the project, which will be financed by a EBRD loan, and it will form the basis for project appraisal and approval by the EBRD in addition to the Government of Belarus.
- Baseline study including socio-economic data, organisational and institutional review, tariff setting and subsidy payment policy, affordability, analysis of local-central fiscal relations and budgeting system, as well as due diligence on the proposed lending structure
- Technical assessment comprising of water supply and wastewater services, the water supply and wastewater system, water and wastewater treatment, in addition to sludge management and disposal
- A long-term investment strategy and institutional development options
- Priority investment programme (PIP)
- Financial analysis
- Environmental and social assessment
WaterFlows – Insight into Water Footprints and Worldwide Water Resources, Austria
WaterFlows – Insight into Water Footprints and Worldwide Water Resources
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.08.2016

A series of interactive school workshops were performed on the subject of direct and indirect water consumption, with the aim to develop knowledge and awareness about worldwide water resources, including:
- The importance of the resource water and the sustainable use of it.
- “Virtual Water” used in agricultural, industrial and manufacturing processes
- The use of the “water footprint” concept to measure the amount of water used to produce goods and services.
- Water supply and consumption, including examples from developing and transition countries.
- Measuring and monitoring individual water consumption.
- Workshop organisation and facilitation
- Education
- Community liaison
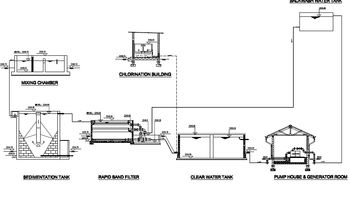
Supervision and Coordination of Works for Independent Water Supply Downstream of Thika Dam (Gatanga Water Supply), Kenya
Supervision and Coordination of Works for Independent Water Supply Downstream of Thika Dam (Gatanga Water Supply)
Country: Kenya, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.12.2017
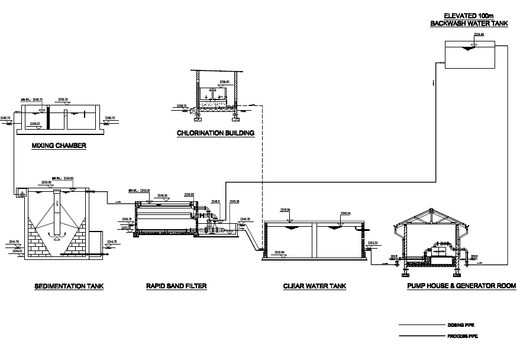
One component of the Kenya Water Supply and Sanitation Improvement Project (WaSSIP) is the development of an Independent Water Supply Scheme Downstream of Thika Dam near Gatanga. Athi Water Services Board (AWSB) themselves carried out the feasibility study, detailed design and prepared the tender documents for the works. The works have been awarded based on Standard Bidding Document for Procurement of Small Works by World Bank.
This consultancy assignment covers design review, construction supervision, commissioning and performance control during the Defects Liability Period.
The works to be supervised cover:
- 2 no. intake weirs and raw water intakes
- 21.9 km of raw water main of uPVC
- 2 no. water treatment plants with 125m³/h capacity each
- Pump houses with standby generator set and general power connection
- Clear water tanks with 150m³ each featuring chlorination
- All administration buildings and ancillary works
- 9.4km of treated water transmission main
The value of the works is EUR 2.3 million
- Overall project management
- Design review of all works to be implemented
- Process design review of the 2 no. water treatment plants
- Claim management
- Short-term expert inputs and backstopping of the supervision team

Technical Assistance to Mykolayiv Vodokanal Project, Ukraine
Technical Assistance to Mykolayiv Vodokanal Project
Country: Ukraine, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 30.04.2021


Mykolayiv is the 9th largest city in Ukraine with a population of approximately 510.000. Previously the Water Utility had been supported to identify its priority investment needs in a “Short Term Investment Programme” (STIP).
The aim of this project is now to provide Technical Assistance to support the PIU in all aspects of STIP implementation, which covers approx. 30 mio euro investments in water and wastewater including rehabilitation of treatment plants, pumping stations and networks, establishing SCADA, sectorization of water supply systems and installation of DMAs. For these design, procurement and construction supervision will be performed using WB contracts.
In addition hydraulic modelling of water and wastewater will be performed, a GIS / MIS and interlinked billing system will be established, support will be provided for creation of a NRW unit within the utility and capacity building of the PIU will be carried out.
- Designs refined and completed and Tender Documentation prepared using WB tender docs
- Procurement
- Support PIU in Construction Supervision and in Contract Administration.
- Establishment of SCADA systems and water sectorization (DMAs)
- Procurement, training and implementation of GIS and Management Information System, connected with the consumer and billing database, with functionality for real time benchmarking and reporting of performance indicators
- Support in establishment of new NRW unit for maintaining the GIS and asset management.
- Institutional development and capacity building to the water utility and municipality

Kiribati Adaptation Project III (KAPIII) - Non-Revenue Water Reduction, Kiribati - South Tarawa
Kiribati Adaptation Project III (KAPIII) - Non-Revenue Water Reduction
Country: Kiribati - South Tarawa, Pacific
Project end: 01.08.2018


This project is part of the Government of Kiribati’s Climate Change Adaptation Program III, which aims at improving Kiribati’s resilience to the impacts of climate change on freshwater supply and coastal infrastructure. The piped water supply system of South Tarawa is managed by the Public Utilities Board (PUB). Supply to consumers is on an intermittent basis, two hours every second day, due to high non-revenue water (NRW) of around 67% and limited sweet water resources.
The main objectives of this assignment are leak detection, repair of transmission mains and reservoirs, physical improvement of the water distribution systems in three pilot zones, trainings for PUB staff in leak detection and repair, introduction of a basic asset management system, as well as the establishment of a leak detection unit at the utility. Further prepare bidding documents for material and works, assist PUB in tendering and contract preparation, perform construction supervision and construction management for the works, partly implemented through contractors, partly through force account.
Please click here for a video published by the PUB on the project.
- Procurement of leak detection equipment and water supply material
- Physical leak detection, supervision of repair works
- Development of a repair concept for leaking reservoirs, tender documents, and construction supervision
- Distribution system mapping and assessment
- Network modelling and calibration
- Establishment of a leak detection and repair unit at the utility
- Development and introduction of an asset management system at the utility

Water Supply Veliko Gradište, Site Supervision Contract, Serbia
Water Supply Veliko Gradište, Site Supervision Contract
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 01.05.2017


Under this project a new water supply system is to be constructed for the town of Veliko Gradiste, Serbia. The scope of this assignment is Construction Supervision and performing the duties of the Engineer according FIDIC and the duties and responsibilities of the technical Supervisor (strućni nadzor) according to the Planning and Construction Law of Serbia.
The works to be supervised comprise:
- Rehabilitation of wells with capacities of 30l/s each
- Construction of raw water pressure pipeline DN400
- Water treatment Plant with 100l/s
- Reservoir with 1,500 m³ capacity and pumping station at the WTP with capacity of 90l/s
- Pressure pipeline up to the water tower – 2.5km DN400
- Water tower “Beli Bagrem” with 1,200m³ volume and 54 m height.
All works have been tendered as a single FIDIC Design & Built Contract (Yellow Book) and total value of works is EUR 4.14M.
- Overall project managementLiaison with the Client, Financier and all stakeholdersDesign review of the Contractor’s design Construction supervision according FIDIC Yellow Book
- Assistance in training and commissioning
- Advice the Financer and the Employer

Technical Due-diligence Services for 8 SHPP’s, Georgia
Technical Due-diligence Services for 8 SHPP’s
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.04.2014


Our assignment includes Technical Assessments and Technical Due-Diligences for the small hydro power plants Bzhusha, 12.2MW (1956), Alazani I, 6.06MW (1942), Alazani II, 6.06MW (2013), Ritsuela, 6.3MW (1956), Racha, 11.0MW (2013), Kakhareti, 2.1MW (1957), Igoeti, 1.8MW (1953), Triponi, 3.2MW (1951).
The assessment covers newly-built and existing hydropower plants as it can be seen at the construction dates with a nominal capacity in a range between 1.8MW up to 12.2MW.
The hydro power plants are scattered all over Georgia, but are mainly situated in the northern-, eastern- and south part where the landscape is characterized by high mountain ranges. All hydro power plants are diversion schemes, mostly consisting of a water intake structure, a headrace channel, headpond, penstock and turbine house.
- Technical evaluation of the existing civil structures
- Technical evaluation of the existing E&M equipment
- Plausibility check of hydrological data
- Assessment of current O&M conditions
- Assessment of current energy production and determination of possible energy production after implementation of feasible technical implementations
- Determination of monetary plant value
- Risk Analysis
- OPEX Evaluation
- OPEX Estimation for short and long term operation
- CAPEX estimation for the implementation of feasible technical improvements
- Financial analyses for the different investment scenarios

Program for the Promotion of Renewable Energies II - Georgia, Georgia
Program for the Promotion of Renewable Energies II - Georgia
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.08.2018


The Technical Assistance (TA) project aims to implement a Programme to establish a credit line at the Bank of Georgia (BoG) and to enhance the investments in the development and rehabilitation of small and medium hydropower plants in Georgia. The TA comprises 2 components, namely i) SHPP Component to support project developers, owners and operators of SHPP eligible under the Program in realizing their respective construction, rehabilitation, or expansion project; and ii) Banking Component to support BoG with a focus on support in the evaluation of credit applications against the Programme’s criteria but also to assist BoG in developing procedures for longer term lending operations for infrastructure projects as well as the enhancement of BoG’s capacity to monitor and manage credit risks.
The outcome of the project shall be at least 3 SHPP projects implemented and a sustainable know-ledge transfer to BoG strenghting its capacity in financing infrastructure projects.
The Programme as well as the TA is financed by KfW and the Austrian Development Bank (OeEB).
- Establishing the final eligibility criteria for the Programme
- Technical review and assessment of project applications
- Preliminary and final design review and assistance
- Implementation planning
- Procurement assistance

Elaboration of a Feasibility Study for the Project “Improvements in Drinking Water Supply and Waste Water Collection and Treatment in the City Of Donetsk”, Ukraine
Elaboration of a Feasibility Study for the Project “Improvements in Drinking Water Supply and Waste Water Collection and Treatment in the City Of Donetsk”
Country: Ukraine, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.07.2014


The aim of the project is to carry out a comprehensive feasibility study for investments in the municipal infrastructure of city of Donetsk with some 750,000 inhabitants. The feasibility study shall cover all technical, financial and economic aspects of the water supply system, the wastewater collection and treatment system as well as the stormwater system. The legal framework has to be assessed together with an institutional analysis of the service provider Dongorvodokanal.
The project comprises data collection and assessment of the actual situation followed by the elaboration of a project concept including option analysis for the various improvement measures which are then all summarized in the actual feasibility study.
The activities to be performed include financial, economic and socio economic assessments and analysis of the supply area, flow and pressure measurements with subsequent modelling of the networks, technical assessment of the current assets, and full consideration of the environmental aspects and performance of a Health Impact Assessment.
- Overall project management and liaison with the Client as well as with KfW
- Technical assessment of the water supply infrastructure
- Technical assessment of the wastewater treatment plants and sludge management
- Hydraulic modelling of the networks including flow and pressure measurements
- Elaboration of investment concepts and programme for water supply and wastewater treatment

Provision of Additional Work on the Feasibility Study for Karura Hydro Power Project, Kenya
Provision of Additional Work on the Feasibility Study for Karura Hydro Power Project
Country: Kenya, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.12.2015


In 2009 P&P performed a feasibility study for a new hydropower plant at the Tana river being part of the KenGen operated Seven Forks cascade of 5 existing HPPs.
The new site is located about 150km north-east of Nairobi in the districts of Mwingi and Mbeere. The previously identified dam option for the HPP is currently considering socially not feasibility and therefore P&P have been assigned with further investigation of a tunnel off the river HPP option clearly minimizing the social and also the environmental aspect of the investment.
Investment costs have been preliminarily estimated to be in the range of EUR 200-250 million.
- Overall project management and liaison with the Client
- Defining the geological and geotechnical investigation programme
- Preliminary design of all civil works including the tunnel itself
- Preliminary design of the electro-mechanical equipment
- Environmental assessment including sanitary flow aspect
- Cost estimates and financial analysis

Technical Assistance to the Project Coordination Unit for Implementation of the Rolling Program of Interventions for Additional Supply of Water for the Gaza Strip , Palästine
Technical Assistance to the Project Coordination Unit for Implementation of the Rolling Program of Interventions for Additional Supply of Water for the Gaza Strip
Country: Palästine, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.07.2016


The overall objective of the project is to improve quality and quantity of water supply and irrigation in the Gaza Strip. This shall be achieved by implementing the Rolling programme of interventions defined in the Comparative Study of Options for an Additional Supply of Water for the Gaza Strip (CSO-G).
The action plan includes i) establishment of a programme coordination unit (PCU), ii) water and health monitoring, iii) improvement of domestic water supply, iv) enhance water import from Israel, v) construction of short-term low-volume desalination plants, vi) a regional desalination plant, vii) increased reuse of treated wastewater and viii) other interventions in the agricultural sector.
This project provides project management support and technical assistance (TA) to the Palestinian Water Authority (PWA) for establishing and operation and management of the PCU.
- Project management and operational support to the PCU
- Procurement of consultancy services and material
- Technical review of studies, designs and bidding documents for water supply, groundwater infiltration, desalination, wastewater treatment projects and groundwater and health monitoring programmes
- Monitoring the implementation of projects for water supply, desalination, wastewater treatment and water reuse
- Support in ministerial and regulatory activities

Technical Due-diligence Services for SHPP Lopota, Georgia
Technical Due-diligence Services for SHPP Lopota
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.06.2013


The 1.8MW plant is located at the river Lopota in Napareuli, Region Kakheti, East Georgia. Generally the plant is not state of the art and has several deficiencies resulting in a energy production shortfall. As a result of these deficiencies, additional to the Technical Assessment and the Technical Due-Diligence feasible technical improvements were developed which should be implemented to achieve a higher energy production and to guarantee a further plant operation.
- Technical evaluation of the existing civil structures
- Technical evaluation of the existing E&M equipment
- Plausibility check of hydrological data
- Assessment of current O&M conditions
- Assessment of current energy production and determination of possible energy production after implementation of feasible technical implementations
- Determination of monetary plant value
- Risk Analysis
- OPEX Evaluation
- OPEX Estimation for short-/long term operation
- CAPEX estimation for the implementation of feasible technical improvements
- Financial analyses for the different investment scenarios

Ust-Kamenogorsk Environmental Remediation Project - UKER CS 01, Kazakhstan
Ust-Kamenogorsk Environmental Remediation Project - UKER CS 01
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.12.2016


General objectives of the Ust-Kamenogorsk Environmental Remediation Project for Kazakhstan are to: (i) prevent the groundwater contamination plume's further migration towards the residential areas, the city's sources of drinking water supply and eventually into the Irtysh River; and (ii) strengthen institutional mechanisms for groundwater quality monitoring to enable control of ongoing groundwater pollution from local municipal and industrial sources.
- Design review
- Construction supervision
- Contract management
- Claim management
- Financial management of works contract
- Review of bidding documents for re-tendered Lots
- Liaison with all stakeholders

Consultancy Services for Conducting Pre-feasibility and Feasibility Studies of Mini Hydro Schemes , Uganda
Consultancy Services for Conducting Pre-feasibility and Feasibility Studies of Mini Hydro Schemes
Country: Uganda, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.11.2015
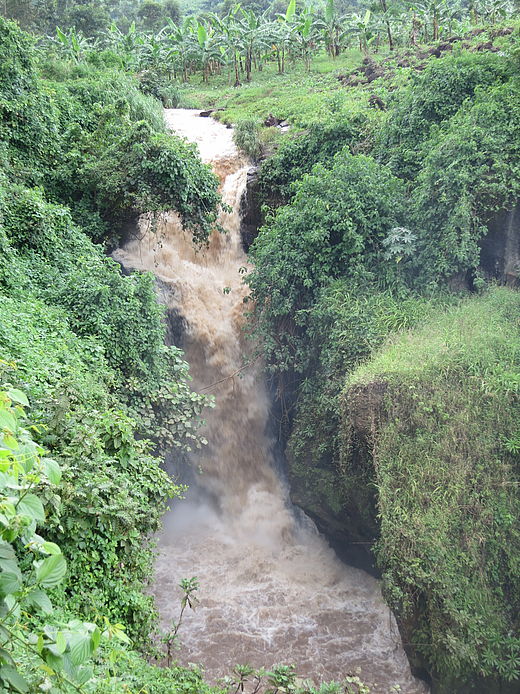


The level of electrification in Uganda is very low, in spite of the fact that the country possesses abundant natural resources of hydropower potential. To develop Uganda’s energy sector the Government of Uganda with the support of the World Bank implements the second phase of the Energy for Rural Transformation Programme (ERT II) of which the main objective is a greater access to and use of renewable energy in rural areas.
Therefore the main objective of this assignment is to develop comprehensive Feasibility Studies for 3 selected SHPP projects out of 10 shortlisted sites. The Muyembe project has been identified by the MEMD to be taken directly to the feasibility study level. For each of the 9 remaining sites a Pre Feasibility Study has to be prepared. The ranking of the results of these Pre Feasibility Studies will lead to the selection of the most attractive 2 sites, for which then also a Feasibility Study will be elaborated.
Also tender documents for the 3 sites on the Feasibility Study level have to be prepared for the client.
- Project management and team leader, site visits and desktop studies
- Design and layout of new SHPP schemes, hydro structures and electro & mechanical hydropower equipment
- Hydrology assessment and calculation of power production capacity
- Contracting and supervision of the works of topographical survey, geological investigations, hydrological measurements and analysis, environmental & social investigations
- Financial and economic analysis of the SHPP projects
- Preparation of tender documents for SHPP CW structures and E&M equipment

Renewable Energy Project – Small Power Plant Scheme and Rehabilitation Plan, Samoa
Renewable Energy Project – Small Power Plant Scheme and Rehabilitation Plan
Country: Samoa, Pacific
Project end: 01.12.2013


Samoas power utility EPC is operating several thermal diesel plants and 5 small hydropower plants (SHPP) to provide the required electrical power to Samoa. In order to become less dependent on fuel imports and reduce costs of electricity, the Government of Samoa (GoS) embarked on an ambitious renewable energy programme, in particular developing additional SHPPs. In December 2012 the cyclone Evan damaged seriously 3 of the 5 SHPPs, which should be rehabilitated urgently.
ADB has agreed to assist the GoS in both endeavours. The JV of P&P and STR have been awarded from ADB to perform the Project preparatory technical Assistance (PPTA). The main components of this PPTA are: due diligence on 7 existing feasibility studies for new SHPP projects (comprising technical, financial, economic, social & environmental issues), rehabilitation schedule and investment plan for the power transmission and distribution network, tender assistance for the rehabilitation works of the damaged SHPPs, concept design for a seasonal storage dam project, procurement strategy, capacity strengthening programme (operation, maintenance, trainings).
- Project management and team leader, site visits and desktop studies
- Design and layout of new SHPP schemes, hydro structures and electro & mechanical hydropower equipment
- Assessment of damages and layout of rehabilitation measures on hydro structures and electro & mechanical hydropower equipment
- Environmental investigations on site and reports preparation acc. ADB safeguards
- Hydrology assessment and calculation of power production capacity
- Financial and economic analysis of the new SHPP projects
- Assistance to EPC in preparation of tender documents for rehabilitation works on SHPP CW structures and E&M equipment

Technical Supervision on Waste Water Treatment Plant Reconstruction in the city of Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine
Technical Supervision on Waste Water Treatment Plant Reconstruction in the city of Ivano-Frankivsk
Country: Ukraine, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.11.2013


The project comprises the technical supervision of the works for rehabilitation and modification of the municipal wastewater treatment plant of the city of Ivano-Frankivsk with a population of some 250,000. Technical supervision includes the review and approval of the Detailed and Working Design (Stage R design according to Ukraine legislation) and the actual supervision of the physical works at the WWTP to ensure timely and satisfactory completion of the works and compliance with the signed works contracts as well as with Ukrainian law and regulations.
- Project management and coordination including QA/QC
- Process design review
- Detailed and working design approval
- Construction supervision
Small and Medium Hydropower Climate Risk Assessment in South-eastern Europe, Turkey & Caucasus, South-eastern Europe, Turkey & Caucasus
Small and Medium Hydropower Climate Risk Assessment in South-eastern Europe, Turkey & Caucasus
Country: South-eastern Europe, Turkey & Caucasus, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2015
Hydrology is a key driver for the annual energy yield of hydropower plants (HPP) and since hydrology is quite variable, it poses a risk to such investments. It is in turn very sensitive to climatic conditions and consequently to climate change. Small and medium HPPs are particularly exposed to climate risks i.e. climate change and climate variability.
The study aims at better understanding the influence of these factors on small/medium hydropower plants, the risk on such investments and degree and type of uncertainty and their effect on the banks project finances and decision-making.
The study carries out an analysis of such risks in South-east Europe, Turkey and the Caucasus, using a river basin approach for a number of selected major river basins. The analysis shall lead to a methodology providing the bank with recommendations to assist decision-making on future small and medium hydropower investments.
- Compile climate data, conduct regional overview of historical climate change impacts
- Select major river basins on the basis of particular criteria and case studies
- Evaluate potential for water availability changes, climate change impact on competing water uses
- Analyse how financial performance of hydropower plants may be affected by climate variability and climate change
- Recommend decision setting criteria for financial performance of hydropower investments
- Comment on required adaptation of environmental and social action plans
- Recommend methodology for future assessment of hydropower projects

Rehabilitation of District Water Supply System Nisporeni, Varzaresti and Grozesti, Moldova
Rehabilitation of District Water Supply System Nisporeni, Varzaresti and Grozesti
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.07.2016


Construction of the Nisporeni district water supply system for some 60,000 people had to be terminated in 1992 due to lack of financing. The objective of this programme is to revive, revise and complete phase I of the system which is the supply of Nisporeni town, Varzaresti and Grozesti municipalities, in total some 20,800 inhabitants.
P&P was entrusted with the multi-annual programme management and institutional strengthening services. This includes establishing, heading and managing the Project Implementation Unit (PIU) which includes representatives of all 3 municipalities as well as the procurement of 3 no. design & supervision service contracts and 3 no. works contracts necessary to implement the programme, reporting to the project donors and financiers which include the European Union (EU), the Austrian Development Agency (ADA), the Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC), the Moldovan Ministry of Ecology, the Nisporeni Rayon and City Administrations and organising and reporting to the Steering Committee.
The total investment volume is EUR 14.5M.
Austrian Broadcasting also had a look on this project: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XwB7wxc2llA
- Procurement and contract management for works and services for design & supervision, construction works and IT & office equipment
- Preparation of Rules of Order for the Steering Committee; organize meetings, secretarial functions
- Compliance with visibility criteria, coordination and reporting to multiple donors.
- Establishing regional utility serving several municipalities; drafting the required documents
- Introduction of a computerized metering, billing and accounting system
- Preparation of a tariff model and implementation of the tariffs
- Development of an organization structure of Apa Canal tailored to the particular needs
- Public relation works, customer awareness building
- Establishing water balances performing non-revenue water reduction activities.

Mid-term Review of Maseru Wastewater Project within the European Union Water Facility Grant Scheme, Lesotho
Mid-term Review of Maseru Wastewater Project within the European Union Water Facility Grant Scheme
Country: Lesotho, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 08.10.2012
This Technical Assistance assignment is to undertake a Mid-Term review of the Maseru Wastewater Project (MWWP) implemented by the Lesotho Water and Sewerage Company (WASCO) under EU financing.
New Agric College WWTW and Upgrades to the Existing Ratjomose WWTW:
(i) a new wastewater treatment works at Agric College with a design flow of 7.2 Ml/day;
(ii) refurbishment of the biofilter arms, the biofilter recycle pump station, the primary sludge pump station and to provide new floating aerators for a facultative pond on an existing WWTW as well as repair of the leaking pond
Rehabilitation, upgrading and construction of sewer networks and pumping stations in Ratjomose and Agric College districts:
(i) New sewerage network with some 5,200 new household connections
(ii) 2 new pumping stations and including rising mains and grabity mains to convey the sewerage to the WWTWs
- quantitative and qualitative assessment of the work carried out since the beginning of the project
- assessment of the project’s ability
- assessment of the perception of the project’s results
- assessment of the sustainability of the project’s outcomes
- identification of the problems, technical, managerial or otherwise encountered in the implementation of the project and propose possible measures to address them.
- assessment of the project performance against the established OVIs including review to what extent they are still consistent and descriptive of the project.
- assessment of the organization, management and follow-up of programmes activities, as well as the management of budget, human resources, and PR

HPP Andelsbuch – Water Intake Bezau – Rubber Dam, Austria
HPP Andelsbuch – Water Intake Bezau – Rubber Dam
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.05.2015

In order to improve the flood water alleviation of the water intake structure of the HPP Bezau an existing bypass channel shall be equipped with a rubber dam. The by-pass channel was constructed after the big flood event in 2005 and features currently a fuse plug. The current situation is not satisfactory in terms of sediment management and frequently the HPP operator has to excavate accumulated sediments upstream the water intake in order to provide the required freeboard to 2 bridges over the river.
The awarded consulting services comprise analysis of the existing structures, detailed design and structural analysis of the concrete weir, conceptual layout and detail design of the rubber dam, analysis and detailed design of the flood water channel, preparation of the tender documents for the civil works and the rubber dam.
- Conceptual layout and preliminary design
- Detailed design
- Structural analysis
- Tender documents
- Implementation design

Preparation for an Investment Programme for the Water and Sanitation Sector in the Cook Islands, 20 African countries
Preparation for an Investment Programme for the Water and Sanitation Sector in the Cook Islands
Country: 20 African countries, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.06.2012


The objective of the study is to prepare a socially affordable investment programme for improving the water supply and sanitation situation on Rarotonga and Aitutaki, the main islands of the Cook Islands, for potential financing under the EU Water Facility Pooling Mechanism and the EIB.
- Project identification
- Preparation of priority investment study
- Preparation of EU Water Facility financing application documents

Feasibility Study and Design of the Hydropower Plant Axamer River, Austria
Feasibility Study and Design of the Hydropower Plant Axamer River
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 28.02.2022

Posch & Partner identified this hydropower plant (HPP) site, developed an initial concept and managed to market the project idea to the Municipality of Axams and the Axamer Lizum AG, the latter being the owner and operator of the Axamer Lizum Skiing Resort. With the support of Posch & Partner, the two entities founded the company Wasserkraft Axams GmbH, who then became the project Promoter for the 900 kW HPP, whereby Posch & Partners performed extensively over the entire period the functions of the Project Promoter.
The assignment included the following stages:
- Installation and operation of two river flow gauging stations and monitoring for a period of 10 years
- Hydrological analysis, residual flow studies
- Option analysis for a run-off river, peak power and pumped storage HPP
- Preparation of feasibility study and business plan with option analysis on grid connection to public grid and/or supply to municipal enterprises and/or to the Axamer Lizum Skiing Resort
- Technical designs
- Environmental impact studies including flora, fauna and ornithological site investigations and mapping and impacts during constructio
- Geological investigations
- About 20 project presentations to representative of the Municipality and the Axamer Lizum AG. as well as multiple consultations and discussions with all concerned Provincial Government Authorities of Tirol including the Torrent and Flood Control Department
- Obtaining the Construction Permit, the Environmental Permit, Forestry Permit, Electrical Permit and consent of the Fishery Association
Fields of Specialisation:
- Hydropower option analysis
- Feasibility study
- Business plan, design
- Project presentation to Promoter and Government Authorities
- Installation of gauging stations
- Hydrological studies
- Obtaining construction permit and all precedent permits
- Project identification
- Marketing of project idea and finding investor and project promoter
- Option studies, feasibility studies
- Design
- Stakeholder management, in particular presenting the project in many municipal council meetings (with changing political members over the long period of time) and winning their project support
- Obtaining construction permit and all underlaying permits

Water Supply and Sanitation Project for 15 Towns in Ethiopia: Contract for Works Supervision, Ethiopia
Water Supply and Sanitation Project for 15 Towns in Ethiopia: Contract for Works Supervision
Country: Ethiopia, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.04.2014


The overall objective of the project is to improve the living conditions of about 500,000 inhabitants by rehabilitating existing systems and extending the water supply infrastructure in 15 towns spread over 4 regions of Ethiopia. The works in the 15 towns have been awarded in 4 lots to a single Contractor under EDF conditions of contract. Works in the towns comprise the drilling of new and rehabilitation of existing boreholes – up to 300m deep, construction of collector and transmission mains, construction of service reservoirs and supply and installation of all E&M equipment for the well fields and pumping stations. One town also features a surface water treatment plant. Numerous administration and ancillary buildings have to be constructed in all towns in addition to access roads to the sometimes remote well field sites. Total works contracts value is 37.5 MEUR.
This project comprises the performance of the duties of the Supervisor according EDF conditions of contract and PRAG, e.g. Day to day supervision, review and approve Contractor’s submittals, record keeping and reporting, progress monitoring, measurement of works, check and clearance of Interim payments, checking and ensuring quality of works, managing claims and assisting in dispute resolution, identify defects and supervise remediation measures during the maintenance period, prepare and issue Final Acceptance Certificate and Final Statement of Account, re-design and re-tendering of remaining works after works contract termination.
- Design review
- Construction supervision
- Contract management
- Claim management
- Financial management of works contract
- Review of bidding documents for re-tendered Lots
- Liaison with all stakeholders

Batumi Stormwater Project, Georgia
Batumi Stormwater Project
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.09.2011


In order to most effectively address storm water management objectives, consideration of storm water runoff needs to be fully integrated into the urban planning and design process. This involves a more comprehensive approach to site planning and a thorough understanding of the physical characteristics and resources of the site. The purpose of these investigations is to provide a framework for including effective and environmentally sensitive storm water management into the urban development process and to encourage a greater uniformity in storm water management site plan preparation.
- Data collection
- Definition of appropriate design input data
- Simulation of existing design by using input data
- Assessment of deficiencies, problems encountered in existing design
- Formulation of improvement measures
- Preparation of a storm water master plan

Supervision of Water Supply and Sewerage Improvements and Construction of Wastewater Treatment Plant in the Municipality of Drniš, Croatia
Supervision of Water Supply and Sewerage Improvements and Construction of Wastewater Treatment Plant in the Municipality of Drniš
Country: Croatia, Balkans
Project end: 01.05.2014


The water supply and wastewater infrastructure in Drniš is in bad condition and currently a pollution load of estimated 3800PE is discharged untreated into Krka river. In order to improve the municipal infrastructure, to protect the water resources and to implement the EU Environmental acquis rehabilitation works shall be done on the water supply and sewer systems and a new WWTP with 5,000 PE shall be constructed.
Hrvatske vode contracted the services to carry out supervision of the following to works contracts procured under PRAG:
- “Design and Build Construction of the WWTP Drniš” (FIDIC Yellow Book)
- “Construction Works of the Water supply, Wastewater and Stormwater Networks in the town of Drniš” (FIDIC Red Book)
The scope of works under this project comprises sound management and successful implementation of both investment measures and performing the duties and authorities of the Engineer as per FIDIC and national legislation from the preparation phase including design review and verification of the Contractor’s WWTP design until end of the Defects Liability Period.
- Project management
- Process and detailed design review and verification of the Yellow Book
- Contract management according to PRAG and Hrvatske vode’s requirements.

Consulting Services on design and supervision of works concerned with construction of main sewerage collector in Mogilev town, Belarus
Consulting Services on design and supervision of works concerned with construction of main sewerage collector in Mogilev town
Country: Belarus, Central and Eastern Europe


The objectives of the assignment are to carry out a feasibility study for the water supply, wastewater and stormwater systems for Mogilev Oblast Capital with some 370,000 population. The study shall focus on proposals for improvement of the reliability of the town’s sewerage system and shall identify a first priority investment phase. Focus shall be drawn on the wastewater system comprising energy and treatment efficiency of the existing WWTP.
Pre-identified measures will comprise the renewal of 3.6km of sewer collector for which required investigations and surveys shall be carried out followed by preliminary and detailed design. Technical specifications and drawings for bidding documentation according to World Bank STBs for works shall be prepared and assistance shall be given to the Client and Beneficiary during contract negotiations and award.
The design and tender documentation has to undergo the required national approval procedure before start of construction.
The services under this project also include construction supervision for the first investment phase.
- Project management and reporting
- Technical assessment of waters supply, wastewater collection and treatment facilities
- Feasibility study and identification of least cost investment measures
- Design of wastewater infrastructure
- Preparation of WB Bidding Documents and procurement assistance
- Construction supervision and construction management

Water and Sewerage Programme in Medium Sized Municipalities in Serbia – Phase II, Serbia
Water and Sewerage Programme in Medium Sized Municipalities in Serbia – Phase II
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2013


The overall objective of the Water and Sewerage Programme in Medium-Sized Municipalities in Serbia is to ensure a sustainable, continuous and hygienically acceptable supply of drinking water and the improvement of sewage disposal for the population in selected Municipalities at socially acceptable costs.
Phase II comprises design, tendering and construction of physical infrastructure and institutional support of the utilities in improving their efficiency and in implementing required tariff increases.
- Preparation of Tender documents according to FIDIC Yellow Book
- Bid evaluation and assistance in contract negotiations
- Review tariffs, update tariff model;
- Present the findings and assist utilities in implementing the required tariffs

Consulting Services for Development of the EU Identification Study for the Moyamba Mini Hydroelectric Project, Sierra Leone
Consulting Services for Development of the EU Identification Study for the Moyamba Mini Hydroelectric Project
Country: Sierra Leone, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.10.2010


The Delegation of the European Union in Sierra Leone contracted the services to prepare an Identification Study of the Moyamba Mini Hydroelectric Project with the overall objective to provide the decision makers in the Government of Sierra Leone and the EU Delegation with sufficient information to justify acceptance and select the preferred option amongst different alternatives of this hydropower project.
- Project Management on-site in Sierra Leone
- Contacting the local institutions and stake holders
- Review of existing study, data collection and processing
- Site visits of the project area and on-site stakeholder workshop
- Layout of the technical conceptual design, cost estimate, financial analysis for the SHPP options
- Layout of the transmission network
- Options identification and evaluation
- Preparation of the Final Identification Study

Consulting Services for Development of Detailed Engineering Design, Bidding Documents and Supervision for Wastewater Treatment Plant and Effluent Sewer Collector in Orhei, Moldova
Consulting Services for Development of Detailed Engineering Design, Bidding Documents and Supervision for Wastewater Treatment Plant and Effluent Sewer Collector in Orhei
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.10.2014


With the help of EC funds managed through the World Bank a new WWTP shall be constructed in the city of Orhei. Previous studies foresee a multi stage constructed wetlands to replace the existing WWTP in Orhei having a population of approx. 33,000 population.
The overall project objectives are the improve the quality of sanitary services in Orhei, to reduce the discharge of pollutants, including nutrients, from Orhei municipal sources that flow into the River Raut and eventually may reach the Black Sea and to demonstrate and disseminate cost-effective nutrient reduction technologies for municipal wastewater sources.
The objective of this assignment is to perform the preliminary and detailed design, prepare bidding documents and construction supervision for an optimized constructed wetland able to treat the wastewater load generated by the connected population.
In the October 2014 edition of Water21 magazine by IWA Publishing a technical article has been published about this WWTP project, which is one of the biggest constructed wetlands in the world.
- Project Management
- Assessment of the actual situation and existing data and studies
- Process and detailed design of constructed wetland
- Preparation of Tender Documents according to FIDIC
- Construction supervision

Vitebsk Water and Wastewater Sub-Project Feasibility Study, Belarus
Vitebsk Water and Wastewater Sub-Project Feasibility Study
Country: Belarus, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.08.2010

The EBRD in partnership with the Nordic Investment Bank (NIB), the Government of Belarus and several participating cities has developed a Municipal Environmental Infrastructure Financing Framework for Belarus. The Vitebsk Water and Wastewater Sub-Project is to be prepared and financed within this Framework. The investment programme would focus on energy efficiency improvement, reduction of leakage, improvement of the quality of service and water metering of the City of Vitebsk (population: approx. 350,000).
The objective of this assignment was to perform a Feasibility Study, including due diligence of the company, to determine the investments to be financed by the EBRD loan and which will be a basis for project appraisal and approval by the EBRD.
- Assessment of the present status of the water and waste water services in the City
- Assessment of the existing water and waste water systems including operation, physical condition and treatment technology
- Development of an affordable, least cost strategic investment programme for the entire water and wastewater infrastructure in the City according to best applicable technology and with strong environmental benefits.
- Preparation of a financial analysis of the Company and its financial projections;
- Performing an organisational and institutional assessment of the Company
- Proposal of a new tariff system including affordability analysis
- Preparation of environmental analysis and audit and an Environmental Management Plan

Technical Advisory and Auditing Services to Support the Open Joint Stock Company Azersu and the PIU`s in Ganja and Sheki, Azerbaijan
Technical Advisory and Auditing Services to Support the Open Joint Stock Company Azersu and the PIU`s in Ganja and Sheki
Country: Azerbaijan, Caucasus
Project end: 01.08.2010


The overall objective of the “Open Programme Municipal Infrastructure II” is to improve living conditions, raise public health standards and promote economic growth in the country to be achieved by improvement of quality, reliability and sustainability of water supply and sanitation services in the cities of Ganja (population: approx. 310,000) and Sheki (population: approx. 60,000).
The programme comprises the reconstruction and extension of the water supply and sewerage systems as well as the wastewater treatment plants of both cities.
The purpose of the assignment is to assist the two local consulting firms in the process of an adequate updating of the existing design and tender documents with the main objective to enable Azersu to start the tender process of work contracts.
- Assessing the current status and quality of achievement of the existing design and tender documents
- Defining and prioritizing in detail improvement measures required in order to upgrade the documents
- Proposing appropriate standards for improving the documents
- Actively advising and assisting the local consultant in the process of preparing satisfactorily upgraded design and tender documents
- Verifying and approving the documents, drawings prepared by the local consultants
- Task related effective know-how transfer to PMU

15 Small Towns Water and Sanitation Project in Ethiopia – Assistance for the Evaluation of the Works Tender, Ethiopia
15 Small Towns Water and Sanitation Project in Ethiopia – Assistance for the Evaluation of the Works Tender
Country: Ethiopia, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.04.2010

The 15 Towns Water and Sanitation Project is one of several water supply projects that have been identified to meet the Millennium Development Goals for 2015. The project will improve the living conditions of about 500,000 inhabitants by rehabilitating existing water supply systems and extending the water supply and sanitation infrastructure as well as providing adequate training for Town Water & Sanitation Services (TWSS) staff. The tender for the works (four lots for four regions) was problematic and all participating tenderers were invited to make new offers.
The overall objective of the assignment is to observe that the tender evaluation activities are carried out in accordance with the EC guidelines and rules.
- Assistance in the evaluation of the tenders received for the four lots for the 15 Small Towns Water and Sanitation Project
- Preparation of the evaluation report

Design and Supervision of Works for the Construction of an Iron-removal Plant in Bobruisk Town at “Solomenka” Water Intake, Mogilev Oblast, Belarus
Design and Supervision of Works for the Construction of an Iron-removal Plant in Bobruisk Town at “Solomenka” Water Intake, Mogilev Oblast
Country: Belarus, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.12.2013


The Republic of Belarus has received a loan from the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) to implement Water Supply and Sanitation Projects. The overall objectives are to improve the quality, effectiveness and sustainability of water supply and wastewater services in six participating Oblasts covering about 1.7 million consumers. One beneficiary is the Town of Bobrujsk (population: approx. 220,000).
The objectives of the assignment is to carry out the feasibility studies, investigations and surveys, preliminary and detailed designs and supervision of construction of iron-removal plant in Bobrujsk Town, Mogilev Oblast.
The expected project implementation effect is improvement of consumer supply with water satisfying health standards on iron content.
- Preparation of feasibility study, with necessary investigations
- Preliminary design
- Detailed design
- Financial, economic, social and environmental assessment
- Supervision of construction works

Hydropower Plant Project KARURA, Kenya
Hydropower Plant Project KARURA
Country: Kenya, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.09.2011


The client KenGen intends to increase its hydropower production capacity. The aim of this consulting assignment is to elaborate a Feasibility Study of the Karura hydropower project, which will exploit the residual head between the existing Kindaruma and Kiambere powerstations of the Tana River. Several alternatives must be studied and a recommendation for the most convenient option must be given. Expected power potential: 60 MW.
- Dam engineering
- Hydrology
- Hydraulic engineering
- Survey and reservoir silting
- Electrical engineering
- Hydropower-option study
- Preliminary design
- Feasibility study

Small Hydropower Plant Bergbahn Lofer, Austria
Small Hydropower Plant Bergbahn Lofer
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.10.2009


The client operates an existing snow making system in the project area. The aim of the Pre-Feasibility Study was to design the technical options and evaluate and opine the technical and economical feasibility of the extension by a Small Hydropower Plant of the existing snow making system and introduce this project to the local authorities.
- Design of technical options and construction works
- Evaluate the technical and economical feasibility
- Introduce the project to the local authorities

Small Hydropower Plant Thermorema, Greece
Small Hydropower Plant Thermorema
Country: Greece, Western Europe
Project end: 01.06.2010


The existing SHPP with 2.7 MW shows several deficencies in operation:
- Flushing of grit chamber is not efficent and accumulated sediments must be removed by hand;
- Flow velocities in grit chamber are partly too high to allow sand to settle;
- Tyrolean weir at the intake is regulary blocked by sediments after flood events;
- Algae problem due to surface water inflow just upstream intake;
- Land slide at the penstock section.
The aim of the project is to analyse the current situation and to design the details for improvement measures to optimize the plant operation.
A SCADA system shall be installed to allow state-of-the-art operation and monitoring of the power plant.
- Analysis of present operational problems
- Detailed design of improvement measures
- Detailed design of SCADA system
- Detailed design of automated flushing system for grit chamber
- Detailed design for automated flow measurements in river, intake and environmental flow

Technical Assistance to Podgorica Water and Sewer Company, Montenegro
Technical Assistance to Podgorica Water and Sewer Company
Country: Montenegro, Balkans
Project end: 01.11.2009


The aim of the technical assistance project is to help Podgorica Water and Sewer Company and its owner, the Capital City of Podgorica, in their effort to upgrade and expand the water and waste water services and of operation efficiency improvement, possibly with PSP and commercial sources of finance.
- Assessment and analysis of the regulatory, legal and financial market framework, including review of sources of finance likely to be available.
- Assessment and analysis of the local economic base and demographic demands, including demand forecast scenarios for water supply and sewerage services, analysis of tariff system and social affordability.
- Assessment and analysis of the operational and financial performance of the utility, including budgeting, planning and accounting procedures, financial projections for improvement scenarios, financing plans of capital expenditures and relationship between utility and municipal finances.
- Assessment and analysis of the management and governance structure, including accountability of utility towards customers and owner, tariff setting standards, options for improving any management and governance weaknesses.
- Development of upgrading options and capacity development needs, covering an improvement strategy for physical improvements, costing of capital works, financing and cost recovery, reforms to management and governance, capacity building and training.

Feasibility Study on the Implementation of Natural Procedures of Treatment of Urban Wastewater of Smaller Towns and Settlements in the Territory of BiH , Bosnia and Herzegovina
Feasibility Study on the Implementation of Natural Procedures of Treatment of Urban Wastewater of Smaller Towns and Settlements in the Territory of BiH
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.07.2010

A comprehensive study shall be elaborated for BiH addressing the application of non conventional technologies (NCT) for treatment of urban wastewater for small towns and settlements with population ranging from 500 to 10,000. A feasibility study shall identify the most suitable and economically feasible option for wastewater treatment in villages of the concerned size depending on topography, local circumstances, climate and other factors influencing the selection process.
A GIS shall be established summarizing all influencing factors on application of NCT WWTPs as well as information on existing and planned water supply and wastewater collection and treatment systems
A nation wide mplementation strategy shall be elaborated and general guidelines for planning, design, operation and maintenance of NCT WWTPs shall be prepared.
Preliminary design of 3 pilot plants each in a different size range shall be done for low-cost and low-energy water treatment plants
- Description of available NCT treatment facilities
- Feasibility Study
- Establishment of a GIS based Data Bank
- Strategy for NCT implemetation
- Design Criteria and Guidelines
- Action Plan
- Preliminary Designs for Pilot Plant

Vez Svoghe Mini Hydro Project - Lender's Engineer, Bulgaria
Vez Svoghe Mini Hydro Project - Lender's Engineer
Country: Bulgaria, Balkans
Project end: 01.10.2015
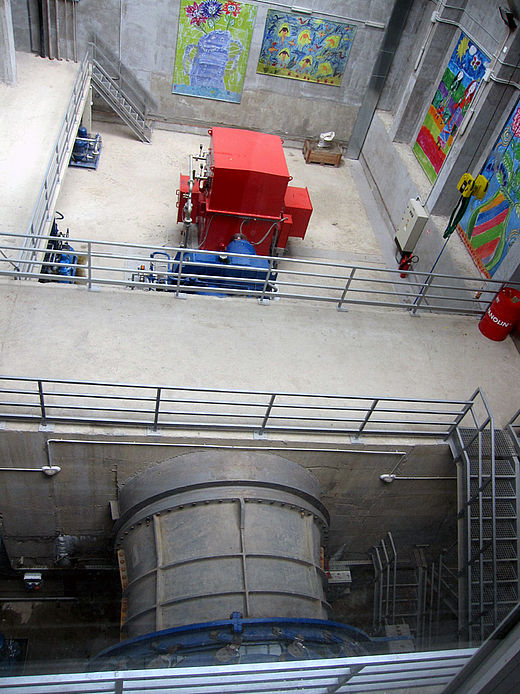


The aim of the project is to evaluate and opine on the construction and operation of in total 9 no. small hydropower plants projects along the Iskar river. A loan agreement was signed between EBRD and an Investor company where the 9 plants are divided into 3 phases of construction and tranche payments of the loan.
The SHPPs have a capacity between 2.5 and 3.5 MW and are all of the same run-off the river type. Upon project start 2 of the SHPPs were already constructed and commissioned.
The Bank assigned P&P performing the role of the Lender’s Engineer and to check if all conditions of the loan agreement are fulfilled, if the technical quality is according to the design and relevant norms and if electricity production is according to the estimates and financial analysis on which the project is based.
The project foresees quarterly visits to the plants and monitor their construction, assess the management of the various contracts by the Owner’s team and to control the project costs.
Only once the Lender’s Engineer gives his okay on all issues and certifies the completion the loan shall be disbursed.
- Assessment of technical quality of design and construction works
- Check of compliance with state-of-the-art technology and approved design documents
- Review of contract management and book-keeping of the Owner’s implementation team
- Monitoring of the construction and supervision of the commissioning of the SHPPs
- Review of operational arrangements

Rehabilitation of Municipal Infrastructure in Batumi -Phase II, Georgia
Rehabilitation of Municipal Infrastructure in Batumi -Phase II
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.11.2014


We are pleased to annouce that Wastewater Treatment Plant Adlia, Batumi, Georgia is Winner of the 2013 IWA Project Innovation Awards – Development - Global Honour Award!!!
The project is the second out of three project phases, formulated in the feasibility study prepared by our company in 2005/2006. This Phase foresees investments for a total of 50. Mio EURO and covers the following investments for the city of Batumi:
Rehabilitation (exchange) of 100 km of drinking water pipelines, rehabilitation of 50 km of sewers, construction of a new WWTP for 200.000 PE including a 3.6 km sea outfall into the black sea. For all above investments project management, detailed design, procurement and construction supervision as well as assistance to the PEA (project implementation agency) is provided.
In addition the project includes the implementation of a wastewater disposal system for the Adjara coastal strip between the Turkish border and Batumi, which is the main focus area of tourism development in the region. These measures cover investments into a pumping sewer line of 17 km length (by 4 pumping stations) and secondary sewers for all settlements (5 villages with in total 10.000 inh.) along the coastline (100 km of secondary sewers incl. house connections). Also for these investments project management, detailed design, procurement and construction supervision is provided.
- Overall Project Management
- Procurement
- Detailed design
- Hydraulic modelling
- Dilution modelling for sea outfall design
- Leak detection, developing concepts for reduction of UFW
- Construction Supervision
- Assistance to PEA

Small Hydro Power Plant Potential Assessment, Albania, FYR Macedonia, Montenegro
Small Hydro Power Plant Potential Assessment
Country: Albania, FYR Macedonia, Montenegro, Balkans
Project end: 01.08.2009

IFC is committed to increasing its support for renewable energy investments in the Balkan region. The objective of this Project is to assess in Albania, Macedonia and Montenegro the small hydropower (SHP) potential, identify potential and barriers for SHP development, to assess the legal and regulatroy framework, current situation regarding SHP development and conditions regarding feed-in tariffs, conditions for connection to the public grid and financing condtions.
- Assessment of the natural and the technical feasible SHPP potential
- Current status of SHP development
- Legal and regulatory framework
- Grid access (technical and legal requirements)
- Preferential tariffs
- Financing potential
- Kyoto Protocol status

Hydropower Plant Qukes, Albania
Hydropower Plant Qukes
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.11.2008
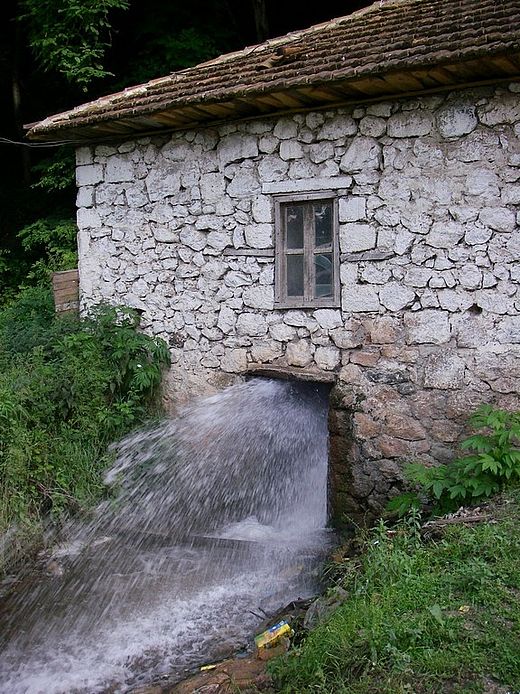


The project includes the assessment of the feasible hydropower potential of a defined river section of Shkumbin river, to prepare a feasibility study for the hydropower cascade, to prepare a business plan and to assist the investor in preparing all relevant documents for obtaining the concession. The project includes a cascade of four hydropower stations with a total installed capacity of about 50 MW.
- Assessment of feasible hydropower potential
- Hydrological, topographical and ecological assessment and analysis
- Preparation of feasibility study with financial analysis
- Preparation of business plan
- Compilation of proposal for obtaining the concession

Zhytomyr Water and Wastewater Project - Feasibility Study, Ukraine
Zhytomyr Water and Wastewater Project - Feasibility Study
Country: Ukraine, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.10.2008


The EBRD considering lending to Zhytomyr Water and Wastewater Company, to finance a capital investment programme of the municipal water and wastewater assets serving a population of some 300,000. The investment programme focuses on energy efficiency improvement, reduction of leakage, improvement of service quality and water metering.
The objective of this assignment is to perform a feasibility study, including due diligence of the company and to fix the investment program to be financed from the EBRD loan which in turn is the basis for project appraisal and approval by the EBRD.
- Assessment of the existing status of the water and waste water services in the City.
- Assessment of the existing water and waste water systems including operation, physical condition and treatment technology.
- Development of an affordable, least cost strategic investment programme for the entire water and wastewater infrastructure in the City according to best applicable technology and with strong environmental benefits.
- Preparation of a financial analysis of the Company and its financial projections.
- Performing an organisational and institutional assessment of the Company.
- Proposal of a new tariff system including affordability analysis.
- Outlining a Service Agreement between the City and the Company
- Preparation of environmental analysis, environmental audit and an Environmental Management Plan.

Fenes Small Hydropower Plant, Romania
Fenes Small Hydropower Plant
Country: Romania, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.10.2008


Services provided include the assessment and monetary valuation of the 1.6 MW hydropower plant facilities and determination of rehabilitation requirements.
- Preparation of feasibility study
- Preparation of business plan

Water and Sewerage Programme in Medium Sized Municipalities in Serbia – Phase I, Serbia
Water and Sewerage Programme in Medium Sized Municipalities in Serbia – Phase I
Country: Serbia, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2009


The overall objective of the project is to ensure a sustainable, continuous and hygienically acceptable supply of drinking water for eight medium-sized municipalities (50,000 – 200,000 inhabitants) at socially acceptable costs. Phase I includes preparation of feasibility studies for investment measures in the amount of 3 – 5 million Euro for each municipality, including dynamic prime cost calculation and institutional support such as preparation of business plans, tariff models and service level agreements.
- Review of proposed improvement measures
- Preparation of detailed designs and/or review of proposed designs for immediate measures
- Preparation of Tender documents and procurement assistance
- Conducting feasibility studies for the Investment Projects scheduled for Phase II
- Tariff studies aiming at full cost recovery
- Institutional support of the water companies, including commercialisation and preparation of business plans

Croatia Coastal Cities Pollution Control , Croatia
Croatia Coastal Cities Pollution Control
Country: Croatia, Balkans
Project end: 01.06.2009


The World Bank supports Croatia in wastewater collection, treatment and disposal for the coastal cities on the Adriatic sea.
The objective of this assignment is to assist the World Bank team in reviewing the proposed investments, the submitted feasibility studies and to prepare tariff models to ensure positive project appraisal. The task inluded further the financial and economic analysis of six sub-projects Pula, Cres, Male Losinj, Bol/Brac, Hrvar and Metkovic, including assessment of the respective five municipal enterprises. Tariff models were prepared based on current household tariffs, applied project surcharges and social affordability levels.
- Evaluation of proposed waste water investments and review of feasibility studies
- Financial and economic analysis of sub-projects and assessment of Municipal Water Companies.
- Preparation of tariff models considering social affordability
- Analysis of institutional arrangements

Water Supply and Waste Water Disposal in Adjara, Feasibility Study, Georgia
Water Supply and Waste Water Disposal in Adjara, Feasibility Study
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.07.2008


The project comprises the elaboration of a feasibility study for German funded (KfW) investments in the water and wastewater system of the project area south of Batumi, Georgia, with the aim of ensuring that proposed investments will be carried out in a cost effective and environmentally friendly way in line with a sustainable long term strategy.
The area is anticipated to experience strong growth in levels of tourism and this must be accounted for in terms of the future demand. The feasibility study shall provide all information required for the appraisal of the project and the measures required to eliminate deficiencies in water supply and to conciliate wastewater disposal with the environment.
-
Data collection and assessment of the present situation (water, wastewater).
-
Preliminary design, cost estimates and a phased implementation plan for improvement measures of the water and sewerage system.
-
Detailed formulation and design of investment packages (water, waste water).
-
Institutional and financial assessment of the current water service situation in the area, assessment of the impacts of the intended project measures and design of possible concepts for improvement.
-
The preparation of a water and wastewater tariff setting model.
-
A socio-economic assessment, focusing on the poverty relevance of the project and its impacts on the target groups.
-
Elaboration of a concept for technical assistance, training and advisory services.
- Outlining an appropriate community awareness campaign.

Construction Supervision for the Yntumak Reservoir Rehabilitation and Technical Re-equipment , Kazakhstan
Construction Supervision for the Yntumak Reservoir Rehabilitation and Technical Re-equipment
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.12.2012


The project comprises the construction supervision of the 29 million USD rehabilitation of the Yntumak reservoir on the Nura river in Central Kazakhstan and its technical re-equipment. Works include a 1.6km long and up to 40m deep slurry wall in the earth filled main dam; construction of a rubber dam regulated spillway with a capacity of 3,000 m³/s, including apron, chute and stilling basin; refurbishment of the existing bottom outlet and the installation of a small hydro power unit in the bottom outlet (~700KW). The assignment involves all tasks required to act as “The Engineer” according to FIDIC.
Construction supervision according to FIDIC conditions of contract (Red Book) featuring:
- Supervision of all health & safety requirements
- Financial and time control of the works contracts
- Technical assistance to the contractors

Municipal Infrastructure Development Project, Bulgaria
Municipal Infrastructure Development Project
Country: Bulgaria, Balkans
Project end: 01.03.2008
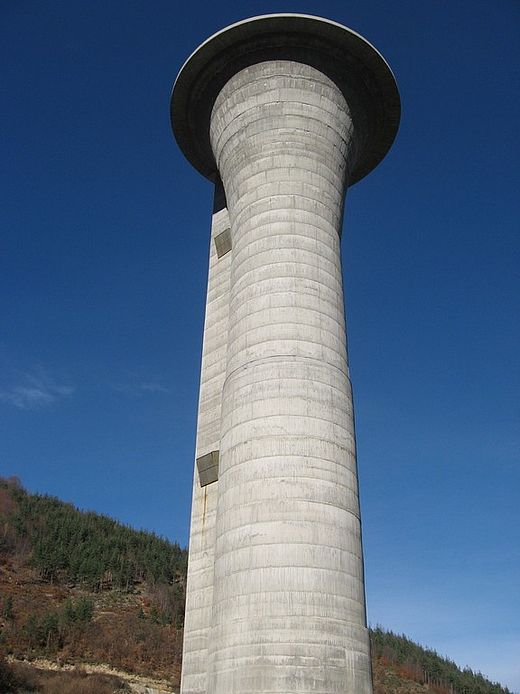


Financial and technical appraisal of proposed investments for improving the water supply systems of six Regional Water Companies. Proposals included the rehabilitation of drinking water systems and the completion of dams. Previous economic analysis was assessed, including the review of water demand and the tariffs. All projects were analysed for their compatibility with EU guidelines on the provision of water.
- Assessment of previous economic analysis
- Review of water demand
- Review of tariffs
- Compatibility analysis with EU guidelines on the provision of water

Southern Coast Development Plan, Albania
Southern Coast Development Plan
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.05.2008


The southern coast of Albania has been highlighted as having a high tourist potential. In order to ensure a controlled and sustainable development of the region, the Government contracted the preparation of a regional development plan. This was accompanied by a complementary infrastructure development plan that included water supply, sewerage, wastewater treatment, roads, sea and air transport, power supply and solid waste management.
- Preparation of a complementary infrastructure development plan (included water supply, sewerage, wastewater treatment, roads, sea and air transport, power supply and solid waste management).
- Responsible for infrastructure issues.
- Preparation of all maps.

Preparation of technical documentation and a management set-up for the Regional Water Supply System Lička Jasenica-Plitvička Jezera-Slunj, Croatia
Preparation of technical documentation and a management set-up for the Regional Water Supply System Lička Jasenica-Plitvička Jezera-Slunj
Country: Croatia, Balkans
Project end: 01.01.2009

The overall objective was to ensure safe, reliable and sustainable water supply services in the project area, which covered five municipalities and the National Park "Plitvicka Jezera". Future investments in the water supply and wastewater collection and treatment system were identified and a feasibility study, detailed design and tender documents were produced for the required works. The Institutional setup for an operating company was also established, including a model performance contract, and an economic and financial analysis and tariff calculations were carried out to ensure future sustainable operation.
- Identification of future investments
- Detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents
- Institutional setup
- Financial analysis
- Tariff calculations

Small Hydropower St. Walburgen, Austria
Small Hydropower St. Walburgen
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.12.2008
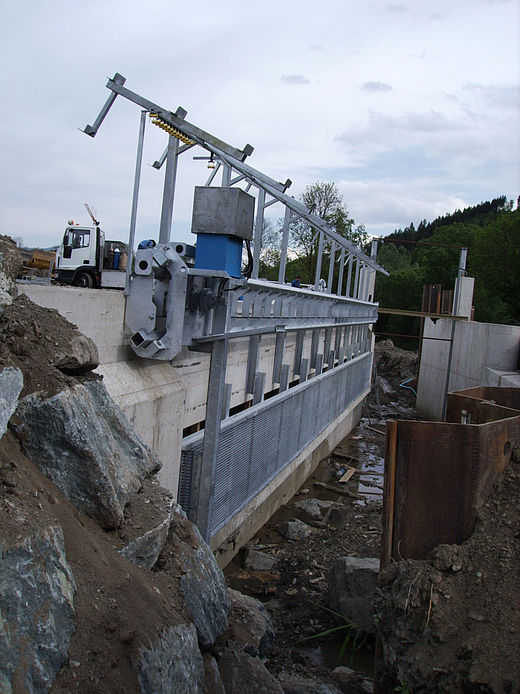


The project includes general design, detailed design and tender documents for the 500 kW power plant St. Walburgen. The water intake is realised by an inflatable weir of 9 m length and 1.85 m height. The works include a tripple line sand settlement basin, a DN1500 penstock of 1,830 m length, an underground power house and lowering of the trail race channel by one meter to increase system head.
- Preparation of feasibility study
- Preparation of detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents

Design of Rehabilitation and Renewal Works for Blantyre and Lilongwe Water Boards, Malawi
Design of Rehabilitation and Renewal Works for Blantyre and Lilongwe Water Boards
Country: Malawi, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.10.2008


The water supply systems of the two biggest cities in Malawi had been suffering numerous problems to meet the actual and short-term water demand. The project aimed at the identification of hydraulic bottlenecks in the primary supply systems, a detailed facility inventory and the formulation of rehabilitation and renewal measures.
Some studies had been previously carried out for both Water Boards and the results from these and the associated documentation was verified and updated.
The main focus was on the upgrading of the treatment plants and renewal of the electro-mechanical equipment to prevent total system breakdown on the main supply lines in the near future.
The works in Blantyre needed to be more substantial as the entire system was outdated and the city experienced regular interuptions in the water supply services.
- Detailed facility inventory
- Hydraulic modelling and identification of bottlenecks
- Process engineering of the water treatment plants
- Social and environmental assessment
- Preliminary design
- Detailed design
- Tender documents and cost estimates
- Procurement assistance

Ponor, Medna – Sklop und Sokocnica Small Hydro Power Plants, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Ponor, Medna – Sklop und Sokocnica Small Hydro Power Plants
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2009


Based on preliminary studies, WEB ENERGO d.o.o. won the concession for small hydro power plants, Ponor (400kW), Medna – Sklop (600kW) and Sokocnica (800kW), which were located near Mrkonjjć-Grad, Republic Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Technical Characteristics:
Ponor
Design flow: 2,6m³/s; Actual power output: 9,99MW; Average annual energy production: 53.337.000kWh; Cross head: 495,30m
Medna - Sklop
Design flow: 1,6m³/s; Actual power output: 830kW; Average annual energy production: 4.229.000kWh; Cross head: 66,48m
Sokocnica
Design flow: 0,9m³/s; Actual power output: 750KW; Average annual energy production: 3.574.000kWh; Cross head: 103,60m
- Preparation of pre-feasibility studies
- Preparation of feasibility studies
- Preparation of business plans
- Preparation of detailed designs
- Preparation of tender documents

Ritten Pumped Storage Hydropower Plant , Italy
Ritten Pumped Storage Hydropower Plant
Country: Italy, Western Europe
Project end: 01.07.2008
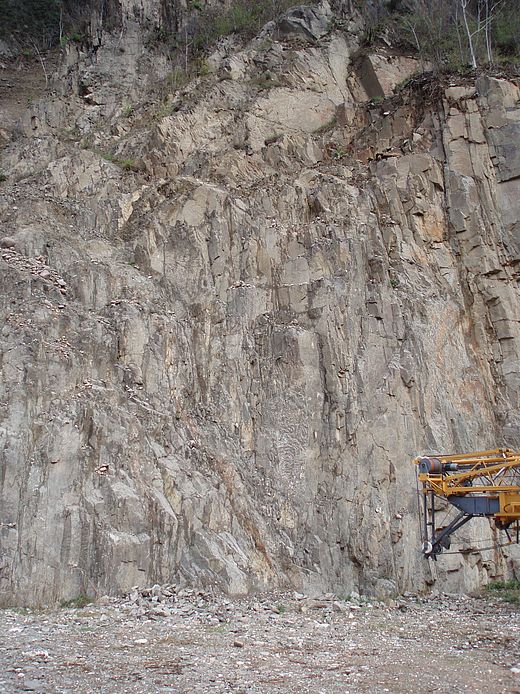


P&P were engaged by an Austrian private investor to prepare a feasibility study, concept design and environmental impact assessment study for a 225 MW pumped storage hydropower plant. All main plant components were designed in an underground cavern so as to minimise environmental impacts.
- Preparation of feasibility study
- Preparation of concept design
- Preparation of environmental impact assessment study

Rehabilitation of Municipal Infrastructure in Batumi – Phase I , Georgia
Rehabilitation of Municipal Infrastructure in Batumi – Phase I
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.02.2014


Batumi, with a population of 123,000, is the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Adjara and situated in the south-east of Georgia. The existing water supply situation in the town was unsatisfactory, with per capita production rates of 900l/c,d necessary to cover the demand including losses. The existing sewer system was also in poor condition and a source of serious contamination when the streets were flooded. This occured regularly because the storm water system could not cope with the high precipitation rates and was characterised by many false connections. Waste Water Treatment was no longer existent, causing further contamination of the already endangered Black Sea.
Following a feasibility study on the rehabilitation of communal infrastructure conducted in 2005-2006, rehabilitation was scheduled to be implemented in 3 Phases.
In Phase I the water supply and sewer system are being rehabilitated, which in fact means that most of the existing systems require replacement. A new water reservoir of 10,000m3 is also being constructed. Raw water treatment plants are being rehabilitated, including the construction of new intakes, new flow limitation devices and new filter units. Two new waste water pumping stations are also being rehabilitated, including the complete exchange of the M&E equipment.
- Update, review and crosschecking results (and proposed investment measures) of the Feasibility Study.
- Detailed design for implementation of the necessary improvement measures as proposed in the FS for Phase I.
- Preparation of tender documents according to FIDIC and all other necessary documents.
- Procurement assistance to the PEA (Municipality of Batumi) for all necessary supplies, works and services.
- Implementation of a parallel program for reduction of losses and for reducing the tremendously high specific water consumption.
- Construction supervision and monitoring of the implementation of the investments.
- Assessment of the Water Utilities and the PEAs operation and management capacities and formulation of an assistance programme.

Water Supply and Sanitation for the Municipality of Cantemir , Moldova
Water Supply and Sanitation for the Municipality of Cantemir
Country: Moldova, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.10.2010


The beneficiary of the Project is the Municipality of Cantemir (6,000 PE) together with the Municipality owned Water Utility “APA Canal”.
Cantemir WSS, which is based on surface water extraction from the nearby River Pruth, as well as its sewer system and treatment facilities, were designed and constructed for the fruit and vegetable processing factory which used to dominate the city until 1994, when production stopped. The system was constructed between 1963 and 1965, has not been rehabilitated or repaired since, and is therefore in a pitiful state. Since it was designed mainly for industrial needs, many components are highly over dimensioned for its present requirements, resulting in extremely inefficient operation of mechanical and electrical equipment.
In the frame of the project the following project components are being financed:
- Rehabilitation of the raw water intake, raw water pumping station, raw water transmission main and of the main pumping station to the distribution system
- Rehabilitation of the distribution system and supply of material for house connections
- A feasibility study for wastewater disposal including an assessment of the condition of the sewer system
- Supply of operation and maintenance equipment for APA Canal
- Institutional strengthening and support (training) to the Water Utility
- A public awareness campaign for water issue
- Assessment of existing system and Identification of rehabilitation measures.
- Detailed design and preparation of tender documents.
- Procurement and Construction supervision based on FIDIC.
- Preparation of a feasibility study on sanitation system.
- Institutional support to the water utility APA Canal and Public awareness campaign.

Langerica Small Hydropower Plant , Albania
Langerica Small Hydropower Plant
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.08.2007


Pre-feasibility and feasibility study for Langerica SHPP and assistance in obtaining concession permits.
- Pre-feasibility study
- Feasibility study
- Assistance in obtaining concession permits

Qarrishta – Letmi Small Hydropower Plant, Albania
Qarrishta – Letmi Small Hydropower Plant
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2006


Pre-feasibility study on hydro-power potential in the area of Qarrishta – Letmi.
- Pre-feasibility study

Construction Supervision for the Nura River Clean-Up Project Complex, Kazakhstan
Construction Supervision for the Nura River Clean-Up Project Complex
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.05.2013


The project comprises the supervision and coordination of the first 2 works contracts within the World Bank financed Nura river clean-up Project, i.e. the construction and operation of the Apan landfill, the demolition and clean-up of the Karbide factory and adjacent sites and the clean-up of the Nura river and Zhaur swamp.
The former Karbide factory, origin of the mercury contamination in the Nura river valley, is being demolished, with adjacent areas partly cleaned-up or contained. In and alongside the Nura river more than 2 million cubic meter of contaminated material must be removed. River sediment is being excavated by hydraulic dredge and material from river banks and flood plains using excavators. Transfer stations are used to prevent the spread of contamination during transport works.
A hazardous waste landfill is also being constructed near to Temirtau where all contaminated material shall be disposed in two different hazardous waste classes. 24 hours operation is required for all transport works and the landfill to allow implementation of the works within the scheduled 4 year period.
The entire works implementation is based on strict H&S requirements and a strict black – white zone concept featuring special sluices for personnel and equipment is enforced on all construction sites. Parallel environmental monitoring has to be performed by the Contractors under the supervision of the Engineer.
http://www.worldbank.org/en/results/2013/07/15/kazakhstan-eliminating-mercury-and-controlling-floods
Construction supervision according to FIDIC conditions of contract (Red Book) featuring:
- Supervision of all Health & Safety requirements
- Assistance to the Contractor in mobilization, start of works and liaison with related state agencies
- Supervision of the environmental monitoring programme
- Final approval of cleaned areas
- Financial and time control of the works contracts
- Technical assistance to the Contractors
- Design revision

Imst Small Hydropower Plant, Austria
Imst Small Hydropower Plant
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.12.2009


Development and realization of a rehabilitation concept for the SHPP Imst, which consisted of 4 small units along the Pigerbach river, including application for the revised water right permits and limnological impact assessment.
The rehabilitation concept consisted of the rehabilitation of the first upper unit and an improvement of the existing design, with the replacement of the three lower units with one new unit.
In the upper unit the three existing Francis Turbines were improved, as well as the intake structure, the headrace channel and the surge tank. A new steel frame storage and maintenance building was constructed alongside the upper unit, and a new bypass installed so that the upper unit could be shut down. The tailwater channel of the upper unit was also newly built, using precast concrete components.
For the new lower unit, a 2000m long penstock of GRP diameter 1800 (50% of the distance) and diameter 1600 (50% of the distance) was intstalled. This replaced an existing open channel.
- Limnological and ecological impact assessment
- Detailed design
- Production of tender documents
- Construction supervision
General:
The Imst small hydro power plant originally consisted of four small hydro power plants, arranged as one main upper stage and three lower stages. It was operated by an adjacent textile company, the former Textilverarbeitungs- und Vertriebs GmbH.
For the operation of the hydro power plant water was taken from the Pigerbach stream and after the final stage the water was discharged through a tunnel directly into the River Inn.
Following the closure of the textile company, the power plants were bought by the company WEB Windenergie AG, who contracted Posch & Partners to design and supervise the rehabilitation and optimization of the plants. The main upper stage has now been rehabilitated and the three lower stages have been replaced by a single new small hydro power plant.
Upper Stage:
The upper stage was completely rehabilitated, which mainly comprised concrete repair works at the weir, the water intake and the head race channel, the electrical mechanization of all the existing gates and the full automation of the existing rack cleaner.
A new by-pass was also constructed for the upper stage to facilitate maintenance works and additional storage space was created by the construction of a new storehouse besides the existing plant.
Additional works included the installation of an automatic water level turbine control system and renewal of the energy supply and switchgear. The side walls of the stream channel behind the power house were also raised. Following the rehabilitation works the power production was enhanced and the maximum turbine power of the upper stage is 512 kW.
The automatic turbine control system for the upper stage was supplied by Andritz AG and the automatic turbine control system for the lower stage was supplied by Siemens AG. A challenge for our electrical engineers was the installing of a network between the upper- and lower stage so that automatic control was possible.
The existing water intake of the upper stage, which was built in 1912, also acts as the water intake for the lower stage. This was redesigned to ensure a (dynamic) residual flow is maintained in the stream below the water intake and a fish ladder was installed.
A base amount of 160 l/s flows through the new installed fish ladder. The discharge of the remaining base amount, which is 340 l/s during the months of May to July, flows over a newly installed roller gate. The required dynamic residual flow (15% of the water allocation) is achieved through a hydraulically controlled flushing gate at the weir. The determination of the river water flow is derived from a newly constructed residual water discharge measurement station below the surge tank and an IDM-measurement in the penstock below the surge tank. The hydraulically controlled flushing gate is operated via the PLC system installed in the power house.
The retention water level elevation is at 736.2 m.a.s.l. The consensus water amount of 5 m³/s for the existing upper stage is unchanged. The unlimited water right already conferred was not affected and remains as per the original approved form.
At the power house of the upper stage a by-pass was constructed so that in case of maintenance works on the turbines the water flows through the by-pass to the lower stage. In the power house there are three Francis turbines installed (Andritz AG, 1951). These were completely refurbished, including replacement of the guide vanes, sandblasting and repainting of the entire housing and restoration of the vane regulation.
The tailrace channel of the upper stage has a length of about 176 m, which was originally constructed as a natural, open channel. This tailrace channel was rebuilt with prefabricated concrete elements and a building at the reversal gate on the spillway was also newly constructed. This arrangement provides increased protection from floods and also permits the entire water flow to be discharged into the Pigerbach for maintenance work on the lower stage.
Lower Stage:
For the lower stage the consensus water of 2.5 m³/s (consensus of the former small hydro power plants 2, 3 and 4) was increased to 5.0 m³/s.
The water from the upper stage flows over a height of about 13 m through an 850 m long headrace to the newly constructed lower stage. (About 1595 m total length, including the upper stage) Below the lower stage water is discharged through the existing tunnel directly into the Inn.
The headrace of the lower stage consists of an existing inverted siphon under the Pigerbach, a 72 m long existing tunnel under the so-called Brennbichl and an approximately 780 m long newly constructed penstock made of fiberglass.
Before the new inverted siphon two closing gates were installed that permit the discharge of the entire water flow via the reversal gate into the Pigerbach so as to allow maintenance work on the lower unit.
The penstock is DN1800 between the end of the tunnel and the hotel Neuner and it follows over a length of 368 m the existing headrace channel (former lower stages 2 and 3). Under the hotel Neuner the penstock was installed as an inliner in an existing steel pipe DN 2200.
The penstock route between the hotel Neuner and the new powerhouse follows for a length of 366 m the existing headrace (former lower stage 4). This penstock section was constructed with GRP pipes, DN 1600. Due to the new design level of the penstock the base of the existing channel had to be removed at certain sections.
Since the existing inverted siphon is an insurmountable obstacle (smooth surface, drop height) fish could not pass this section. For this reason the existing disused by-pass channel was adapted to create a fish pass for this section.
The new power house was built at the same location as the former powerhouse of stage 4, within the municipality of the town of Imst. The exterior dimensions of the powerhouse are 13 x 10 m with a maximum height of 7 m. The shape of the roof of the powerhouse is designed in a waveform, symbolizing the energy of the water. The machine sets are 9 meters below ground level, which was necessary so as to make a connection to the existing underground discharge tunnel that leads to the River Inn. Under the current Danger Zone Plan for the Pigerbach stream the power house is located entirely within the yellow danger zone. The Pigerbach can dissipate in this section a water amount of 50 - 60 m³. In a one hundred-year flood event, which would correspond according to the hazard mapping of 120 m³/s, widespread flooding would be expected in this area. For this reason the ground level was raised around the power house and the entire engine house was also designed so that no hazard is created by groundwater or flood events.
During the construction period the dewatering of the excavation for the lower stage was very difficult due to the high groundwater level resulting from the proximity of the Pigerbach and the River Inn. Evidence for the fact that the entire project is in an area vulnerable to flooding is also substantiated by flood events in the years 2001 and 2005.
The powerhouse contains not only the turbine room, but also space for the switchgear and transformer, a workshop / storage room, a rest room for staff, a kitchen, a wash area and space for maintenance works in the turbine room. There is also a small museum which is used to exhibit the old power plant equipment of the former three lower stages.
The electromechanical equipment of the newly constructed lower stage consists of a Kaplan bulb turbine at 712.40 m.a.s.l. (turbine shaft) and a three-phase synchronous generator (rated output ~ 700 kVA). The turbine was developed by Kössler, the generator was supplied from the company Hitzinger and the control system comes from the Siemens AG.
Discharge water flows through the existing tunnel from the former lower stage 3 (Length 348 m, constructed in 1918) directly into the Inn. The tunnel ends at a level of 709.5 m.a.s.l.
In front of the tunnel a new stilling basin was built with a ventilation shaft. This ventilation shaft also allows access to the tunnel from above.
Technical Characteristics of the lower stage:
- Catchment area: 188.4 km²
- Design flow: 5000 l / s
- Specific water expansion: 22.8 l / s.km²
- Gross head: 13,32 m
- Net head at QD: 11.36 m
- Max. turbine power : 501 kW
- Max. generator power: 474 kW
- Annual energy production: 3.5 GWh

Peri-urban Water and Sanitation Project, Malawi
Peri-urban Water and Sanitation Project
Country: Malawi, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.04.2007


Review of the feasibility studies and designs for the rehabilitation of the water supply systems of Blantyre (820,000 people) and Lilongwe (670,000 people) including the proposed extension of the service area to low-income areas.
Field inspection and assessment of the technical condition of the water production, transmission and distribution facilities. Preparation of an investment plan and an application for the ACP-EU Water Facility.
Works were to be implemented through a private sector service contract. Preparation of Terms of Reference for the transaction advisor.
Preparation of an outline of the private sector service contract for operation of water kiosks and private operation and maintenance of small distribution districts in low-income areas.
Preparation of a concept for the support of basic sanitation in low-income areas, including using a participatory approach and education in health and hygiene.
- Assessment of rehabilitation requirements
- Preparation of a priority investment program
- Development of a concept for water and sanitation services for low-income areas

Supervision of the Development Infrastructure Work in Sibenik-Knin and Zadar Counties - II, Croatia
Supervision of the Development Infrastructure Work in Sibenik-Knin and Zadar Counties - II
Country: Croatia, Balkans
Project end: 01.10.2007


The project comprises full supervisory services of 5 smaller municipal infrastructure projects with a total investment volume of EUR 3.4 million. The task was performing the functions and duties of the “Supervisor” according to FIDIC conditions of contract and EU procedures. The services included administration and supervision of the various works contract, set-up of the necessary organisation to ensure efficient administration and satisfactory completion of the works, to ensure timely implementation and efficient use of financial resources.
Short summary of the 5 sub-projects:
Kistanje water supply: replacement of a damaged transmission main from Kistanje to Macure Pumping Station incl. construction of a 1,800m long DN300 and a 3,400m DN250 main.
Skabrnja – Zemunik Water Supply: construction of appox. 1,300m DN400 and 11,700m DN80-400 water distribution network.
Marici channel: reconstruction of the Marici drainage channel of approx. 1,645m
Podi Business Zone: construction of roads and all services for the first 20 ha of a business zone in Podi, including approx. 1.4 km of roads, 2.5 km water distribution system, 2.2 km wastewater sewer and a package treatment plant, 3 km of rainwater drainage system with oil separator, 2.7 km electricity cable network incl. 4 transformers and street lighting system with 76 lighting poles.
Mandalina Office complex – refurbishment of the former “Remont” complex to provide office facilities.
- Heading a team of engineers for construction works supervision according to FIDIC and EU procedures.

Promoting the Use of Renewable Energy Resources for Local Energy Supply, Georgia
Promoting the Use of Renewable Energy Resources for Local Energy Supply
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.12.2009


Assessment of the existing institutional and legal framework and formulation of proposals for a national renewable energy strategy.
Project evaluation of existing small hydropower projects and geothermal water supply for the capital city, Tbilisi.
Selection of 6 small hydropower plants for detailed design and implementation.
Training of local personnel and institutional capacity building.
- Project identification
- Advise on legal aspects
- Development of national renewable energy strategy
- Feasibility studies
- Detail design
- Project implementation
- Monitoring

Concept Development for Reforms of the Adjara Water Sector, Georgia
Concept Development for Reforms of the Adjara Water Sector
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.08.2006


The Autonomous Republic of Adjara is located in the southwest of Georgia and has been politically and economically isolated since the early nineties. This has led to a sever deterioration of water and wastewater infrastructure and to weak local institutions.
The project objective was to assist the Government of Adjara in the development of a coherent and comprehensive long-term concept for reforms of the water sector. As part of this, the developments and major deficits of the water sector were identified and the involved stakeholders were supported in defining necessary and reasonable reform steps.
- Collection and evaluation of relevant data about the water sector in Adjara
- Identify sectoral priorities and determine reform steps
- Elaborate a comprehensive Sector Advisory Concept and Terms of Reference for further steps

Municipal Infrastructure Project , Croatia
Municipal Infrastructure Project
Country: Croatia, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2006


The project aimed at identifying and formulating bankable projects in the sectors of water supply, sewerage, wastewater treatment and flood protection. Projects had to be technically, financially and economically feasibly and must be socially affordable to the final beneficiaries. The majority were also designed in a way that they are also eligible for co-financing by EU funds, like ISPA, IPA and others.
The project includes the development of a tariff model which features the calculation of fully cost covering tariffs, socially affordable tariffs for household customers, the calculation of the financing gap in compliance with the EU CBA-guidelines and financial and economic analyses.
- Define project selection and priority ranking criteria
- Review project proposals and provide comments
- Prepare genuine flexible tariff model
- Review financial and economic analysis of projects
- Project appraisal

Waste Water Treatment for Hospital Jasenovo and Water Supply Čaška (Izvor III), The former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia
Waste Water Treatment for Hospital Jasenovo and Water Supply Čaška (Izvor III)
Country: The former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia, Balkans
Project end: 01.10.2006


Firstly, the project aims at the controlled treatment of the wastewater emerging from the Jasenovo hospital. In a previous study it was decided that for that purpose a constructed wetland shall be installed. The wetland is of a subsurface-vertical-flow type with intermittent loading including mechanical pre-treatment. Services included assessment, detailed design, tendering and construction supervision
Secondly, a feasibility study concerning the water supply of the municipality of Čaška was part of the project. A detailed assessment of the existing situation was undertaken. The findings were used to define the optimum solution taking water quality, security of supply and economical aspects into account.
- Basic and detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents and evaluation of bids
- Construction supervision for the constructed wetland
- Preparation of feasibility study for Čaška water supply

Support to Ministry of Agriculture in Creation and Development of Water User Cooperatives in Kazakhstan , Kazakhstan
Support to Ministry of Agriculture in Creation and Development of Water User Cooperatives in Kazakhstan
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.12.2007
The irrigated land in Kazakhstan has reduced in area by about a half compared to the times of the Former Soviet Union period. A law on rural consumer cooperatives of water users was adopted in April 2003 and a new water law was approved in July 2004, permitting the foundation of water user groups. The project aimed at supporting the country to put these laws into practice in the existing water user cooperatives by introducing water use fees and puttling in place international best practice for their organisation and management.
- Provision of financial analyses and technical assistance in institutional aspects
- Technical assessment of the hydraulic structures, their further use and rehabilitation needs
- Development of sector policies and strategies
- Training of key administration staff and key stakeholders

Design of Yntymak Reservoir Rehabilitation and Technical Reequipment, Kazakhstan
Design of Yntymak Reservoir Rehabilitation and Technical Reequipment
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.12.2006


The aim of the project is the completion of the partly constructed Yntymak (Intumak) reservoir at the Nura river in Central Kazakhstan. Construction of the dam was started in the 1980s but spillway and ancillary village protection dams were never completed. The reservoir acted as pollution trap as mercury contaminated sediments settled in the reservoir. A dam safety study revealed unsatisfactory condition of the main dam.
The dam must be rehabilitated, the missing reservoir structures as the spillway and the village protection dams must be constructed in order to gain from an operational water reservoir for the future water supply to Astana and for the Korgalzhyn nature reserve.
- Basic design
- Detailed design
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- Preparation of tender documents
- Tender assistance of the main dam rehabilitation, the ancillary village protection dams, the bottom outlet, hydro power unit and the spillway structure

Municipal Services Project, Romania
Municipal Services Project
Country: Romania, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.02.2006
The aim of the project is the review of feasibility studies of water supply, waste water and solid waste projects in Turkey from an economic, technical, and environmental standpoint.
The Consultant had to ensure
- that the most economic option has been selected for investments, taking into account demand projections and affordability of tariffs.
- that the technical solution proposed is feasible.
- that the environmental benefits, as estimated in the feasibility study, are realistic.
- the validity of the financial analyses made in these reports.
A further task was the preparation of a list of the investments on a priority basis, which was established according to international standards and on base of close cooperation with the World Bank and the Iller Bank.
For the water supply, sewerage and storm water drainage projects:
- Economic Assessment
- Verification of Technical Solutions
- Environmental Benefit Assessments
- Validation of Financial Analyses
- Identification of priority measures
- Presentation to the Bank

Lipjan Wastewater Treatment Plant, Kosovo
Lipjan Wastewater Treatment Plant
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2005


The EAR in its programme 'Development of Wastewater Treatment Programme in Kosovo' had selected Lipjan for the possible construction of a wastewater treatment plant (9.000 PE). The aim of the project was to prepare an outline design, drawings and estimated quantities of works, in order to enable the EAR to invite bids for construction of the works. The foreseen investment for this project phase was limited to the construction of a mechanical treatment train and to primary sludge treatment facilities.
- Preparation of pre-design drawings
- Preparation of tender documents
Further Institutional Support to Water Utility Companies, Kosovo
Further Institutional Support to Water Utility Companies
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.06.2007
Water supply and wastewater services in the country are currently managed by over 30 water utilities. The utilities are strongly engineering oriented. The national water sector concept foresees the consolidation of them to about 4 utilities which shall become be financially viable. There is need to develop sound customer oriented policies and programs which respond to the needs of customers, particularly women who are the main water user and deal primarily with the utilities.
The project aims as finalising the consolidation process, strengthen the utilities capacity in billing and collection activities, decrease of non-revenue water, establish contacts with utilities in the EU, establish cooperation with the water & wastewater regulatory office and improve customer services by considering the gender aspect.
- Provide technical assistance in improving the operation efficiency of the utilities
- Assist the utilities in the consolidation process
- Support utilities in reducing non-revenue water
- Improve revenue collection efficiency

Feasibility Study for the Project: Rehabilitation of Communal Infrastructure Facilities in Batumi, Georgia
Feasibility Study for the Project: Rehabilitation of Communal Infrastructure Facilities in Batumi
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.02.2006


Batumi, the fourth largest city in Georgia, is the capital of the autonomous Republic of Adjara. The water supply situation was unsatisfactory with per capita production rates of 900l/c,d, necessary to cover the demand including losses. The existing sewer system was also in poor condition and a source of serious contamination during regular flooding events.
The aim of the feasibility study was to ensure that the envisaged investments were directed towards the most urgent issues and used most efficiently. The study included first an assessment phase regarding water supply services, wastewater disposal, economic and institutional performance of the water utility, and economic capacity, as well as the needs on the side of consumers. To assess the socio-economic base parameters of the consumers, a household survey was conducted. The water supply system was assessed by hydraulic modelling, with leak detection and flow and pressure measurement campaigns carried out. The sewer system was assessed by manhole inspection and CCTV.
- Household survey to assess socio economic characteristics of the city
- Institutional and economic analysis of the water utility
- Assessment of water and wastewater facilities
- Preparation of a water balance based on leak detection and flow measurement campaigns
- Inventory and mapping in GIS water supply system and sewer facilities
- Hydraulic modelling of water distribution system and development of improvement options
- Assessment of physical condition of the sewer system by manhole inspection and CCTV
- Hydraulic simulation of the existing sewer system and development of rehabilitation options
- Option study for wastewater treatment based on wastewater sampling and analysing campaign
- Formulation of short term, medium term and long term rehabilitation measures based on general designs
Development of Guidelines for Yntumak Reservoir Operation, Kazakhstan
Development of Guidelines for Yntumak Reservoir Operation
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.10.2005
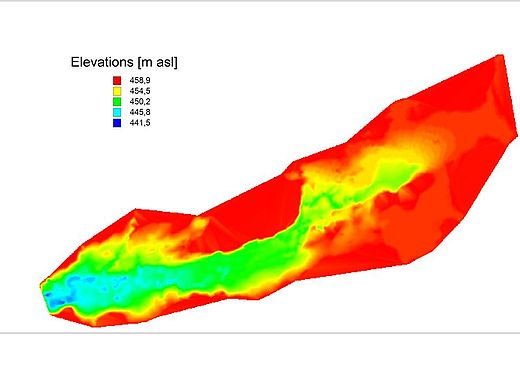
The aim of the project was the development of operational guidelines for the Yntumak reservoir. The reservoir is located on the Nura river in Central Kazakhstan downstream of the Temirtau - Karaganda industrial area. Since its construction the reservoir had acted as a sediment trap for pollution being transported by the Nura River. Mercury contamination in particular had accumulated in the reservoir and the reservoir prevented most of the polluted sediments from drifting further downstream, so limiting the extent of the contamination.
Focus was therefore drawn on the existing mercury contamination in the reservoir, i.e in the bottom sediments in relation to sediment management. As the dam structure was not yet finished, recommendations on the future design of the dam, outlet and spillway structure were also made, so as to guarantee minimal impact on the stakeholders and the environment.
- Study of parallel monitoring and mathematical model project
- Assessment of hydrologic conditions
- Assessment of meteorological situation
- Evaluation of risk due to mercury contaminated sediment
- Establishment of sediment management options
- Development of reservoir operational guidelines

Supervision of the Development Infrastructure Work in Sibenik-Knin and Zadar Counties - I, Croatia
Supervision of the Development Infrastructure Work in Sibenik-Knin and Zadar Counties - I
Country: Croatia, Balkans
Project end: 01.01.2007


The project comprises full supervisory services of 5 smaller municipal infrastructure projects with a total investment volume of EUR 2.3 million. The task was performing the functions and duties of the “Supervisor” according to FIDIC conditions of contract and EU procedures. The services included administration and supervision of the various works contract, set-up of the necessary organisation to ensure efficient administration and satisfactory completion of the works, to ensure timely implementation and efficient use of financial resources.
Short summary of the 5 sub-projects:
Lisičić Water Supply: High density polyethylene (HDPE) water transmission main approximately 1.3km of 355mm dia, 2.1km of 315mm dia. in a existing partially excavated trench, completion of a booster pumping station including all mechanical and electrical equipment.
Podgradina Water Supply: 150mm dia. HDPE transmission main approximately 3.3km long and a 250 cu.m. reinforced concrete reservoir and access road approximately 230m long.
Skradin Wastewater system: construction of a wastewater pumping station (output 15-17l/sec), 180mm dia. HDPE pumping main approximately 0.46km long and wastewater treatment plant (based on the activated sludge process) and 200mm dia. HDPE effluent pipe approximately 1.0km long, to serve a population equivalent of 2,600.
Piramatovci Water Supply: Water distribution system approximately 4.4 km of pipelines (1” – 250mm dia.)
Promina Water Supply: 125mm dia. HDPE distribution main approximately 10km long to serve the villages of Matase, Zelići and Marasovine.
- Heading a team of engineers for construction works supervision according to FIDIC and EU procedures

Institutional Strengthening of the Committee of Water Resources, Kazakhstan
Institutional Strengthening of the Committee of Water Resources
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.11.2005
New legal documents required the Committee for Water Resources of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan to take up an increasing number of tasks. Investment budgets handled by the Committee had increased by more than four times since 2002. The very limited human resource capacity and the current status of the Committee created strong barriers to the efficient management and implementation of those tasks.
In consideration of this, ADB had extended a TA program, for increasing the organizational capacity of the CWR. The main objective of this TA was to strengthen the organizational potential of the CWR, taking into account the increased volume of works during recent years, connected with the implementation of the budget programs and the execution of the many new normative documents with respect to water sector management
- Preparation of the detailed review of the functions, tasks and programs performed by the Committee for Water Resources;
- Preparation of the oral and written recommendations for the local consultants concerning the development of the new structure of the Committee for Water Resources;
- Provision of information on the international experience on organization of the institutional structures of different institutions providing the management of the water resources and water bodies;
- Bring in international experience and lessons learned in different countries with similar conditions to Kazakhstan;
- Develop scenarios and a recommendation for the improvement of the status of the Committee;
- Develop scenarios and a recommendation for the improvement of the internal organisation and capacity raising of the Committee

Rural Area Water Supply and Sanitation Sector Project, Kazakhstan
Rural Area Water Supply and Sanitation Sector Project
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.08.2010


The main objective of the Project was to improve the living and health conditions in selected rural communities, in particular for the poor, through the provision of basic water supply and sanitation services. The Project aimed to achieve its objectives by assisting the central and local governments in delivering WSS infrastructure services and improving the technical and financial capacity of local governments and water consumer groups in the planning, implementation, and O&M of facilities. The project area covered the three oblasts of Akmola, North-Kazakhstan, and South-Kazakhstan and included about 500 villages, with populations ranging from 200 to 6,000 persons. Overall, about 530,000 people, of whom approximately 40% were living below the poverty line, benefited directly from the Project through the provision of potable quality piped water supply facilities, improved wastewater drainage facilities, school and private latrines, and public bath houses.
Physical infrastructure development:
- Development
- Expansion
- Rehabilitation and upgrading of piped water supply systems, wastewater drainage facilities, school and private latrines ans banyas (public baths)
Institutional development:
- Preparation of training programs
- Training of central and local governments staff and other stakeholders to strengthen their capacity to efficiently plan, implement, operate, and maintain the WSS systems

Municipal Services, Turkey
Municipal Services
Country: Turkey, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.09.2005
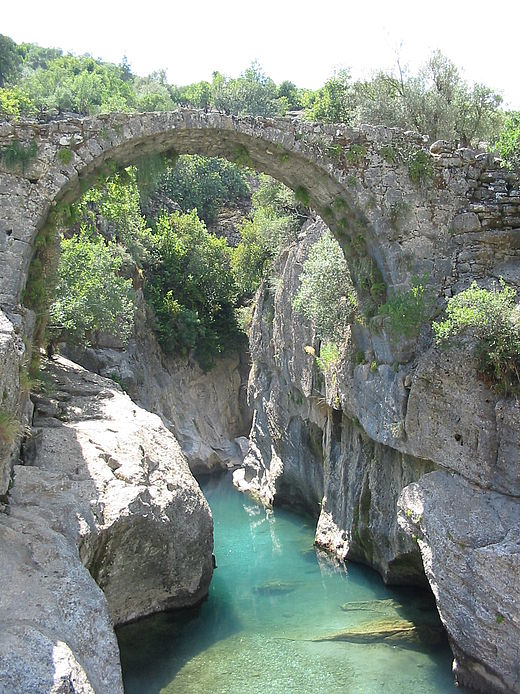


The aim of the project was the review of feasibility studies of water supply, waste water and solid waste projects in Turkey from an economic, technical, and environmental standpoint.
The Consultant had to ensure that the most economic option had been selected for investments, taking into account demand projections and affordability of tariffs. Also, ensured that the technical solution proposed was feasible, that the environmental benefits, as estimated in the feasibility study, were realistic and checked the validity of the financial analyses made in the reports.
A further task was the preparation of a list of the investments on a priority basis, which was established according to international standards and with close cooperation with the World Bank and the Iller Bank.
- Economic Assessment
- Verification of Technical Solutions
- Environmental Impact Assessments
- Validation of Financial Analyses
- Identification of priority measures
- Presentation to the Bank

Kasalinsk Management Contract, Kazakhstan
Kasalinsk Management Contract
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.01.2007


In the overall context of the Aral sea region development program, the KfW decided to support the Cities of Kasalinsk and Novokasalinsk regarding their water supply systems. In 2004 Gelsenwasser AG, together with its partners, won the respective tender.
The project comprised the rehabilitation and reconstruction of the water supply system as well as technical operational and economical support for the local operator Vodokanal. In the first phase the water treatment plant and significant parts of the distribution network were rehabilitated, and additional areas were connected to the existing system. Based on this upgrading of the water supply system, Gelsenwasser AG supported Vodokanal to operate the system in terms of a modern and efficient utility.
The main focus of the assistance measures were training and education of the local personnel, introduction of metering and billing, introduction of international accounting procedures, establishment of costumer relation services and the development of a sustainable maintenance and repair program.
- Reorganisation of utility and institutional strengthening
- Training and education
- Metering and billing
- Accounting standards
- Customer relation services
- Maintenance and repair program

Training Measure for the Staff of Kakanj Water Works, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Training Measure for the Staff of Kakanj Water Works
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.08.2006

KfW had supported the Municipality of Kakanj in the rehabilitation of the entire water supply system. The project included the rehabilitation of the water treatment plant, construction of new storage capacity, reduction of water losses, construction of new distribution lines and installation of water meters.
In order to ensure the sustainability of these capital investments, KfW granted to ViK Kakanj a technical assistance project.
The project should strengthen the capacity of ViK staff, to provide training in the operation and maintenance of the new equipment, to strengthen the entire communal billing and revenue collection cycle, to raise public awareness and the image of ViK and finally to achieve cost coverage.
- Selection, procurement, installation and training on a new fully integrated accounting and communal services billing and collection system;
- Procurement of hard and software including training of staff;
- Preparation of operation and maintenance manuals for the water supply system;
- Special training of staff on the new treatment plant;
- Internal reorganisation of the utility, preparation of job descriptions and assignment of tasks;
- Carrying out survey on performance and image of utility; developing and implement public awareness raising campaigns;
- Development and introduction of a basic management information system;
- Development of business plans;
- Revision / up-dating of the tariff model

Guideline Design of Skenderaj Wastewater Treatment Plant, Kosovo
Guideline Design of Skenderaj Wastewater Treatment Plant
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2004

The aim of the project was to provide the outline design, drawings, technical specifications and estimated quantities of work to enable the EAR to let a contract for the construction of the works. Based on previous study reports the treatment process applied Imhoff tanks and biological treatment by trickling filters. Sludge treatment was undertaken by a static sludge thickener and sludge drying beds.
- Process engineering for treatment plant
- Guideline design of plant components
- Preparation of technical specifications and Bill of Quantities

Small Towns Infrastructure and Capacity Building, Kyrgyzstan
Small Towns Infrastructure and Capacity Building
Country: Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.04.2005


The project included the assessment of the existing infrastructure for urban water and sanitation system of 7 selected towns with a total population of about 320,000. To upgrade existing systems the most economic and efficient measures within an emergency investment program for the subsequent period of about 4 years were specified.
- Assessment of existing water supply infrastructure
- Assessment of existing waste water infrastructure
- Identification of priority measures
- Preparation of TOR for services, works and supplies

Elaboration of (Technical) Base Data for “The Regional Water Supply and Waste Water Program South-West Kosovo”, Kosovo
Elaboration of (Technical) Base Data for “The Regional Water Supply and Waste Water Program South-West Kosovo”
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.06.2004


The water utility “Hidrosistemi Radoniqi” supplies a population of 160,000 capita in the Western region of Kosovo. The utility was managed under a management contract financed by the World Bank, which expired in January 2005. KfW, as the main donor in the water sector in the South West of the Country intended to take over the management contract and contracted Posch & Partners to collect data and assess the situation on site, on the basis of which the new project would be designed.
- Evaluation of existing situation
- Institutional building of water supply

Nura River Clean-up Project, Kazakhstan
Nura River Clean-up Project
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.05.2006


The remediation design of the mercury contaminated river Nura, including flood plains, river banks and the former sludge disposal site Zhaur Swamp. An estimated 2 Mio m³ of contaminated soil have to be excavated and transported to a safe landfill site.
- Verification of data provided by previous studies
- Determination of the clean-up level
- General design of the clean-up methodology
- Detailed design of the clean-up works
- Preparation of Tender Documents
- Assistance in tender evaluation

Institutional Support to Sanski Most Water Utility, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Institutional Support to Sanski Most Water Utility
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans


The town of Sanski Most had received financial support from the European Union for the construction of a completely new water treatment plant and water storage facilities. The institutional support program was formulated to ensure the sustainability of this investment. The program comprised the improvement of the internal utility organisation; the introduction of computer based billing and revenue collection system; measures to improve the revenue collection ratio; an image and public awareness building campaign; a program for reduction of non-revenue water; and the preparation of a tariff model, with assistance in tariff setting and in the political acceptance of new tariffs.
- Technical assistance to water utility, especially regarding the improvement in efficiency of operations
- Improved revenue collection
- Preparation of a tariff model, public image advice and awareness raising

Water and Wastewater Sectors Financing Study, Bulgaria
Water and Wastewater Sectors Financing Study
Country: Bulgaria, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2004

The aim of the project was the validation of the Government’s financing plans for the water and wastewater sectors, taking into account the experience of other EU members and accession countries with regards to the need of public sector financing, use of EU grants, and flow of private capital.
A detailed review of existing water legislation and policy was performed, including a comparison with other European countries. The current status with regard to achieving the requirements for joining the EU and the various financing mechanisms were assessed.
- Review of current Bulgarian legislation related to water supply and waste water treatment, as well as the relevant commitments undertaken by Bulgaria during the EU accession negotiations
- Analysis of Government plans to restructure the water sector and change the ownership of the water and waste water assets
- Review the progress and the current plans for the establishment of the Water Sector Regulator
- Analyze the legally available options and experience in attracting the private sector in water supply and waste water treatment
- Review of all existing literature regarding the costs to upgrade the Bulgarian water and the wastewater sectors to meet EU standards
- Description of the institutional responsibilities in the country and the measures taken to promote the introduction of the private sector for operations
- Organising workshops with international participation

Burrel Water Supply Rehabilitation Project, Albania
Burrel Water Supply Rehabilitation Project
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 01.02.2004


Feasibility study to ensure reliable water supply to the city of Burrel and the connected villages.
- Process selection
- Preliminary design
- Cost estimates for surface water treatment

Development of Options for Sewage Treatment Works, Kosovo
Development of Options for Sewage Treatment Works
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2003


Identification of alternative options for sewage treatment works, including centralised versus de-centralised solutions, and appropriate treatment technologies for all major towns in the country. Description of alternatives and ranking of measures which could be accomplished within the given budget ceiling. Definition of additional funding required to achieve higher levels of treatment.
- Site assessment
- Data collection
- Process layout
- Cost estimation

National Environmental Action Plan, Tajikistan
National Environmental Action Plan
Country: Tajikistan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.09.2004

Technical assistance for the preparation of a NEAP. Identification of priority environmental problems through regional and national workshops, followed by priority ranking and formulation of an action plan. Review of existing drafts, provision of assistance and guidance on project methodology and formulation of priority sustainable projects.
- Organisation of workshops
- Priority ranking
- Formulation of an action plan
- Formulation of priority projects

Promotion of Renewable Energy in Armenia, Armenia
Promotion of Renewable Energy in Armenia
Country: Armenia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.12.2003


Inventory and assessment of all SHP plants in Armenia. Selection of 6 existing SHP plants and pre-feasibility studies for their rehabilitation. Design of setting-up of a revolving investment fund to finance renewable energy projects in Armenia. Guidelines for implementation of support by private industry.
- Countrywide identification of existing small hydropower plants
- Selection of 6 projects for implementation
- Conducting feasibility studies
- Programming for implementation
- Outline for the set-up of a revolving fund to finance small hydropower development with the private sector

Rehabilitation of Kakanj Water Supply, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Rehabilitation of Kakanj Water Supply
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.06.2004


The Kakanj Utility was not any more in a position to provide a 24-hour supply. The system was affected from frequent break-downs, instable supply and poor water quality.
A rehabilitation program was agreed with KfW, comprising the complete rehabilitation of the system. This includes first an inventory and assessment of the complete system, the identification of deficiencies and shortcomings and as a result of this, the formulation of the rehabilitation measures. The original concept foresaw the rehabilitation and expansion of a groundwater source. An extensive well test was carried out, showing that this source was insufficient in capacity and could not sustain the required water quality at large quantities. Consequently, the rehabilitation of an old and deteriorated surface water source became necessary.
The rehabilitation works finally included the construction of a new surface water intake, sand trap, complete conventional water treatment plant for a capacity of 130 l/s, including chemical operation building, the rehabilitation of a groundwater source, rehabilitation of 180km transmission and distribution lines, replacing house connections, metering of all connections, a new SCADA system, optimisation of the treatment plant process and training of staff. The project further includes institutional support to the water utility, preparation of a tariff model and presentation of the results in front of the Municipal Council.
- All services with respect to water production facilities
- Transmission and water storage
- Tariff model
- Presentation to the decision makers

Research Project on Phosphorus Recovery from Wastewater, Austria, Germany
Research Project on Phosphorus Recovery from Wastewater
Country: Austria, Germany, Western Europe
Project end: 01.08.2004

Joint research project with the German Research Centre 'Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe' for the recovery of Phosphates from wastewaters, based on crystallisation on calcites or tobermorits. The objective was to develop an economic and practicable process technology.
- Lead of research program
- Definition of process optimization targets
- Design of experimental treatment plant
- Economic evaluation

Construction of Sanski Most Water Treatment Plant, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Construction of Sanski Most Water Treatment Plant
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.2004


The municipal water supply system of Sanski Most was based on a large carstic spring source. Water turbidity was generally moderate, but increased to high values subsequent to precipitation events. A 150 l/s water treatment plant was constructed comprising full conventional treatment, including sludge treatment, to ensure guaranteed production of WHO quality drinking water. The project was financed by the EU OBNOVA program. P&P provided project management and construction supervision.
- Construction Supervision
- Project Management

Feasibility Study for Phosphate Recovery in the WWTP Ingolstadt, Germany
Feasibility Study for Phosphate Recovery in the WWTP Ingolstadt
Country: Germany, Western Europe
Project end: 01.12.2003

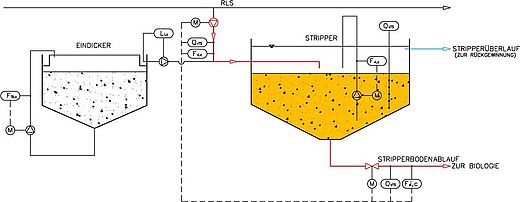
Elaboration of a concept and general layout for recovery of phosphate by means of a combination of the biological side stream process “Phostrip” with crystallisation of the dissolved phosphates on Tobermorit minerals. For the concept and the general design, cost estimates for investments and operation costs were prepared and a cost benefit analysis was carried out. The concept is an innovative approach developed by P&P.
- Process layout
- General design
- Cost estimates
- Economic analysis

Izvor Water Supply and Sewage Project, The former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia
Izvor Water Supply and Sewage Project
Country: The former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia, Balkans
Project end: 01.06.2005


The project aims were the improvement of the existing water supply and sewerage systems of the hospital and the village Izvor. A detailed assessment revealed that spring tapping, transmission lines and reservoir needed to be replaced, new disinfection facilities had to be installed and sections of the distribution and sewerage system had to be rehabilitated. Services included assessment, detailed design, tendering, construction supervision and tariff calculation, with a model for cost splitting for the different consumers.
- General design
- Detailed design
- Procurement
- Preparation of tender documents
- Construction supervision and start up

Mazeikiai Wastewater Treatment and Water Supply, Lithuania
Mazeikiai Wastewater Treatment and Water Supply
Country: Lithuania, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.06.2002
The specific objective of the project is to improve the standard of the water sector in the town of Mazeikiai, Lithuania’s eighth largest city, and bring it to EU levels. The major investment shall be the new construction of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) to treat the city’s wastewater. Since the financial ceiling for this ISPA project is preliminarily limited with approx. EUR 5.8 million, additional measures in the sewage collection system and/or in the water distribution network will receive limited ISPA support. Hence, in order to optimise resources and impacts a 20-year “Water Sector Masterplan” will be an integral part of the “Feasibility Study”. It will be divided into short (0-4 years), medium (5-9 years) and long-term (10-20 years) investment plans. The project proposed for ISPA support shall belong to the short-term investment programme.
- Preparation of feasibility study
- Preparation of EIA
- Preparation of ISPA application
- Preparation of TORs for further stages of the project

Study on Private Sector Participation in Municipal Water Services in CEE and Central Asian Countries, 20 African countries
Study on Private Sector Participation in Municipal Water Services in CEE and Central Asian Countries
Country: 20 African countries, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.06.2002
Assessment of perceptions, market interest and barriers of the private sector, International Financing Institutions (IFIs) and donors to enhance their engagement in municipal water services in Central & Eastern Europe and Central Asian Countries. A survey was carried out among the key donors, private operators and IFIs on the market, based on questionnaires and personal interviews. The results were analysed and presented at the PSP conference organised by the World Bank in Paris in 2002. A conference write-up was prepared and published, in which the results of the study and of the conference were summarised.
- PSP sector survey in the ECA region
- Analysis of results
- Presentation at the PSP conference
- Preparation and publication of the conference write-up

Priority Issues in the Major River Basins, Kazakhstan
Priority Issues in the Major River Basins
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.04.2004


River basin study for the major river basins of Kazkahstan. Project work was carried out in close cooperation with local experts. After determination of the key data of the river basins, regional workshops were conducted in each river basin, with extensive stakeholder participation, to identify the priority problems. These problems were then ranked according to criteria and then converted into priority projects using standard project data sheets. More than 70 priority projects were identified and then presented at senior Government level to create awareness. Short video films were also prepared and disseminated for information sharing.
- River basin study
- Identification of priority issues and their assessment
- Conducting a series of workshops with extensive stakeholder participation
- Reformulation of problems into priority projects
- Presentations at senior Government level

Technical Assistance for Water Utility Management Tesanj, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Technical Assistance for Water Utility Management Tesanj
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.02.2004


The objective of the project was to enhance the commercial and organisational performance of the utlity, so as to make it sustainable and creditworthy for future water supply and sewerage improvements and expansions. Technical assistance was provided for the management and operation of the water utility Tesanj, including inputs in the areas of personnel management, operations procedures, institutional capacity enhancement, transparent tariff setting, public awareness building and advisory services towards PSP.
- Utility operation
- Preparation of a tariff model, conducting tariff workshops with Municipal Council Utility
- Organisation structure improvement
- Organisation of study tour
- Public relation works
- Reduction of Non-Revenue-Water
- Training and advise on the possibilities and pros- and cons of Private Sector Participation models

Atyrau Leakage Analysis and Water Demand Study, Kazakhstan
Atyrau Leakage Analysis and Water Demand Study
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.04.2002


Atyrau is the administrative centre of oil exploration in Kazakhstan and is of high importance. The water supply system of the town was in poor condition and affected by the high salinity of the soil and lack of maintenance and replacement investments. Atyrau was included in the North-East Water Supply Project, which was planned to be implemented in form of a management contract. The study formed the basis for the operator to start work on site and to have a clear view of the priority investments to be made.
- Assessment of facilities
- Flow and pressure measurements
- Leak detection
- Calculation of water demand
- Assessment of utility performance
- Formulation of immediate, medium and long term investment programmes on the basis of cost benefit criteria

Extension of the Waste Water Treatment Plant Braunau , Austria
Extension of the Waste Water Treatment Plant Braunau
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.12.2003


The existing plant, designed for a capacity of 30,000 PE, was extended to a capacity of 60,000 PE, with full enhanced biological nutrient removal. In order to allow the use of existing tank volume the LINDPORR C process combined with the biological side stream process PHOSTRIP were applied. The project included detailed design, procurement, construction supervision and start-up of the plant.
- Process layout
- Detailed design
- Start-up

Sanliurfa Water Supply System , Turkey
Sanliurfa Water Supply System
Country: Turkey, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.05.2002
Water shortage had become a problem critical to the well-being of the population and the development of the fast growing city of Sanliurfa (population greater than one million). Several financiers were implementing projects in the water supply system of the region, e.g. a tunnel diverting water from the Ataturk reservoir for irrigation and water supply purpose and a raw water intake and treatment plant with a capacity of 300,000m³/day. Works on the above projects had already commenced and therefore measures had to be implemented urgently in the water distribution system of the town itself.
A complete new water supply system was financed and implemented through this project. This comprised water treatment, transmission and distribution networks. The transmission system consisted of 5 new reservoirs, each of a volume of 20.000 m3, 35 km of primary distribution mains, cathodic protection equipment and 4 pumping stations, with an installed power between 200 kW and 1.400 kW.
- Preparation of tender documents for service contracts:
- Construction supervision
- Capacity building for management and maintenance
- Preparation of design-build tender documents according to FIDIC and PRAG for the new water supply system for Sanliurfa Municipality

Tender Evaluation Assistance to the EC-WWTP Extension,Trebic, Czech Republic
Tender Evaluation Assistance to the EC-WWTP Extension,Trebic
Country: Czech Republic, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.06.2001
Tender Evaluation (voting member) of the project 'Extension of the existing waste water treatment plant for the town Trebic', the Czech Republic. The planned waste water treatment plant was designed using mechanical-biological treatment, with activation, nitrification and denitrification, anaerobic sludge stabilisation and chemical phosphorus coagulation. Designed WWTP capacity was 12.000 m³ per day.
- Assistance to the EC as voting member in the evaluation committee

Rehabilitation of Batllava Pumping Station, Kosovo
Rehabilitation of Batllava Pumping Station
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.02.2002


Batllava Pumping Station supplied 80% of the Population of Pristina, (400.000 p.e.) with a capacity of 1000l/s at a rated power consumption of 1.5 MW. The project included a feasibility study, detailed design, preparation of tender documents and tender evaluation according to PRAG for the rehabilitation of the pumping station.
- Assessment of existing structure and equipment
- Elaboration of 3 alternatives for reconstruction
- Detail design of 3 new pumps, low voltage and high voltage equipment
- Preparation of tender documents according to PRAG and tender evaluation

Regional Water Supply Plava Voda, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Regional Water Supply Plava Voda
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.06.2002


Feasibility study into the proposal for a 34 km long water supply system to supply water to a number of towns with a combined population exceeding 150,000. The technical viability was assessed, including calculations of demand, the production of preliminary designs and environmental impact assessment. Financial analysis and risk assessments were also carried out, along with tariff calculations.
- Topographical survey
- Negotiating right of way
- Feasibility study with economic analysis and risk assessment
- Detail design
- Tendering
- Construction supervision and technical assistance management
- Operation and maintenance of the regional water supply system
- Site investigation
- Assessment of existing facilities
- Presentation and negotiations with financing institution

Yntumak Dam Safety Study, Kazakhstan
Yntumak Dam Safety Study
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 01.07.2002


Assessment of the stability of the incomplete earth fill dam with a storage capacity of 250 Million m3. Determination of the requirements and feasibility to rehabilitate, complete and convert the irrigation dam into a permanently filled storage dam, with multi purpose functions of water supply for the capital Astana, hydropower production, recreation, fishing and irrigation purposes.
- Assessment of the dam and dam structures
- Identification of least cost solution to seal the dams and to complete the dams and structures
- Preparation of cost estimates and time schedules

Adrasan Water Supply and Waste Water Disposal System, Turkey
Adrasan Water Supply and Waste Water Disposal System
Country: Turkey, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 01.12.2000
Sustainable improvement of the water supply and sanitation situation in smaller touristic municipalities on the Turkish Mediterranean coast was considered essential for future development.
The project consisted of a pilot and market study for Adrasan in order to address the growing infrastructural needs of 14 smaller towns. The study examined sanitary deficits and emerging environmental impacts of the prevailing sanitary situation in the cities, considering the extremely high demand patterns in the summer season.
- Market Study
- Investment study
- Tender design for water and waste water disposal system
- Capacity building through an association

Vranic and Blace Water Supply and Sanitation System Rehabilitation – Phase I-III, Kosovo
Vranic and Blace Water Supply and Sanitation System Rehabilitation – Phase I-III
Country: Kosovo, Balkans
Project end: 01.05.2009


Phase I: Reconstruction and augmentation of the war damaged water supply system, including additional spring tapings, installation of water treatment facilities and water reduction campaign. Improvement of the sanitary situation by construction of eco sanitation toilets (urine diversion dehydration toilets). Establishment of a water committee, which was responsible for the system and preparation of business plans. The services provided comprised design, construction supervision and technical assistance.
Phase II: Project Management for the improvement and extension of the existing water supply to a full piped system. The project includes extensive hydro-geological studies and geophysical investigations to explore suitable water sources for the Blace settlement. Introduction of the Ecosan toilet technology for faecal and wastewater disposal and construction of several pilot units in Vranic and Blace.
Phase III: Detail design, preparation of tender documents and construction supervision for the extension of the existing water supply system Blace to the Mahallas Sekoli, Fanghu, Bajaktari and lower Blace. The project includes investments into 3 reservoirs, each 150 m3, 3 wells, a bosster pumping station and 2 chlorintaion stations, 9 km of primary an secondary distribution lines as well as 500 house connections.
The project also includes institutional support to the water commitee and preparation of a transfer to the public water utility Prizren-Suha Reka.
Phase I
- Assessment of necessary investments
- Identification of water sources
- Hydraulic analysis of existing supply system
- Detail design for improvements in the distribution system
- Detail design of 6 spring toppings
- Preparation of tender documents
- Detail design for low cost on site sanitation devices
- Pilot project for dehydration toilets
- Construction supervision
Phase II
- Implementation of full piped water supply system
- Implementation of waste water system (ecosan toilet technology)
Phase III
- Detailed design
- Tendering
- Construction supervision
- Institutional support
- General project management

Integrated Water Resource Management for Important Deep European Lakes and their Catchment Areas, Austria
Integrated Water Resource Management for Important Deep European Lakes and their Catchment Areas
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.02.2003
Eurolakes wanted to improve the current strategies concerning the long-term management, short-term pollution control, and integrated monitoring regarding deep European lakes and their catchments areas. Project activities could lead to recommendations for European legislation and the EU Water Framework Directive concerning an integrated water management approach. These efforts were supported by specific scientific investigations to describe the seasonal dynamics and quantification of key limnological processes and parameters in deep European lakes. Sets of criteria to substantiate ecological water and ecosystem quality targets for lakes and their surrounding areas were established and a recommended generalized structure of a dedicated lake/catchment model regarding these important water bodies was elaborated.
- Contribution to a FP5 project into the impacts of contaminants

Assessment of Flood Damages and Rehabilitation Works for the Water Supply and Sanitation System of 5 Villages, Mozambique
Assessment of Flood Damages and Rehabilitation Works for the Water Supply and Sanitation System of 5 Villages
Country: Mozambique, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.12.2001


Assessment study for the rehabilitation of the water supply and sanitation systems for the minor urban centres of Namaacha, Moamba, Ressano Garcia, Buzi and Chibabava. The objectives of the study were to identify the damages caused by the heavy rains and floods of February/March 2000 to the systems, to formulate an immediate rehabilitation program, including technical specification and drawings, and to review the medium and long term rehabilitation measures necessary. In addition, management and operation & maintenance practices were assessed and suggestions for improvement made.
- Assessment of the damaged infrastructure and water supply systems
- Formulation of rehabilitation programme

Waste Water Treatment Plant Wallern , Austria
Waste Water Treatment Plant Wallern
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.12.2001

The existing 25,000 PE WWTP designed for carbon removal and nitrification was extended to allow denitrification and enhanced biological P removal for a maximum design load of 50,000 PE. Additionally the excess sludge line was extended by an additional digester and dewatering equipment.
- Process layout
- General design
- Detailed design for enhanced biological P removal
- Preparation of Tender Documents
- Construction supervision
- Start-up

River Restructuring and Restoration , Austria
River Restructuring and Restoration
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 01.02.2000


Man imposes a variety of physical changes on water courses, such as channelization and land drainage. The ecological consequences can be manifold, one example being the obstruction of faunal migration and a reduction in biodiversity resulting from these human activities and impacts on the environment. This project consisted of the restoration of the Inzinger Lacke, a channalized tributary that was disconnected by a non-return gate from the river Inn, the main river system in Tirol. The main objectives were the reintegration of the tributary into the fluvial system and the restructuring and restoration of the riparian zone, including re-vegetation planning, in order to re-establish up- and downstream migration of aquatic organisms. Based on this, a modern ecological orientated fishery management program could be formulated.
- Environmental assessment
- Feasibility study
- Detail design

Small Hydro Power Plant, Dolena Doklece, Slovenia
Small Hydro Power Plant, Dolena Doklece
Country: Slovenia, Central and Eastern Europe
Project end: 01.02.2000
Pre-feasibility study for development of SHP plant
- Pre-feasibility Study

Market Assessment Study, Namibia
Market Assessment Study
Country: Namibia, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 01.02.2000
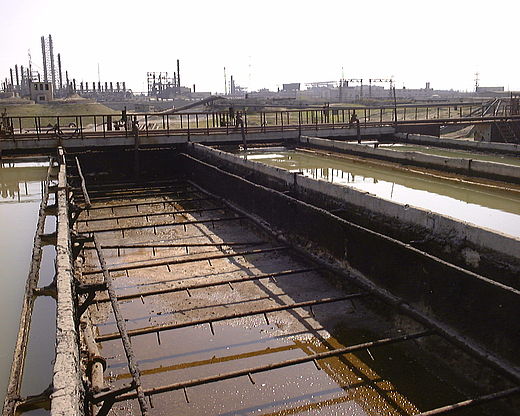

General assessment of the infrastructure facilities in the water, wastewater and solid waste sectors in the country, including waste reduction programmes, residual waste treatment, waste splitting strategies and composting. Further the establishment of potential for direct investment projects in these sectors.
- Evaluation of existing projects in water, waste water and solid waste
- Preparation of studies highlighting infrastructure deficits and priority projects
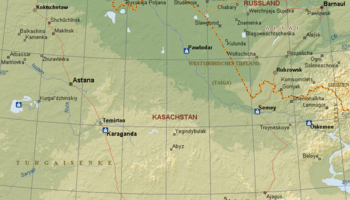
Water Sector Note for North East Kazakhstan, Kazakhstan
Water Sector Note for North East Kazakhstan
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 31.12.2000
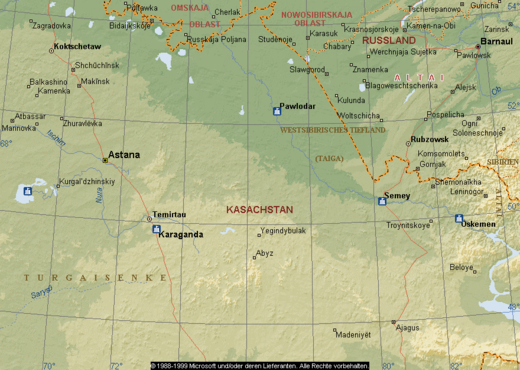
Preliminary assessment and evaluation of water resources and the existing water infrastructure in the north-eastern region of Kazakhstan. The project examined the growing gap between supply and demand for municipal and industrial water services, the status of water pollution, the low efficiency of these services and low cost recovery, resulting from service inefficiency and inadequate tariffs.
- Assessment of municipal water supply and sewerage disposal facilities
- Preparation of a water sector note for the north-eastern region of Kazakhstan

Evaluation of the Danube River Basin Pollution Reduction Programme, Austria
Evaluation of the Danube River Basin Pollution Reduction Programme
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.2000
End-of-project evaluation of this project financed by UNOPS and supported by EU Phare and Tacis. Review of the project concept and underlying assumptions, assessment of the project effectiveness, progress made and impact achieved. Also responsible for financial aspects of the project and the establishment of an environmental trust fund.
- End of project evaluation

Small Hydro Power Market Assessment Study for Northern Greece, Greece
Small Hydro Power Market Assessment Study for Northern Greece
Country: Greece, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.1999


Greece needed to import substantial amount of electric energy, therefore a program for the development of small hydropower schemes through private investors was launched by the government.
This project consisted of the assessement of hydropower potential in the provinces of Epirus and Macedonia.
- Preparation of an SHPP assessment study to be used to decide further investments

Small Hydropower Plant Antholz, Italy
Small Hydropower Plant Antholz
Country: Italy, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.2000

Rehabilitation and efficiency improvement of the existing and outdated 50 kW SHP design and preparation of tender documents.
- Feasibility study
- Detail design
- Preparation of tender documents

Small Hydropower Plant Duge, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Small Hydropower Plant Duge
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 31.12.2000

Development of a 1 MW hydropower plant in the central region of Bosnia for the supply of a local village with electric energy and to feed excess energy into the public grid.
- Feasibility study
- Detail design
- Advisory services in finding project financing, including co-financing by IFI
- Environmental study

Evaluation of the Sumgait Environmental Rehabilitation Project, Azerbaijan
Evaluation of the Sumgait Environmental Rehabilitation Project
Country: Azerbaijan, Caucasus
Project end: 31.12.1999


The chemical and industrial complex of Sumgait had caused severe environmental pollution. UNOPS had drafted a project for environmental rehabilitation of the complex with plans for future pollution mitigation.
As part of this, a mid term project evaluation of the project was carried out, with P&P being in charge of the financial aspects including questions of project sustainability and the need of establishing an environmental trust fund.
Mid term project evaluation, including:
- Financial assessment
- Sustainability Assessment
- Environmental trust fund requirements

Small Hydropower Plant Nestorio I , Greece
Small Hydropower Plant Nestorio I
Country: Greece, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.2000


Development of a 1.5 MW hydropower plant for private investors.
- Financial and economic analyse
- Environmental impact assessment
- Feasibility studies
- Shareholder participation

Hydropower Plants, Gudauri, Georgia
Hydropower Plants, Gudauri
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 01.03.2001


Georgia suffered from serious electricity shortages. For the modern ski and tourist resort in Gudauri reliable and sufficient electricity supply was of great importance to its continued survival and development. Therefore it was planned to implement two small hydropower plants, Gudauri 1 and Gudauri 2, with a capacity of 1.2 and 7.5 MW.
In totally about 55 GWh could be produced over one year.
- Project layout
- Investment studies
- Environmental impact studies
- Detailed design
- Institutional and tariff structures
- Project financing
- Capacity building

Integrated Environmental Programme; Lot b – Shenyang Urban Planning, Liaoning, China (incl. Hong Kong)
Integrated Environmental Programme; Lot b – Shenyang Urban Planning, Liaoning
Country: China (incl. Hong Kong), Asia
Project end: 31.12.2001
Preparation of a 5 year and a long term master plan for the development of the provincial capital Shenyang. The city was dominated by heavy industry causing heavy pollution, had a high population growth rate and high levels of unemployment. The city was looking for new development strategy with a sound and sustainable environmental basis.
- Infrastructure Planning

Water Supply Wastewater Project, Krivogastani, The former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia
Water Supply Wastewater Project, Krivogastani
Country: The former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.2001


For the newly founded Municipality of Krivogastani (formed by a total of 24 settlements in the Pelagonian Flatland) a green field minor urban water supply and sewerage project was prepared.
The project comprised the development of a general water supply concept for a group water supply system for 7 villages with a total population of close to 10.000 inhabitants, and a corresponding wastewater disposal concept for the entire Pelagonain flatland.
The detailed design for the water supply system consisted of ground water production, treatment, transmission, storage, distribution and house connections. The detailed design for the wastewater project included house connections, collectors, interceptors and a biological wastewater treatment plant.
A further project component covered technical assistance for the establishment of a public enterprise, selection of staff, set up of organisation, assistance in management and preparation of business plans for the newly founded water utility
- Site investigation
- Development of masterplan for wastewater disposal
- General masterplan for piped water supply
- Detail design
- Preparation of tender documents
- Construction supervision

Small Hydropower Sector Study (Phases I and II), Georgia
Small Hydropower Sector Study (Phases I and II)
Country: Georgia, Caucasus
Project end: 31.12.2001


Identification of existing barriers hampering the rehabilitation and development of small hydropower plants in the country, including suggestions for their removal.
In Phase II detailed assessment for the rehabilitation and upgrading of 4 existing small hydropower plants, including selling of the produced energy to the communities and to industrial enterprises. The development of the 4 plants served as a show case (pilot projects) which could be duplicated by local private investors.
- Identification of SHP potential
- Assessment of existing barriers for the development of the sector
- Detail design and tender documents for 4 SHPP’s

Small Hydropower Plant Sliven , Bulgaria
Small Hydropower Plant Sliven
Country: Bulgaria, Balkans
Project end: 31.12.2000


Development of the 400 kW hydropower plant on the basis of public private partnership, integrated in the existing water supply system.
- Feasibility study
- Detail design
- Compilation of financing
- Preparation of power purchase and share holder agreements

Municipal Water & Wastewater Project, Albania
Municipal Water & Wastewater Project
Country: Albania, Balkans
Project end: 31.12.2002
Construction supervision of water and wastewater facilities for 5 Albanian towns. The main objective of the project was the supply of clean water to 5 Albanian towns. In addition, the piping to and from several waste water facilities in the project region had to be replaced. P&P provided technical assistance and carried out design, production of tender documents, construction management and supervision.
- Feasibility study
- Detailed design
- Assessment of E&M facilities and transmission lines
- Leak detection
- Hydraulic network analysis

GAP Urban Sanitation Project, Turkey
GAP Urban Sanitation Project
Country: Turkey, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 31.12.1999


The name GAP means “Southeast-Anatolian Project” (Turkish for für Güneydoğu Anadolu Projesi). The project comprised a feasibility study for waste water and solid waste disposal alternatives applicable for 10 cities in Southeast Anatolia and definition of a GIS for the city of Diyarbakir. The project area covered 75,000 km2 with a population of 6.0 million. Technical assistance was provided to the Project Management Unit of GAP by developing a strategy for wastewater management in the area, including studies on alternative waste water treatments such as land treatment. An assessment study for solid waste management was carried out including the formulation of 6 projects for sanitary land fills and transfer stations. Also, design / tendering of landfill sites and transfer stations, design of water treatment facilities, design of non-revenue water reduction programme for several towns and rehabilitation and upgrading of 30 drinking water systems have been developed.
- Pre-feasibility and feasibility studies
- Technical assistance and project preparation
- Tender documents for sanitary landfill, transfer stations and drinking water supply systems
Water, Waste Water, Solid Waste Programme, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Water, Waste Water, Solid Waste Programme
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 31.12.1999
Project identification, project formulation and project appraisal for the assistance programme of the Government of Austria to several towns in Bosnia-Herzegovina in the sectors of water supply, waste water and solid waste for the fiscal years 1998 to 2000.
- Project identification
- Project formulation
- Project appraisal

Water Supply Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Water Supply Bosnia-Herzegovina
Country: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkans
Project end: 01.12.1996
Rehabilitation of water supply systems for 6 selected towns due to war damages. Evaluation of the demand for repair of the pipe network, pumping stations and treatment plants, delivery of tools. Preparation of tender documents and cost estimation.
- Site investigation
- Hydraulic tests
- Assessment of facilities
- Elaboration of tender documents

Feasibility Study for the Kjustendil Water Company, Bulgaria
Feasibility Study for the Kjustendil Water Company
Country: Bulgaria, Balkans
Project end: 01.09.1996
The Regional Water Company (Veika) of Kjustendil was responsible for water supply, sewerage and waste water treatment for eight municipalities in the region. The population supplied was over 130,000.
The previously fully state owned water company had been recently restructured. To assist the young company in the planning of investments and future operations, a feasibility study was carried out under the supervision of The World Bank and the PMU of the Ministry of Regional Development and Construction in Sofia. Main objectives were to assess the present status of the water supply and waste water facilities as well as the organisation of Veika, on the basis of this to formulate a three year investment programme and to improve the water and waste water facilities and the efficiency of Veika.
- Assessment of the existing facilities including water treatment, sewerage systems, and mechanical / biological waste water treatment.
- Formulation of proposals for efficiency improvement and reduction of water losses.
- Assessment of organisation and management of the water company, including capacity building, improved meter reading and revenue collection.

Deriner Dam and Hydropower Project, Turkey
Deriner Dam and Hydropower Project
Country: Turkey, Middle East and North Africa
Project end: 31.12.2001
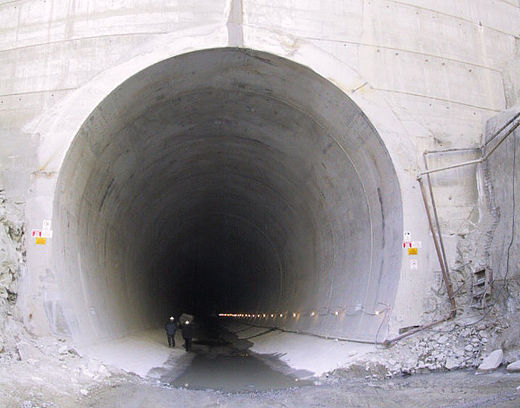


The Deriner Dam and Hydropower Project was constructed on the Coruh River in the north-eastern part of Turkey and consisted of a 260m high arch dam (3rd highest in the world at the time) and a hydropower plant with 600 MW installed capacity.
- Specialist studies on concrete technology
- Design of all site facilities
- Setup of a project information system
- Development of most economic work methodologies
- Assistance to contractor on project management
- Assistance for special equipment procurement

National Environmental Action Plan (NEAP), Kazakhstan
National Environmental Action Plan (NEAP)
Country: Kazakhstan, Central Asia
Project end: 31.12.1998
Technical assistance in the preparation and formulation of the National Environmental Action Plan (NEAP) and Local EAPs for the Republic of Kazakhstan. Work carried out included data collection and data evaluation, the identification and assessment of hot spots, evaluation of environmental impacts and possible solutions for remediation and clean-up projects.
In addition, an assessment of the institutional situation was carried out, assistance was provided in the priority setting process, mitigation projects were evaluated economically, and an action plan was prepared. Also, the NEAP prepared by the local experts was reviewed. Final results were presented at senior Government level workshops.
- Technical assistance and advisory services in the preparation of a NEAP for the media water.

Community Water Supply, Ghana
Community Water Supply
Country: Ghana, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 31.12.1997

The World Bank provided support to the country’s rural water supply sector by paying utmost attention to community based integration and approachs. This included wells equipped with hand pumps and other simple isolated water supply systems that were constructed solely by community participation. For water supply systems of small towns, simple centralized systems were introduced. To enable the involvement of local contractors, who lacked the capacity to deal with complicated and complex contracts, a standard contract document was required together with standard specifications and corresponding drawings.
Posch & Partners were commissioned to prepare such documents, covering a wide variety of technical solutions and split up into different volumes, which could be put together into a single document suitable for each particular case.
- Detailed design
- Preparation of:
- simplified standard contract documents
- standard specifications
- standard drawings.
Small Hydropower Reshun , Pakistan
Small Hydropower Reshun
Country: Pakistan, Asia
Project end: 31.12.1998
GTZ provided assistance to the Small Hydropower Development Organization (SHYDO) for the preparation of feasibility studies and the construction of one small hydropower plant as a pilot project, a 4 MW plant at Reshun in the Citral Region.
P&P supplied technical assistance by providing the Team Leader for Civil Engineering, with the main responsibility of pushing the implementation of the pilot project and securing technical assistance and construction management for the local companies involved. The Team Leader was also actively engaged in the preparation of feasibility studies for a number of small to large dimensioned hydropower plants in the country.
Provided civil engineering Team Leader for:
- Preparation of feasibility studies
- Construction supervision
- Construction management

Waste Water Treatment Plant Hofkirchen, Austria
Waste Water Treatment Plant Hofkirchen
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.1997


Construction of a 7.000 PE wastewater treatment plant with application of Phostrip II process combined with simultaneous sludge stabilisation. Services comprised project design, detailed design, tendering, construction supervision and process optimisation.
- Design of the entire sludge line, facilities, pre-stripper and electro-mechanical equipment for the pumping station
- Preparation of tender documents
- Construction supervision
- Commissioning start up

Small Hydropower Plant Bistritsa, Bulgaria
Small Hydropower Plant Bistritsa
Country: Bulgaria, Balkans
Project end: 31.12.1995

Assessment of present situation, evaluation of the possibilities to add 6 to 8 small hydro power plants to the existing water supply system for the city of Blagoevgrad. Provision of guidelines for privatization.
Technical Characteristics:
Design flow: 26,0m³/s
Actual power output: 1.389kW
Average annual energy production: 9.638.000kWh
Cross head: 7,60m
- Field mission of experts
- Cost estimates
- General design
- Proposal for privatisation of operations

Water Supply Potsdamer Hütte, Austria
Water Supply Potsdamer Hütte
Country: Austria, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.1995


The Potsdamer Hütte is a mountain shelter with full board facilities in the Stubaier Alps in Tyrol at an elevation of 2012 m.a.s.l. The present water sources do not comply with the regulations concerning the quality as well as the quantity. Also the civil structures at the spring have to be rehabilitated.
A hydrological study was carried out as well as bacteriological investigations on the water and proposals for improvement determined.
Also a precipitation run-off model will be made to establish possible hydro power potential to supply the mountain shelter with electric energy.
- Field investigations
- Field survey
- General design for the water supply system
- General design for the small hydro power station

Central Treatment Plant, Darmstadt, Germany
Central Treatment Plant, Darmstadt
Country: Germany, Western Europe
Project end: 31.12.1995

The main wastewater treatment plant of Darmstadt could not cope any more with the new legal requirements and the present wastewater organisation. Consequently, complete rehabilitation of the old plant and augmentation to a capacity of 300,000 people equivalent was commenced in 1992, capable of eliminating Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Due to the excellent results previously obtained at the Eberstadt plant, the Phostrip-process was also selected for Phosphorous elimination at Darmstadt.
- Licence for Phostrip-process and integrated pre-stripper
- Phostrip process design
- Specification of measure and control devices
- Commissioning of plant
- Optimisation of plant operation

Water Sector Rehabilitation Project (Area B), Ghana
Water Sector Rehabilitation Project (Area B)
Country: Ghana, Sub-Saharan Africa
Project end: 31.12.1997


35 water supply schemes (Area A and Area B) were rehabilitated and extended under this World Bank project. The schemes needed urgent replacement of electro-mechanical equipment and rehabilitation of civil structures. Comprehensive planning studies were carried out for all 20 water works, including groundwater studies and hydro-geological investigations, to determine the long run least cost rehabilitation solutions. This was followed by detailed design of all systems, preparation of tender documents and construction supervision. Construction works were co-financed by three different donors. This required special inputs and flexibility, to satisfy each of them regarding their special financing and administrative conditions.
- Hydrological and hydro-geological survey
- Electro-mechanical inspection and testing of existing equipment
- Feasibility studies
- Detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents
- Construction supervision

Small Hydropower Plant Rangjung, Bhutan
Small Hydropower Plant Rangjung
Country: Bhutan, Asia
Project end: 31.12.1992


A pre-feasibility study was carried out for the three possible sites and the Rangjung alternative in East Bhutan was selected. For the feasibility study and the detailed design all available hydrological data was collected, evaluated and computerized. The results are based on extensive topographical, hydrological and geological survey and comprise power generation, transmission and distribution. The final design included static calculations of civil and hydro steel works. Tender documents were prepared. The 1100 kW plant with a head of170 m included a Tyrolean weir intake with settlement basin and a power conduit partly within a tunnel.
- Geological, hydrological and topographical surveys
- Energy consumption assessment
- Demographic, sociological and environmental assessments
- Economic analysis
- Soil mechanics
- Detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents

Water Management Project Namche Bazar, Nepal
Water Management Project Namche Bazar
Country: Nepal, Asia
Project end: 31.12.1991

The Himalayan villages Namche Bazar, Khunde and Khumjung, situated about 3.500 - 3.900 m.a.s.l., had became a tourist centre, with the associated benefits and impacts. For health reasons, the provision of drinking water to the local population and for tourists had become an urgent requirement, as the existing supply was unsatisfactory. In addition to improving the drinking water supply, new sewerage and waste water treatment facilities were also constructed.
- Geological and hydrological survey
- topographical survey
- pre-feasibility study
- energy consumption assessment
- biological and environmental assessment
- detailed design
- cost estimation
- preparation of tender documents
- tender evaluation
- procurement service and assistance
- training of personnel
- construction supervision
- project management
- start-up assistance

Small Hydropower Plant Namche Bazar, Nepal
Small Hydropower Plant Namche Bazar
Country: Nepal, Asia
Project end: 31.12.1993


The electrification of Namche Bazar and the adjacent villages Khunde, Khumjung and Thamo was of fundamental importance for the survival and development of the whole region, as no other form of energy was available in the future due to deforestation.
The plant, with a capacity of 600 kW and a net head of 210 m, was located at an elevation of 4000 m.a.s.l. and was not accessible by road (140 km distance to the next road connection).
The project not only covered the energy production; it started at the spring in the glacier region and ended at the kitchen stoves and heating systems in the Sherpa houses. New concepts for efficient energy utilization were developed, with also the necessary infrastructures to operate, maintain, repair and expand the system in the future. The planning and implementation of drinking water, biological waste water treatment and waste disposal was also included in this project.
- Geological, hydrological and topographical surveys
- Pre-feasibility study
- Energy consumption assessment
- Biological and environmental assessment
- Detailed design
- Preparation of tender documents
- Tender evaluation and procurement assistance
- Construction supervision
- Start-up assistance